| 201. Man: Hieroglyph of the Universe: Lecture I
09 Apr 1920, Dornach Tr. George Adams, Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| I have mentioned before how the impossibility of building a bridge between the two, between the world of Necessity and the world of Morals, led Kant to write two critiques, the Critique of Pure Reason in which he applies himself to investigating the nature of simple Necessity, and the Critique of Applied Reason in which he inquires into what belongs to Moral Cosmogony. |
| 201. Man: Hieroglyph of the Universe: Lecture I
09 Apr 1920, Dornach Tr. George Adams, Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Today I shall try to give a wider view of a subject already often touched upon. I have frequently pointed out how, for modern man, moral and intellectual conceptions diverge. On the one hand we are brought, through intellectual thinking, to recognition of the stern Necessity of Nature. In accordance with this necessity we see everything in Nature under the law of Cause and Effect. And we ask also, when man performs an action: what has caused it, what is the inner or outer cause? This recognition of the necessity for all events has in modern times acquired a more scientific character. In earlier times it had a more theological character, and has so still for many people. It takes on a scientific character when we hold the opinion that what we do is dependent on our bodily constitution and on the influences that work upon it. There are still many people who think that man acts just as inevitably as a stone falls to the ground. There you have the natural scientific colouring of the Necessity concept. The view of those more inclined to Theology might be described as follows. Everything is fore-ordained by some kind of Divine Power or Providence and man must carry out what is predestined by that Divine Power. Thus we have in the one case the Necessity of natural science, and in the other case unconditioned Divine Prescience. One cannot in either case speak of human Freedom at all. Over against this stands the whole Moral world. Man feels of this world that he cannot so much as speak of it without postulating the freedom of the decisions of his will; for if he has no possibility of free voluntary decision, he cannot speak of a morality of human action. He does however feel responsibility, he feels moral impulses; he must therefore recognise a moral world. I have mentioned before how the impossibility of building a bridge between the two, between the world of Necessity and the world of Morals, led Kant to write two critiques, the Critique of Pure Reason in which he applies himself to investigating the nature of simple Necessity, and the Critique of Applied Reason in which he inquires into what belongs to Moral Cosmogony. Then he felt compelled to write also a Critique of Judgement which was intended as an intermediary between the two, but which ended in being no more than a compromise, and approached reality only when it turned to the world of beauty, the world of artistic creation. This goes to show how man has on the one side the world of Necessity and on the other the world of Free Moral Action, but cannot find anything to unite the two except the world of Artistic Semblance, where—let us say, in sculpture or in painting—we appear to be picturing what comes from Natural Necessity, but impart to it something which is free from Necessity, giving it thus the appearance of being free in Necessity. The truth is, man is not able to build a bridge between the world of Necessity and the world of Freedom unless he finds the way through Spiritual Science. Spiritual Science, however, requires for its development a fulfilment of the aphorism which won respect centuries ago, the saying of the Greek Apollo: “Know thyself!” Now this admonition, by which is not intended a burrowing into one's own subjectivity but a knowledge of the whole being of man and the position he occupies in the Universe—this is a search that must find a place in our whole spiritual life. From this point of view we may really say that the course taken by the development of the spiritual Movement directed to Anthroposophy has in the last few days taken a step forward; it has begun to show clearly to the spiritual life of humanity, how we must seek to illuminate modern methods of thought with a knowledge of Man; for it is a fact that the knowledge of Man has to a very great extent been lost in modern times. This was our aim in the course of lectures that has just been held for doctors, where an initial attempt was made to throw light in a positive way upon matters with which medical science has to concern itself. [*Published by Rudolf Steiner Nachlassverwaltung, Dornach, 1961, (third edition) with the title: Geisteswissenschaft und Medizin. English translation (now out of print) entitled: Spiritual Science and Medicine, can be borrowed from the Library, Rudolf Steiner House, London, N.W.I] In the series of lectures given by our friends and myself, we tried to show how a connection must be made between the individual sciences and what these can receive from Spiritual Science. It is very desirable that within our Movement there should be a strong consciousness of the need for such attempts; for if we are to succeed it is absolutely necessary to make clear to the outer world—in a sense, to compel it to understand—that here no kind of superficiality prevails in any domain, but rather an earnest striving for real knowledge. This is often hindered by the way in which things reach the public from our own circles, so that it is supposed, or may easily be maliciously pretended, that all kinds of sectarianism and dilettantism are allowed here. It is for us to convince the outer world more and more how earnest is the striving underlying all that this Movement represents. Such attempts must be carried further afield, and they must be carried further by the forces of the whole Anthroposophical Movement; for we have now made a beginning with a true knowledge of Man which must form the foundation of all true spiritual culture. It is true to say that from the middle of the fifteenth century, man's earlier concrete relation to the world has been growing more and more abstract. In olden times, through atavistic clairvoyance man knew much more of himself than he does today, for since the middle of the century intellectualism has spread over the whole of the so-called civilised world. Intellectualism is based upon a very small part in the being of Man, a very small part; and it produces accordingly no more than an abstract network of knowledge of the world. What has knowledge of the world become in the course of the last centuries? In its relation to the Universe, it has become a mere mathematical-mechanical calculation, to which in recent times have been added the results of spectra analysis; these again are purely physical, and even in the physical domain, mechanical-mathematical. Astronomy observes the courses of the stars and calculates; but it notices only those forces which show the Universe, in so far as the Earth is enclosed in it, as a great machine, a great mechanism. It is true to say that this mechanical-mathematical method of observation has come to be regarded simply and solely as the only one that can actually lead to knowledge. Now with what does the mentality which finds expression in this mathematical-mechanical construction of the Universe reckon? It reckons with something that is founded to some extent in the nature of Man, but only in a very small part of him. It reckons first with the abstract three dimensions of space. Astronomy reckons with the abstract three dimensions of space; it distinguishes one dimension, a second (drawing on blackboard) and a third, at right angles. It fixes attention on a star in movement, or on the position of a star, by looking at these three dimensions of space. Now man would be unable to speak of three dimensional space if he had not experienced it in his own being. Man experiences three-dimensional space. In the course of his life he experiences first the vertical dimension. As a child he crawls, and then he raises himself upright and experiences thereby the vertical dimension. It would not be possible for man to speak of the vertical dimension if he did not experience it. To think that he could find anything in the Universe other than he finds in himself would be an illusion. Man finds this vertical dimension only by experiencing it himself. By stretching out our hands and arms at right angles to the vertical we obtain the second dimension. In what we experience when breathing or speaking, in the inhaling and exhaling of the air, or in what we experience when we eat, when the food in the body moves from front to back, we experience the third dimension. Only because man experiences these three dimensions within him does he project them into external space. Man can find absolutely nothing in the Universe unless he finds it first in himself. The strange thing is that in this age of abstractions which began in the middle of the fifteenth century, Man has made these three dimensions homogeneous. That is, he has simply left out of his thought the concrete distinction between them. He has left out what makes the three dimensions different to him. If he were to give his real human experience, he would say: My perpendicular line, my operative line, my extensive or extending line. He would have to assume a difference in quality between the three spatial dimensions. Were he to do this, he would no longer be able to conceive of an astronomical cosmogony in the present abstract way. He would obtain a less purely intellectual cosmic picture. For this however he would have to experience in a more concrete way his own relationship to the three dimensions. Today he has no such experience. He does not experience for instance the assuming of the upright position, the being in the vertical; and so he is not aware that he is in a vertical position for the simple reason that he moves together with the Earth in a certain direction which adheres to the vertical. Neither does he know that he makes his breathing movements, his digestive and eating movements as well as other movements, in a direction through which the Earth also moves in a certain line. All this adherence to certain directions of movement implies an adaptation, a fitting into, the movements of the Universe. Today man takes no account whatever of this concrete understanding of the dimensions; hence he cannot define his position in the great cosmic process. He does not know how he stands in it, nor that he is as it were a part and member of it. Steps will have now to be taken whereby man can obtain a knowledge of Man, a self-knowledge, and so a knowledge of how he is placed in the Universe. The three dimensions have really become so abstract for man that he would find it extremely difficult to train himself to feel that by living in them he is taking part in certain movements of the Earth and the planetary system. A spiritual-scientific method of thought however can be applied to our knowledge of Man. Let us therefore begin by seeking for a right understanding of the three dimensions. It is difficult to attain; but we shall more easily raise ourselves to this spatial knowledge of Man if we consider, not the three lines of space standing at right angles, but three level planes. Consider for a moment the following. We shall readily perceive that our symmetry has something to do with our thinking. If we observe, we shall discover an elementary natural gesture that we make if we wish to express decisive thinking in dumb show. When we place the finger on the nose and move through this plane here (a drawing is made), we are moving through the vertical symmetry plane which divides us into a left and a right Man. This plane passing through the nose and through the whole body, is the plane of symmetry, and is that of which one can become conscious as having to do with all the discriminating that goes on within us, all the thinking and judging that discriminates and divides. Starting from this elementary gesture, it is actually possible to become aware of how in all one's functions as Man one has to do with this plane. Consider the function of seeing. We see with two eyes, in such a way that the lines of vision intersect. We see a point with two eyes; but we see it as one point because the lines of sight cross each other, they cut as shown in the drawing. Our human activity is from many aspects so regulated that we can only understand its regulation by reference to this plane. We can then turn to another plane which would pass through the heart and divide man back from front. In front, man is physiognomically organised, behind he is an expression of his organic being. This physiognomical-psychic structure is divided off by a plane which stands at right angles to the first. As our right and left man are divided by a plane, so too are our front and back man. We need only stretch out our arms, our hands, directing the physiognomical part of the hand (in contrast to the merely organic part) forwards and the organic part of the hands backwards, and then imagine a plane through the principal lines which thus arise, and we obtain the plane I mean. In like manner we can place a third plane which would mark off all that is contained in head and countenance from what is organised below into body and limbs. Thus we should obtain a third plane which again is at right angles to the other two. One can acquire a feeling for these three planes. How the feeling for the first is obtained has already been shown; it is to be felt as the plane of discriminative Thinking. The second plane, which divides man into front and back (anterior and posterior) would be precisely that whereby man is shown to be Man, for this plane cannot be delineated in the same way in the animal. The symmetry plane can be drawn in the animal but not the vertical plane. This second (vertical) plane would be connected with everything pertaining to human Will. The third, the horizontal, would be connected with everything pertaining to human Feeling. Let us try once more to get an elementary idea of these things and we shall see that we can arrive at something by this line of thought. Everything wherein man brings his feeling to expression, whether it be a feeling of greeting or one of thankfulness or any other form of sympathetic feeling, is in a way connected with the horizontal plane. So too we can see that in a sense the will must be brought into connection with the vertical plane mentioned. It is possible to acquire a feeling for these three planes. If a man has done this, he will be obliged to form his conception of the Universe in the sense of these three planes—just as he would, if he only regarded the three dimensions of space in an abstract way, be obliged to calculate in the mechanical-mathematical way in which Galileo or Copernicus calculated the movements and regulations in the Universe. Concrete relations will now appear to him in this Universe. He will no longer merely calculate according to the three dimensions of space; but when he has learnt to feel these three planes, he will notice that there is a difference between right and left, over and under, back and front. In mathematics it is a matter of indifference whether some object is a little further right or left, or before or behind. If we simply measure, we measure below or above, we measure right or left or we measure forward or backward. In whatever position three metres is set, it remains three metres. At most we distinguish, in order to pass from position to movement, the dimensions at right angles to one another. This we do, however, only because we cannot remain at simple measurement, for then our world would shrink to no more than a straight line. If however, we learn to describe Thinking, Feeling and Willing concretely in these three planes, and to place ourselves thus in space as psychic-spiritual beings, with our Thinking, Feeling and Willing—then just as we learn to apply to Astronomy the three dimensions of space as found in man, so do we learn to apply to Astronomy the threefold division of man as a being of soul and spirit. And it becomes possible if we have here (drawing) Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, Sun, Venus, Mercury and lastly Earth, then it becomes possible, if we look at the Sun, to observe it in its outer manifestation as something separating, as a dividing element. We must think of a plane passing through the Sun, and we shall no longer regard what is above the plane and what is below as merely dimensional, but must regard the plane as a dividing plane and distinguish the planets as being above or below. Thus we shall no longer say: Mars is so many miles distant from the Sun, Venus so many miles; but we shall learn to apply the knowledge of Man to the knowledge of the Universe, and say: It is no mere question of dimensions when I say that the human head in respect of the nose is at such and such a distance from the horizontal plane which I have called the plane of Feeling, and the heart at such and such a distance; but I shall bring their position and distance above and below into connection with their formation and structure. So too I shall no longer say of Mars and Mercury that the one is at such a distance and the other at such another distance from the Sun, but I shall know that if I regard the Sun as a dividing partition, Mars being above must be of one nature and Mercury being below of another. I shall now be able to place a similar plane perpendicularly through the Sun. Thus the movements of Jupiter, let us say, or of Mars, will be such that at one time it will stand on the right of this plane and then go across it and stand on the left. If I simply proceed abstractly, according to dimensions, I shall find it is sometimes on the right and sometimes on the left, and such and such a number of miles. But if I study cosmic space concretely, as I must [study] my own being as man, it is not a matter of indifference whether a planet is at one time on the left and at another time on the right, but I say there is the same kind of difference whether it is on the right or left as there is between a left and right organ. It is not sufficient to say that the liver is so many centimetres to the right of the symmetrical axis, the stomach so many centimetres to the left, for the two are dissimilar in formation because the one is a right organ and the other a left. Here it is so, that Jupiter, according as he is on the right or the left, to the eye appears different. In the same way I might make a third plane, and must again form a judgement in accordance with that. And if I extend my knowledge of Man to the Universe, I shall be obliged, as I connected the one plane with human Thinking, and the second plane with human Feeling, to consider the third plane as connected with human Will. By all this I wanted only to show how modern cosmogony has no more than a last remnant of external abstraction when it speaks of the three planes perpendicular to one another, to which the positions and movements of the stars are quite indifferently related, and then according to these positions the whole Universe calculated out as a machine. In the astronomical conception of Galileo, only this one thing is taken into consideration for the Universe—abstract space, with its point relationships. This knowledge can however be enlarged to become an active and powerful knowledge of Man. One can say: Man is a thinking, feeling and willing being. As an external being, he is connected by Thinking with one plane, with another at right angles to it by Willing, and with a third at right angles to both by Feeling. This must apply also in the external world. Since the middle of the fifteenth century, man has really known no more than that he extends in three directions; all else is just material collected for observation. A true knowledge of Man must be regained, and indirectly a knowledge of the Cosmos by the same method. Then man will understand how Necessity and Free Will are related, and how both can apply to Man, since he is born from the Cosmos. Naturally if one only takes this last remnant of the human being—the three dimensions at right angles to one another—if that is all one wants to imagine, then the Universe appears terribly poor. Poor, infinitely poor is our present astronomical view of the Universe; and it will not become richer until we press forward to a real knowledge of Man, until we really learn to look into Man. The anthroposophical conception of the universe leads directly into a real spiritual knowledge of the matter. Do not such things as Thinking, Feeling and Willing appear to human knowledge as terribly bare abstractions? Man does not investigate himself thoroughly enough. He does not ask himself what these things are for him to which he applies the words. So much has become mere phrase. One should really ask oneself conscientiously, when using the word Thinking, whether it presents any clear idea—not to speak of Feeling and Willing. But our speech becomes clear and plain, directly we pass from the mere making of phrases, the using of lofty words, and go back to pictures; even when we take just that one picture for Thinking—putting the finger to the side of the nose! We do not need to do it always, but we know that this gesture is often naturally made when we have to think hard, just as we point the finger to the chin when we want to indicate we are paying attention! We enter this plane precisely because we wish to judge there concerning something to which we are related. We bisect our organism as it were into right and left; for we really act quite differently with our right and left sense-organs. This we can appreciate if we observe that with the left sense-organ we undertake as it were, the handling of outer objects; and in our thinking too, there is a sort of handling or feeling of external objects. With the right sense-organ we as it were ‘feel our feeling’ of them. It is then that they first become our own. We could never have attained to the ego-concept if we were not able to perceive, together with what we experience on the right, also that which we experience on the left. By simply laying the hands one over the other we have a picture of the ego-concept. It is indeed true that by beginning to use clear images instead of living merely in phraseology, man will become inwardly richer and will gain the faculty of visualising the Universe in greater detail. Having entered on this path, we shall find that the Universe comes to life again for us, and that we ourselves as human beings share in its life. Then we shall learn again how to build a bridge between Universe and Man. When this is done man will be able to perceive whether there is in the Universe an impulse of Natural Necessity for all that is in Man, or whether the Universe in some measure leaves us free; whether it wholly determines us, or leaves us in a certain sense free. As long as we live in abstractions, we cannot build a bridge between Moral and Natural Law. We must be able to ask ourselves how far Natural Law extends in the Universe, and where something enters in which we cannot include under the aspect of Natural Law. Then we arrive at a relation which has its significance for Man too, a relation between what comes under Natural Law and what is Free and Moral. In this way we learn to connect a meaning with the statement: “Mars is a planet far from the Sun, Venus a planet nearer the Sun.” By simply stating their distances in abstract numbers we have said nothing or at least very little, for to define in this way according to the methods of modern Astronomy, is equivalent to saying: I look at the line which passes through man's two arms and hands, and I speak of an organ that is 2.5 decimetres from this line.—Now this organ may be so and so far under the line, and another organ so and so far above it; it is not, however, the distance that makes the difference, but the fact that one organ is above and the other below. Were there no difference between above and below, there would be no difference between the nose or eyes and the stomach! The eyes are only eyes because they are above, and the stomach is only a stomach because it is below, this line. The inner nature of the organ is conditioned by the position. Similarly the inner nature of Mars is qualified by its position outside the Sun's orbit, and that of Venus by its position within the Sun's orbit. If one does not understand the essential difference between an organ in the human head and an organ in the human trunk—the one lying over and the other under this line—then one cannot know that Mars and. Venus, or Mars and Mercury are essentially different. The ability to think of the Universe as an organism depends on our learning to understand the hieroglyph of the organism we have before us. We must learn to perceive Man as a hieroglyph of the Universe, for he gives us the opportunity of seeing near at hand how different are above and below, left and right, before and behind. We must learn this first in Man, and we shall then find it in the Universe. Because the modern view of the Universe held by Natural Science really gives a cosmogony omitting Man—recognising him only as the highest of the animals, that is to say an abstraction—because Man is not in it at all, therefore to this conception the Universe appears as a mathematical picture only, in which the universal origin of Freedom and Morality can never be recognised. It is, however, of the utmost importance that we should learn to perceive scientifically the connection between Moral Law and Natural Necessity. Today I have endeavoured to show you, in perhaps rather subtle concepts, how a knowledge of the Universe is to be gained from a Knowledge of Man. To the doctors I was able to show in a strictly scientific way how this path has to be sought in Medicine, Physiology and Biology. In these lectures it will be our task to perceive how it must be sought if we are to form aright our general understanding of the world; and the social life in which we find ourselves in these times has great need of such understanding. |
| 201. Man: Hieroglyph of the Universe: Lecture XIV
14 May 1920, Dornach Tr. George Adams, Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Let us reflect however, how in all that is considered in natural science, this secondary effect is wholly omitted. The men of the nineteenth century, and even Kant in the eighteenth, formed their view of the origin of the Universe simply out of the principles which Julius Robert Mayer so sharply defined, when he separated out what belongs to nature alone from all that was for him merely secondary effect. |
| 201. Man: Hieroglyph of the Universe: Lecture XIV
14 May 1920, Dornach Tr. George Adams, Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The essential part of our present study is to recognise how the two streams of the world's history, the heathen stream and the Christian stream, meet in our life, how they work into one another and are connected with the events in the whole Universe. In order to search more closely into this, we must first consider the following. It is essential that we should discriminate as exactly as possible wherein the heathen world-conception, taking it in the widest sense (for indeed, it is still and must remain at the basis of our modern conception of the Universe)—wherein this heathen world-conception differs from the Christian, which has only in a very small degree, in its full reality, passed into the minds of men. The point is, as I have often pointed out, that we have now come to a time when what we may call the cosmogony of Natural Science, and what we call the Moral Order of the Universe—to which of course, also belongs the religious view of the world—stand side by side, utterly unconnected. For the man of today, more than he is aware of, the occurrences belonging to natural and moral happenings are two things wholly apart, which he cannot at all unite if he wishes honestly to hold the position of modern cosmogony. That is why the greatest part of the advanced theology of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries actually has no Christology. I have often remarked on the existence of such books as Adolf Harnack's The Nature of Christianity, in which there is no reason whatever why the name of Christ should be mentioned; for what appears therein as ‘Christ’ is no other than the Deity met with in the Old Testament as the God Jehovah. There is really no actual difference between Harnack's ‘Christ’ and the God Jehovah—that is, there is no difference between what is said of the Christ-Being and what followers of the Old Testament view of the Universe said of their Jehovah. If we take the idea of Christ held today by many persons and compare it with what they have otherwise as their view of life, there is no reason whatever why they should speak of Christ and Christianity, for to speak of Christ and Christianity—and Nationalism, for example—as many do today is an absolute contradiction. These things only escape notice because people today avoid courageously drawing the logical conclusion of what they see before them. The widest rift however, the widest gulf, exists between the view of things held by natural science and what is held by Christianity; and the most important task of our time is to build a bridge over the gulf. The conception of the Universe held by natural science is absolutely the off-spring of the nineteenth century; and it is well not always to describe these things in the abstract, but to look into them a little in a concrete way. I have often mentioned the name of a prominent personality of the nineteenth century, one who directs our attention directly to the conception of the Universe held by natural science—I refer to Julius Robert Mayer, whom we must associate with the nineteenth century view although in his case it leads to some misunderstanding. You know how in a popular way it has been said that the assertion of the law of the conservation of force originated with him—or, to speak more accurately, the law that the Universe contains a constant sum of forces which can be neither increased nor lessened, and can only be changed into one another. Heat, mechanical force, electricity, chemical force, all change one into the other; yet the quantity of the force existing in the Universe remains always the same. Every modern physicist holds this view. Although in popular consciousness men are not aware of this law of the conservation of force and energy, they think of natural phenomena in a way that they can only be thought of when one is under the influence of this law. I want you clearly to understand what I mean. There may be something in the action of a being that corresponds to a certain principle, even when that being is not in a position to understand that principle. Suppose, for instance, that one wished to make a dog understand that a double quantity of meat means that a single quantity has been taken twice over; it could not be done. The dog could not take that in consciously, but practically he will act according to this principle; for if he has the chance of snapping at a small piece or at one twice the size, he will as a rule, seize the larger, other conditions being equal. And a man can stand under the influence of a principle without explaining it to himself in abstract form as such. Thus we may say: Certainly most people do not think of the law of conservation of force, but they do picture the whole of Nature in a way that is in accordance with the law, because what they were taught in school was taught on the assumption that the law of conservation of force exists. It is interesting to see how Mayer's line of thought expressed itself when he had to put it clearly to others who did not as yet think along the same lines. Julius Robert Mayer had a friend who kept a record of many of their conversations. He relates many interesting facts, facts by which one can examine thoroughly the mode of thought of the nineteenth century. In the first place, to give something quite external, I will choose the following. Julius Robert Mayer was so thoroughly steeped in the whole mode of ideas leading to that of the conservation of force, of the mere transmutation of one force into another, that as a rule, whenever he met a friend in the street he could not help calling to him from a distance: ‘Out of nothing, nothing comes!’ Visiting his friend one day—Rümelin was the friend's name—knocking at the door and opening it, these were his first words, even before greeting his friend: ‘Out of nothing, nothing comes.’ So deeply was this saying rooted in Mayer's consciousness. Rümelin tells of a very interesting discussion in which he, not as yet knowing very much of the law of the conservation of force, wished to have its nature explained. Julius Robert Mayer, who came from Heilbronn—(his monument stands there)—said ‘If two horses are drawing a carriage and they go for some distance, what will happen?’—‘Well’, said Rümelin, ‘the travelers in the carriage will arrive at Ohringen.’—‘But if they turn and go back without having done anything in Ohringen, and return to Heilbronn?’ ‘Well,’ replied Rümelin, ‘in that case the one journey has so to speak cancelled the other, so that there is apparently no result; yet there is the actual effect that the travelers came and went between Heilbronn and Ohringen.’ ‘No’, said Mayer, ‘that is only a secondary effect; it has nothing to do with what actually happened. The outcome of the expenditure of force on the part of the horses, that is something quite different. Through this expenditure of force, first the horses themselves grew hotter, secondly the axles of the carriage round which the wheels moved became hotter, and thirdly if we were to gauge with a delicate thermometer the grooves made by the wheels in the road, we should find that the warmth within them was greater than at the sides. That is the actual result. In the horses themselves, matter was also consumed through the transmutation of substance. All this is the actual effect. The other effect, that the people traveled backwards and forwards between Heilbronn and Ohringen is a secondary effect, but not the actual physical occurrence. The actual physical occurrence was the spent force of the horses, the transmutation into increased heat of the horses, the increased heat in the axles, the heat-consumption of cart-grease through friction in the wheels, the warming of the tracks on the road, and so forth.’ When one measures—as Mayer then did and specified the corresponding amount—one finds that the whole of the force which the horses exerted passed without remainder into heat. The rest is all a secondary matter, a side issue. This has of course a certain influence on our conception of things, and the ultimate result is that we must say: ‘Well, we must free natural occurrences from everything that is a side issue in the sense of strict scientific thought, for side issues have nothing to do with scientific thought in the sense it is understood in the nineteenth century. The secondary effect is right outside the bounds of the events of natural science.’ If, however, we ask: How does what we may call natural moral law come to expression? In what are human worth and human dignity expressed? Certainly not in the fact that the force (energy) of the horses is transmuted into the heat of the carriage axles; no, in this case the secondary effect is the chief point! Let us reflect however, how in all that is considered in natural science, this secondary effect is wholly omitted. The men of the nineteenth century, and even Kant in the eighteenth, formed their view of the origin of the Universe simply out of the principles which Julius Robert Mayer so sharply defined, when he separated out what belongs to nature alone from all that was for him merely secondary effect. If we bear this clearly in mind, we are obliged to say: The Universe must thus be constructed from the principle we recognise as Nature-Principle; all that has taken place through Christianity, for instance, is just a secondary effect, like the fact of the persons journeying by coach from Heilbronn to Ohringen, for what they had to do there does not come into consideration in the view of Natural Science. Yet, do these two streams not cross in some way or other? Let us suppose Rümelin had not been satisfied, but had raised the following objection—I know it does not hold good for the physicist of today, but it is applicable to the construction of a general view of the Universe—suppose the following was said: If the people who were traveling from Heilbronn to Ohringen had chosen not to do so, the horses would not have expended their force, the transmutation into heat would not have taken place, or it would have happened at a different place and under different conditions. Thus in our consideration of what happened in accordance with natural science, we are limited to that part of the event which does not lead us to the ultimate cause. The event would never have taken place if the travelers had not supposed they had something to do in Ohringen. Thus what natural science must regard as a side-issue enters notwithstanding into natural occurrences. Or, suppose that the travelers had something to do in Ohringen at a definite hour. Suppose the carriage axles not only became hot, but that one of them broke—in that case they could not have continued their journey. What happened, the breaking of the axle, would then of course be explicable scientifically, but what occurred through this natural phenomenon—namely, that something planned could not be carried out—might, as can easily be imagined, have tremendously far-reaching consequences, leading moreover to other natural processes, which would in their turn have led to further consequences. Thus we see that even when one stands on purely logical grounds very significant and grave questions arise. We must at once say, that these cannot be answered by the conception of the Universe arising from the hypothesis of our modern training; they cannot be answered without Spiritual Science. They can in no wise be answered without it; for before the tendency to the natural-scientific mode of thought arose, which was first brought to such exactness by Julius Robert Mayer, there was not that sharp line of division between the natural-scientific mode of thought and moral thought. If we consider the twelfth or thirteenth century, we find that what people had then to say of the moral order and the physical order always harmonised. Today people no longer read seriously; but if you read such works—I might say, there are not many things left from olden times which have come down to our days quite unadulterated—but if you take works which are like stragglers of the old cosmic conceptions, you will discover many things that prove how in earlier times the Moral was carried into the Physical, and the Physical raised to the Moral. Read one of these—now already somewhat falsified yet still fairly readable—read one of the writings of Basil Valentine. When you read there about metals, planets, medicinal drugs, in almost every line you will come across adjectives applied to the metals—good, bad, sagacious metals, and the like; which show that even in this domain some moral thinking was introduced. That of course could not be done today. Abstraction has gone so far that natural phenomena have been severed from all the secondary effects, as we may see in Julius Robert Mayer; one cannot say that it was the kindness of the horses' feet which moved them to use up the axle-grease by the warmth produced by their movement! It is not possible in this scientific connection to bring in any kind of moral category. There are two domains, the natural and the moral, and these stand quite definitely side by side. If the world-happenings were as shown by that kind of presentation, man could not exist at all in our world, he would not be there—for what is the reason for the present physical form of man? When I speak here of the physical form of man, I must ask you to take the word ‘form’ seriously. The natural philosophers of today do not take the expression ‘human form’ seriously. What do they do? Like Huxley and others, they count the bones of man and of the higher animals, and from the number of these they draw the conclusion that Man is only a more highly evolved stage of the animal. Or they count the muscles and so forth. We have repeatedly had to point out that the essential point is that the line of the animal spine is horizontal, while the human spine is vertical; and although certain animals raise themselves, the position with them is not characteristic, what is characteristic of the animal is the horizontal line of the spine. Upon this depends the whole formation. Thus I ask you to take seriously what I wish to express by the word ‘form’. This form of man; where must we look for its origin, its primary physical origin, in a spiritual way in the Universe? I have already touched on this point in these lectures, I have pointed to the starry heavens which move—whether apparently or actually is immaterial at the moment—round the Earth; the Sun also. Thus the Sun takes the same way; but if we take into consideration what we now know, namely that the Sun shifts its point of departure every Spring, remaining behind a little in relation to the stars, we come to a specially important fact. The change in position of the Vernal Point can be seen in the fact that the constellation in the following year rises earlier than the Sun and sets earlier, showing us that the Sun remains behind. I have pointed out that even the old Egyptians knew that if the circle is divided into 360 degrees, the Sun remains one day behind in 72 years. That is, in 360 times 72 years, or 25,920 years, it remains the whole circle behind, and returns to the star from which it started 25,920 years before. Thus we have the fact that in the Universe the stars travel round, and the Sun goes round—I will not go into the question as to whether this revolution is only apparent or not, the important point under consideration is that the Sun travels more slowly, remaining behind one degree of the cosmic circle in 72 years; and 72 years, as I have already indicated, is the normal maximum duration of a man's life. Man lives 72 years, exactly the period the Sun remains one degree behind the other stars. We have lost the right feeling for these things. Even as late as in the Hebraic Mysteries, the teacher still impressed very strongly upon his scholars that it is Jehovah who brings it about that the sun lingers behind the stars and, with the force which the Sun thus kept back, He fashioned the human form, which is His earthly image. Thus, mark well, the stars run their course quickly, the Sun more slowly, and so a slight difference arises which, according to these ancient Mysteries, was that which produced the human form. Man is born out of time, he is so born that he owes his existence to the difference in velocity between the cosmic day of the stars and the cosmic day of the Sun. In modern parlance we should say: If the Sun were not in the Universe as it is, if it were just a star like other stars, having the same velocity as other stars, what would be the consequence? It would be that the Luciferic powers alone would rule. That this is not so, that man is able to withhold himself from the Luciferic powers with the whole of his being, is due to the circumstance that the Sun does not share in the velocity of the stars but lags behind them, not developing the Luciferic velocity but the velocity of Jehovah. Again, if there were only the Sun velocity and not that of the stars, man would not be able to run on in front of the rest of his development with his mental powers, as he does at present. Such a condition would not fit well into his whole evolution. In our time this is very striking. If we have studied Spiritual Science seriously, we know that a man of 36, for instance, understands things he could not at 25. Experience is necessary for the comprehension of certain things. This is not admitted today, for a man of 25 feels himself complete. He is only complete as regards mental powers, but not in experience, for experience is gained more slowly than understanding. If this were taken into account, we should not find that the young people of today have already formed their point of view, for they would know that they could not do so before acquiring a certain amount of experience. Understanding travels with the stars, experience with the Sun. Assuming that human life is 72 years (unless events of Nature intervene causing Man to die older or younger), we say that it lasts the time the Sun takes to retrograde one degree. Why is this? The reason lies in a certain fine adjustment in the Cosmos. Our preliminary study obliges me to ask you to follow me for a little while into this domain. If we consider a lunar eclipse occurring in a certain year, then there will be a certain date when the eclipse can occur. The lunar eclipse occurs on the same date about every 18 years, and in the same constellation. There is a periodical rhythm in the lunar eclipse, a rhythm of 18 years. That is just a quarter of a cosmic day and just a quarter of a man's life. Man, if I may so express it, endures four such periods of darkness. Why? Because in the Universe everything is in numerical harmony. On the average, Man has in accordance with the rhythmic activity of his heart, not only 72 years of life, but 72 pulse beats, and approximately 18 respirations—again the quarter—in the minute. This numerical accord is expressed in the Universe by the rhythm between the 18 years—the Chaldean Saros period, so-called because the Chaldeans first discovered it—and the Solar period; and it is the same rhythm as is also to be found in man in the inner mobility between his respiration and his pulse-beats. Plato said, not without reason: ‘God geometrises, arithmetises’ ... Thus our 72 years of life, to which is co-ordinated also our heart and pulse activity, goes through the Saros period four times; because in our heart and pulse activity we have our breathing activity, as it were, four times over. Our whole human organism is constructed on the lines of the Universe, but we only see into its significance when we bear in mind another connection. As I said in one of the foregoing lectures, we only gauge correctly the movement of the Moon, its revolution round its axis, when we connect its revolution not with the day of the Sun, but with the day of the stars. If we have the solar time in view, we must consider a shorter time, 27.5 days for the revolution of the lunar day. I have told you that the Moon's revolution is not such as quite to accord with that of the Sun, but with the time of the stars. Hence we only understand our lunar movement aright when we do not think of it as belonging to the solar movement, but to that of the stars. In a certain sense therefore, the solar movement is outside the system to which the Moon and stars belong. Thus we are so situated in the Universe that on the one hand we are co-ordinated to the stellar-lunar system, and on the other to the solar movement. Here we see the gradual divergence of the solar and the stellar astronomy. As we have seen, if we have one astronomy only, everything falls into confusion. We can only reach a right understanding if, not limited to one astronomy, we say: On the one hand we have the starry system which, in a certain respect, contains within it the Moon; and on the other, the system to which the Sun belongs. They mutually interpenetrate. They work together. But we are wrong if we apply the same law to the two. When we realise that we have two quite different astronomies, we shall say: The cosmic happenings in which we are involved have two origins, but we are so placed that these two streams flow together in us. They fuse in us human beings. What is it then that takes place in us? Suppose that only what is admitted by the natural scientist took place in us—all sorts of things would take place in the human organism, movements of substances and so forth; these would extend over the whole organism, also to the brain and consequently to the senses. What then would the consequence be if the whole transmutation of substances which goes on in the human organism and which is inserted into the Cosmos as I have explained—if this metabolism were to extend to the brain? We should never be able to have the consciousness that we ourselves think. Oxygen, iron and other substances, carbon and so forth—of these we should say, in their mutual relations, ‘they think in us’. But as a matter of fact we are not conscious of any such thing. There is no question of its being in our consciousness. What we have as a fact of consciousness is the content of our soul-life. That can exist under no other hypothesis than that the whole of this quite material happening is demolished, is annihilated, and that in us there actually is no conservation of force and substance, but room is made by the annihilation of substance, for the development of the thought life. In fact, Man is the one arena in which an actual annihilation of substance takes place. We shall never realise it so long as we are only conscious of what is outside ourselves. Now, if we start from the assumption that after 72 years the Sun lags one degree behind in the celestial sphere, that there is this difference of velocity between the movement of the stars and that of the Sun (which difference works in us, converges, as it were, in us); and if we then picture to ourselves how the formation of our head comes from the starry heavens, and how when we, according to a very beautiful saying, first ‘see the light’, we become involved in the Sun's movement, then we must say: There is in us a continual tendency to work with a lesser velocity over against the more rapid velocity of the stars. The action of the stars in us is opposed. What is the effect of this opposition? It is the destruction of what the stars bring about in us materially, its destruction; thus, the destruction of the purely material law comes about through the solar activity. Hence we may say: In our progress through the world as human beings, if we kept pace, as it were, with the stars, we should accompany them in such a way as to be subject to the material law of the Universe. But this we are not. The solar laws oppose it, they hold us back. There is something within us which holds us back. The resultant of the two activities in us could be exactly calculated, for instance, in the following case. (The calculation cannot be followed up here, first because it would take too long and secondly because you would not be able to follow it). Here, let us say, a certain movement occurs (arrow pointing downwards), i.e. a flow takes place with a certain velocity; and the stream then fuses with another stream—it must be assumed that the other flow is going not in the same 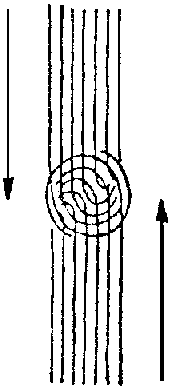 but in the opposite direction (arrow upwards). The two streams flow therefore into one another. Or imagine a wind whirling with a certain velocity from above downwards, and another from below upwards, and they whirl into one another. If we take the difference of velocity between the downward and the upward current, relating the latter to the former in such a way that a difference in velocity results bearing the same relationship as the difference in velocity between the stellar time and the solar time, then through the rotation a condensation arises which receives its own distinct form. One whirls downwards, and because the other whirls upwards driving with a greater velocity, the lesser velocity would be that driving downwards, which gives here (see diagram) through the collision, a condensation, a certain figure. This figure, disregarding imperfections, is a silhouette of the human heart. Thus, through the meeting of the Lucifer stream and the Jehovah stream, it is possible to construct exactly the figure of the human heart. It is constructed simply out of the revelations of the Universe. It is absolutely true; the Sun-movement is an expression of a slower movement which meets a quicker movement, and we are so inserted into the two movements that the silhouette of our heart arises; and on to it the rest of the human form is fitted. We see from this what Mysteries are actually hidden in the Cosmos, for as soon as we admit we have two astronomies, which work together in their results—what is the result? The human heart. The whole outlook of modern natural science is based on the fact that it does not distinguish these two streams from one another. This brings upon it the tragic fate, that the harmonious working is split apart, leaving on the one hand, the events in Nature, as reasoned by Julius Robert Mayer; and on the other hand, the ‘secondary results’, because people are unable to unite cosmically in thought what works together from these two streams. Thus for man's thinking the world falls asunder in two extremes. Here lies the cosmic aspect of something tremendously significant in regard to the understanding of Man and the Universe. Unless man can renew, on that basis of thought which we are giving today, the knowledge contained in the ancient Mysteries at the time when man was awaiting Christianity—as I have described in the book, Christianity as Mystical Fact—unless we can bring this ancient knowledge to life in a present form, as must be done, all knowledge remains an illusion; for that which comes to expression with such clarity in the human heart is to be found everywhere. Everywhere the events that happen are explainable through the union of two streams, arising from different sources. In the insertion of the Mystery of Golgotha into the evolution of our Earth, we have to do with an Event of a totally different nature from all the rest of the happenings of Earth-evolution; and this we shall never understand unless we begin by learning to understand the Cosmos itself. What I have said today is intended as a preparation or groundwork on which we shall be able to build up in our lectures of tomorrow and the day after. |
| 254. The Occult Movement in the Nineteenth Century: Lecture I
10 Oct 1915, Dornach Tr. Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| But that too was necessary, in order that the purely materialistic talents of men might develop unhindered by occult faculties. A materialistic philosopher such as Kant, a materialistic philosopher from the standpoint of the Idealists of the nineteenth century—you can easily read about this in my book Riddles of Philosophy—could not have appeared if the occult faculties had not drawn into the background. |
| 254. The Occult Movement in the Nineteenth Century: Lecture I
10 Oct 1915, Dornach Tr. Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
You will have realised from lectures given recently that in our times a materialistic view of the world, a materialistic way of thinking, is not the outcome of man's arbitrary volition but of a certain historical necessity. Those who have some understanding of the spiritual process of human evolution know that, fundamentally speaking, in all earlier centuries and millennia man participated in spiritual life to a greater extent than has been the case during the last four or five hundred years. We know with what widespread phenomena this is connected. At the very beginning of Earth-evolution, the heritage of the Old Moon clairvoyance was working in mankind. We can envisage that in the earliest ages of Earth-evolution this faculty of ancient clairvoyance was very potent, very active, with the result that the range of man's spiritual vision in those times was exceedingly wide and comprehensive. This ancient clairvoyance then gradually diminished until times were reached when the great majority of human beings had lost the faculty of looking into the spiritual world, and the Mystery of Golgotha came in substitution. But a certain vestige of the old faculties of soul remained, and evidence of this is to be found, for example, in the nature-knowledge which was in existence until the fourteenth and fifteenth, and indeed until the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. This nature-knowledge was very different in character from modern natural science. It was a nature-knowledge able to some extent still to rely, not upon clear, Imaginative clairvoyance but nevertheless upon vestiges of the Inspirations and Intuitions which were then applied and elaborated by the so-called alchemists. If an alchemist of those times was honourable in his aims and not out for egotistic gain, he still worked, in a certain respect, with the old Inspirations and Intuitions. While he was engaged in his outer activities, vestiges of the old clairvoyance were still astir within him, although no longer accompanied by any reliable knowledge. But the number of people in whom these vestiges of ancient clairvoyance survived, steadily decreased. I have often said that these vestiges can very easily be drawn out of the human soul today in states of atavistic, visionary clairvoyance. We have shown in many different ways how this atavistic clairvoyance can manifest in our own time. From all this you will realise that the nearer we come to our own period in evolution, the more we have to do with a decline of old soul-forces and a growth of tendencies in the human soul towards observation of the outer, material world. After slow and gradual preparation, this reached its peak in the nineteenth century, actually in the middle of that century. Little as this is realised today by those who do not concern themselves with such matters, it will be clear to men of the future that the materialistic tendencies of the second half of the nineteenth century had reached their peak in the middle of the century; it was then that these tendencies developed their greatest strength. But the consequence of every tendency is that certain talents develop and the really impressive greatness of the methods evolved by materialistic science stems from these tendencies of the soul to hold fast to the outer, material world of sense. Now we must think of this phase in the evolution of humanity as being accompanied by another phenomenon. If we carry ourselves back in imagination to the primeval ages of humanity's spiritual development, we shall find that in respect of spiritual knowledge, men were in a comparatively fortunate position. Most human beings, in fact all of them, knew of the spiritual world through direct vision. Just as men of the modern age perceive minerals, plants and animals and are aware of tones and colours, so were the men of old aware of the spiritual world; it was concrete reality to them. So that in those olden times, when full waking consciousness of the outer, material world was dimmed during sleep or dream, there was really nobody who would not have been connected with the dead who had been near him during life. In the waking state a man could have intercourse with the living; during sleep or dream, with the dead. Teaching about the immortality of the soul would have been as superfluous in those primeval times as it would be nowadays to set out to prove that plants exist. Just imagine what would happen at the present time if anyone set out to prove that plants exist! Exactly the same attitude would have been adopted in primeval times if anyone had thought it necessary to prove that the soul also lives after death. Humanity gradually lost this faculty of living in communion with the spiritual world. There were, of course, always individuals who used whatever opportunity was still available to develop seership. But even that became more and more difficult. How did men in olden times develop a particular gift of seership? If with insight today we study the philosophy of Plato, or what exists of that of Heraclitus, we must realise—and this applies especially to the still earlier Greek philosophies—that they are altogether different from later philosophies. Read the first chapter of my book Riddles of Philosophy, where I have shown how these ancient philosophers, Thales and Parmenides, Anaximenes and Heraclitus, are still influenced by their particular temperaments. This has not hitherto been pointed out; the first mention of it is in my book. Inevitably, therefore, some time must elapse before it is accepted—but that does not matter. Of Plato, we can still feel: this philosophy still lays hold of the whole man. When we come to Aristotle however, the feeling is that we have to do with an academic, learned philosophy. Therefore to understand Plato requires more insight than a modern philosopher usually has at his command. For the same reason there is a gulf between Plato and Aristotle. Aristotle is already a scholar in the modern sense. Plato is the last philosopher in the old Greek sense; he is a philosopher whose concepts are still imbued to some extent with life. As long as a philosophy of this kind exists, the link with the spiritual world is not broken, and indeed it continued for a long time, actually into the Middle Ages. The Middle Ages did not develop philosophy to further stages but simply took over Aristotelian philosophy; and up to a certain point of time this was all to the good. Platonic philosophy too was taken over in the same way. Now in days of antiquity, as long as at least the aptitude for clairvoyance of a certain kind was present, something very significant took place when men allowed this philosophy to work upon them. Today, philosophy works only upon the head, only upon the thinking. The reason why so many people avoid philosophy is because they do not like thinking. And especially because philosophy offers nothing in the way of sensationalism they have no desire to study it. Ancient philosophy, however, when received into the human soul, was still able, because of its greater life-giving power, to quicken still existing gifts of seership. Platonic philosophy, nay, even Aristotelian philosophy, still had this effect. Being less abstract than the philosophies of modern times, they were still able to quicken faculties of seership inherent in the human soul. And so it came to pass that in men who devoted themselves to philosophy, faculties that were otherwise sinking below the surface were quickened to life. That is how seers came into existence. But because what had now to be learnt about the physical world—and this also applies to philosophy—was of importance for the physical plane alone, and became increasingly important, man alienated himself more and more from the remnants of the old clairvoyance. He could no longer penetrate to the inner depths of existence and it was increasingly difficult to become a seer. Nor will this again be possible until the new methods indicated as a beginning in the book Knowledge of the Higher Worlds. How is it achieved? are accepted by mankind as plausible. We have heard that a period of materialism reached its peak—one could also say, its deepest point—in the middle of the nineteenth century. It is certain that conditions will become more and more difficult but the threads of connection with the earlier impulses in the evolution of humanity must nevertheless not be broken. The following diagram indicates how seership has developed:  Here (yellow) seership is still present in full flower; it vanishes more and more completely until the lowest point is reached in the middle of the nineteenth century, and then there is again an ascent. But understanding of the spiritual world is not the same as seership. Just as in regard to the world, science is not the same thing as mere sensory perception, clairvoyance itself is a different matter from understanding what is seen. In the earliest epochs men were content, for the most part, with vision; they did not get to the point of thinking to any great extent about what was seen, for their seership sufficed. But now, thinking too came to the fore. The line a–b, therefore, indicates seership, vision; line c–d indicates thought or reflection about the spiritual worlds. In ancient times man was occupied with his visions and thinking lay, as it were, in the subconscious region of the soul. The seers of old did not think, did not reflect; everything came to them directly through their vision. Thinking first began to affect seership about three or four thousand years B.C. There was a golden age in the old Indian, Persian, Egypto-Chaldean and also in very ancient Greek culture when thinking, still youthful and fresh, was wedded with vision in the human soul. In those times, thinking was not the laboured process it is in our day. Men had certain great, all-embracing notions, and, in addition, they had vision (e in diagram) . Something of the kind, although already in a weaker form, was present to a marked degree in the seers who founded the Samothracian Mysteries and there gave the monumental teaching of the four gods: Axieros, Axiokersos, Axiokersa and Kadmillos. In this great teaching which once had its home in the island of Samos, certain lofty concepts were imparted to those who were initiated in the Mysteries and they were able to unite with these concepts the still surviving fruits of ancient seership. It may be possible on some other occasion to speak of these things too in greater detail.1 But then seership gradually sank below the threshold of consciousness and to call it up from the depths of the soul became more and more difficult. It was, of course, possible to retain some of the concepts, even to develop them further; and so finally a time came when there were initiates who were not necessarily seers—mark well, initiates who were not necessarily seers. In different places where there were assemblies of these initiates, they simply adopted what was in part preserved from olden times, of which it could be affirmed that ancient seers revealed it—or what could be drawn forth from men who still possessed the faculties of atavistic clairvoyance. Conviction came partly through historical traditions, partly through experiments. Men convinced themselves that what their intellects thought was true. But as time went on the number of individuals in these assemblies who were still able to see into the spiritual world, steadily diminished, while the number of those who had theories about the spiritual world and expressed them in symbols and the like, steadily increased. And now think of what inevitably resulted from this about the middle of the nineteenth century, when the materialistic tendencies of men had reached their deepest point. Naturally, there were people who knew that there is a spiritual world and also knew what is to be found in the spiritual world, but they had never seen that world. Indeed, the most outstanding savants in the nineteenth century were men who, although they had seen nothing whatever of the spiritual world, knew that it exists, could reflect about it, could even discover new truths with the help of certain methods and a certain symbolism that had been preserved in ancient tradition. To take one example only.—Nothing special is to be gained by looking at a drawing of a human being. But if a human form is drawn with a lion's head, or another with a bull's head, those who have learnt how these things are to be interpreted can glean a great deal from symbolical presentations of this kind—similarly, if a bull is depicted with the head of a man or a lion with the head of a man. Such symbols were in frequent use, and there were earnest assemblies in which the language of symbols could be learnt. I shall say no more about the matter than this, for the schools of Initiation guarded these symbols very strictly, communicating them to nobody who had not pledged himself to keep silence about them. To be a genuine knower a man needed only to have mastered this symbolic language—that is to say, a certain symbolic script. And so the situation in the middle of the nineteenth century was that mankind in general, especially civilised mankind, possessed the faculty of spiritual vision deep down in the subconsciousness, yet had materialistic tendencies. There were, however, a great many people who knew that there is a spiritual world, who knew that just as we are surrounded by air, so we are surrounded by a spiritual world. But at the same time these men were burdened with a certain feeling of responsibility. They had no recourse to any actual faculties whereby the existence of a spiritual world could have been demonstrated, yet they were not willing to see the world outside succumbing altogether to materialism. And so in the nineteenth century a difficult situation confronted those who were initiated, a situation in face of which the question forced itself upon them: Ought we to continue to keep within restricted circles the knowledge that has come over to us from ancient times and merely look on while the whole of mankind, together with culture and philosophy, sinks down into materialism? Dare we simply look on while this is taking place? They dared not do so, especially those who were in real earnest about these things. And so it came about that in the middle of the nineteenth century the words “esotericist” and “exotericist” which were used by the initiates among themselves, acquired a meaning deviating from what it had previously been. The occultists divided into exotericists and esotericists. If for purposes of analogy, expressions connected with modern parliaments are adopted—although naturally they are unsuitable here—the exotericists could be compared with the left-wing parties and the esotericists with the right-wing parties. The esotericists were those who wanted to continue to abide firmly by the principle of allowing nothing of what was sacred, traditional knowledge, nothing that might enable thinking men to gain insight into the symbolic language, to reach the public. The esotericists were, so to speak, the Conservatives among the occultists. Who, then—we may ask—were the exotericists ? They were and are those who want to make public some part of the esoteric knowledge. Fundamentally, the exotericists were not different from the esotericists, except that the former were inclined to follow the promptings of their feeling of responsibility, and to make part of the esoteric knowledge public. There was widespread discussion at that time of which the outside world knows nothing but which was particularly heated in the middle of the nineteenth century. Indeed the clashes and discussions between the esotericists and the exotericists were far more heated than those between the Conservatives and Liberals in modern parliaments. The esotericists took the stand that only to those who had pledged themselves to strictest silence and were willing to belong to some particular society should anything be told concerning the spiritual world or any knowledge of it communicated. The exotericists said: If this principle is followed, people who do not attach themselves to some such society or league will sink altogether into materialism. And now the exotericists proposed a way. I can tell you this today: the way proposed by the exotericists at that time is the way we ourselves are taking. Their proposal was that a certain part of the esoteric knowledge should be popularised. You see, too, how we ourselves have worked with the help of popular writings, in order that men may gradually be led to knowledge of the spiritual worlds. In the middle of the nineteenth century things had not reached the point at which anyone would have ventured to admit that this was their conviction. In such circles there is, of course, no voting, and to say the following is to speak in metaphor. Nevertheless it can be stated that at the first ballot the esotericists won the day and the exotericists were obliged to submit. The society or league was not opposed, because of the good old precept of holding together. Not until more modern times has the point been reached when members are expelled or resign. Such things used not to happen because people understood that they must hold together in brotherhood. So the exotericists could do no other than submit. But their responsibility to the whole of mankind weighed upon them. They felt themselves, so to speak, to be guardians of evolution. This weighed upon them, with the result that the first ballot—if I may again use this word—was not adhered to, and—once again I will use a word which as it is drawn from ordinary parlance must be taken metaphorically—a kind of compromise was reached. This led to the following situation. It was said, and this was also admitted by the esotericists: it is urgently necessary for humanity in general to realise that the surrounding world is not devoid of the spiritual, does not consist only of matter nor is subject to purely material laws; humanity must come to know that just as we are surrounded by matter, so too we are surrounded by the spiritual, and that man is not only that being who confronts us when we look at him in the material sense, but also has within him something that is of the nature of spirit and soul. The possibility of knowing this must be saved for humanity. On this, agreement was reached—and that was the compromise. But the esotericists of the nineteenth century were not prepared to surrender the esoteric knowledge, and a different method had therefore to be countenanced. How it came into being is a complicated story. Particularly on occasions of the founding of Groups I have often spoken of what happened then. The esotericists said: We do not wish the esoteric knowledge to be made public, but we realise that the materialism of the age must be tackled.—In a certain respect the esotericists were basing themselves on a well-founded principle, for when we see repeatedly the kind of attitude that is adopted today towards esoteric knowledge we can understand and sympathise with those who said at that time that they would not hear of it being made public. We must realise, however, that over and over again it can be seen that open communication of esoteric knowledge leads to calamity, and that those who get hold of such knowledge are themselves the cause of obstacles and hindrances in the way of its propagation. In recent weeks we have often spoken of the fact that far too little heed is paid to these obstacles and hindrances. Most unfortunate experiences are encountered when it is a matter of making esoteric knowledge public. Help rendered with the best will in the world to individuals—even there the most elementary matters lead to calamity! You would find it hard to believe how often it happens that advice is given to some individual—but it does not please him. When the outer world says that an occultist who works as we work here, exercises great authority—that is just a catchword. As long as the advice given is acceptable, the occultist, as a rule, is not grumbled at; but when the advice is not liked, it is not accepted. People even browbeat one by declaring: “If you do not give me different advice, I simply cannot get on.” This may come to the point of actual threats, yet it had simply been a matter of advising the person in question for his good. But as he wants something different, he says: “I have waited long enough; now tell me exactly what I ought to do.” He was told this long ago, but it went against the grain. Finally things come to the point where those who were once the most credulous believers in authority become the bitterest enemies. They expect to get the advice they themselves want and when it is not to their liking they become bitter enemies. In our own time, therefore, experience teaches us that we cannot simply condemn the esotericists who refused to have anything to do with popularising the esoteric truths. And so in the middle of the nineteenth century this popularising did not take place; an attempt was, however, made to deal in some way with the materialistic tendencies of the age. It is difficult to express what has to be said and I can only put it in words which, as such, were never actually uttered but none the less give a true picture. At that time the esotericists said: What can be done about this humanity? We may talk at length about the esoteric teaching but people will simply laugh at us and at you. At most you will win over a few credulous people, a few credulous women, but you will not win over those who cling to the strictly scientific attitude, and you will be forced to reckon with the tendencies of the age. The consequence was that endeavours were made to find a method by means of which attention could be drawn to the spiritual world, and indeed in exactly the same way as in the material world attention is called to the fact that in a criminal the occipital lobe does not or does not entirely cover the corresponding part of his brain.—And so it came about that mediumship was deliberately brought on the scene. In a sense, the mediums were the agents of those who wished, by this means, to convince men of the existence of a spiritual world, because through the mediums people could see with physical eyes that which originates in the spiritual world; the mediums produced phenomena that could be demonstrated on the physical plane. Mediumship was a means of demonstrating to humanity that there is a spiritual world. The exotericists and the esotericists had united in supporting mediumship, in order to deal with the tendency of the times. Think only of men such as Zöllner, Wallace, du Prel, Crookes, Butlerow, Rochas, Oliver Lodge, Flammarion, Morselli, Schiaparelli, Ochorowicz, James, and others—how did they become convinced of the existence of a spiritual world? It was because they had witnessed manifestations from the spiritual world. But everything that can be done by the spiritual world and by the initiates must, to begin with, be in the nature of attempts in the world of men. The maturity of humanity must always be tested. This support of mediumship, of spiritualism, was therefore also, in a certain sense, an attempt. All that the exotericists and esotericists who had agreed to the compromise could say was: What will come of it remains to be seen.—And what did, in fact, come of it? Most of the mediums gave accounts of a world in which the dead are living. Just read the literature on the subject! For those who were initiated, the result was distressing in the utmost degree, the very worst there could possibly have been. For you see, there were two possibilities. One was this.—Mediums were used and they made certain communications. They were only able to relate what they communicated to the ordinary environment—in the material elements of which spirit is, of course, present. It was expected, however, that the mediums would bring to light all kinds of hidden laws of nature, hidden laws of elemental nature. But what actually happened was inevitable, and for the following reason.— Man, as we know, consists of physical body, etheric body, astral body and ego. From the time of going to sleep to waking, therefore, the real man is in his ego and astral body; but then he is at the same time in the realm of the dead. The medium sitting there, however, is not an ego and an astral body. The ego-consciousness and also the astral consciousness have been suppressed and as a result the physical and etheric bodies become particularly active. In this condition the medium may come into contact with a hypnotist, or an inspirer—that is to say, with some other human being. The ego of another human being, or also the environment, can then have an effect upon the medium. It is impossible for the medium to enter the realm of the dead because the very members of his being which belong to that realm have been made inoperative. The mediums went astray; they gave accounts allegedly of the realm of the dead. And so it was obvious that this attempt had achieved nothing except to promulgate a great fallacy. One fine day, therefore, it had to be admitted that a path had been followed which was leading men into fallacy—to purely Luciferic teachings bound up with purely Ahrimanic observations. Fallacy from which nothing good could result had been spread abroad. This was realised as time went on. You see, therefore, how an attempt was made to deal with the materialistic tendencies of the age and yet to bring home to men's consciousness that there is a spiritual world around us. To begin with, this path led to fallacy, as we have heard. But you can gather from this how necessary it is to take the other path, namely, actually to begin to make public part of the esoteric knowledge. This is the path that must be taken even if it brings one calamity after another. The very fact that we pursue Spiritual Science is, so to say, an acknowledgment of the need to carry into effect the principle of the exotericists in the middle of the nineteenth century. And the aim of the Spiritual Science we wish to cultivate is nothing else than to carry this principle into effect, to carry it into effect honourably and sincerely. From all this it will be clear to you that materialism is something about which we cannot merely speculate; we must understand the necessity of its appearance, especially of the peak—or lowest point—it reached about the middle of the nineteenth century. The whole trend had of course begun a long time before then—certainly three, four or five centuries before. Man's leanings to the spiritual passed more and more into his subconsciousness, and this state of things reached its climax in the middle of the nineteenth century. But that too was necessary, in order that the purely materialistic talents of men might develop unhindered by occult faculties. A materialistic philosopher such as Kant, a materialistic philosopher from the standpoint of the Idealists of the nineteenth century—you can easily read about this in my book Riddles of Philosophy—could not have appeared if the occult faculties had not drawn into the background. Certain faculties develop in man when others withdraw, but while the one kind of faculties and talents develops outwardly, the other kind takes its own inner path. These three, four or five centuries were not, therefore, a total loss for the spiritual evolution of mankind. The spiritual forces have continued to develop below the threshold of consciousness, and if you think about what I have indicated in connection with von Wrangell's pamphlet2 on the subject of what he there calls the “dreamlike”, you will be able to recognise the existence of occult faculties which are merely waiting to unfold. They are present in abundance in the souls of men; it is only a matter of drawing them out in the right way. It was necessary to say these things by way of introduction, and tomorrow we will pass on to the question of the relation between the Living and the Dead, bearing in mind that in one respect the wrong path resulting from the compromise between the exotericists and the esotericists has actually been instructive. To understand the nature of this compromise we must study the questions of birth and death and then show what effect the materialistic methods have had in this connection.
|
| 233a. Rosicrucianism and Modern Initiation: Research into the Life of the Spirit During the Middle Ages
04 Jan 1924, Dornach Tr. Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| There you have the first Act of the drama. The second Act begins with Kant! One has there the hanger and the clothes hanging on it, and one begins to philosophise in true Kantian fashion as to what the “thing-in-itself” of these clothes may be. |
| 233a. Rosicrucianism and Modern Initiation: Research into the Life of the Spirit During the Middle Ages
04 Jan 1924, Dornach Tr. Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In close connection with what I had to bring before you in the lectures given at our Christmas Foundation Meeting, I should like, in the lectures that are now to be given, to speak further of the movement that is leading us in modern times to research into the life of the spirit. I refer to the movement spoken of under the name of Rosicrucianism or some other occult designation, and I should like to take this opportunity of giving you a picture of it in its inner aspect and nature. It will be necessary first of all to say something, by way of introduction, about the whole manner of forming ideas which had become customary round about the ninth, tenth, and eleventh centuries A.D., and which only very gradually disappeared; for it is even to be found here and there among stragglers, as it were as late as the nineteenth century. I do not want today to deal with the matter from a historical point of view, but rather to place before your mind's eye conceptions and ideas that you are to think of as inwardly experienced by certain people belonging to these centuries. In point of fact it is not generally realised that we have only to go back a comparatively short time in history, to find that the men who were accounted to be scholars were possessed of a world of ideas altogether different from our own. In these days we speak of chemical substances, we enumerate seventy or eighty chemical elements; but we have no idea how very little we are saying when we name one substance as oxygen, another as nitrogen, and so on. Oxygen, for instance, is something that is present only under certain well-defined conditions—conditions of warmth, e.g., and other circumstances of earthly life, and it is impossible for a reasonable person to unite a conception of reality with something that, when the temperature is raised by so and so many degrees, is no longer present in the same measure or manner as it is under the conditions that obtain for man's physical life on Earth. It was the realisation of facts like this that underlay research during the early and middle part of the Middle Ages; the life of research of those times set out to get beyond the relative in existence, to arrive at true existence. I have marked a transition as between the ninth and tenth centuries A.D., because before this time man's perceptions were still altogether spiritual. It would never, for example, have occurred to a scholar of the ninth century to imagine Angels, Archangels, or Seraphim as falling short in respect of reality—purely in respect of reality—of the physical men he saw with his eyes. You will find that before the tenth century, scholars always speak of the spiritual Beings, the so-called Intelligences of the Cosmos, as of beings one actually meets in life. The people of that time were of course well aware that the day was long past when such vision had been common human experience, but they knew that in certain circumstances the meeting could still take place. We must not, for instance, overlook the fact that on into the ninth and tenth centuries countless priests of the Catholic Church were quite conscious of how, in the course of their celebration of the Mass, it happened that in this or that enactment they met spiritual Beings, the Intelligences of the Cosmos. With the ninth and tenth centuries, however, the direct and immediate connection with the Intelligences of the Universe began to disappear from men's consciousness; and there began to light up, in its place, the consciousness of the Elements of the Cosmos, the earthy, the fluid or watery, the airy, the warm or fiery. And so it came about that just as hitherto men had spoken of Cosmic Intelligences that rule the movements of the planets, that lead the planets across the constellations of the fixed stars, and so forth, now they spoke instead of the immediate environment of the Earth. They spoke of the elements of earth, water, air, fire. Of chemical substances, in the modern sense of the word, they did not as yet take account. That came much later. It would, however, be a great mistake to imagine that the scholars of the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries—even in a sense, the scholars of the eighteenth century—had ideas of warmth, air, water, earth, that resembled the ideas men have today. Warmth is spoken of today merely as a condition in which bodies exist. No one speaks any longer of actual warmth-ether. Air, water—these have likewise become for the modern man completely abstract. It is time we studied these ideas and learned to enter into a true understanding of them. And so today I should like to give you a picture, showing you how a scholar of those times would speak to his pupils. When I wrote my Outline of Occult Science I was obliged to make the account of the evolution of the Earth accord at any rate a little with the prevailing ideas of the present day. In the thirteenth and twelfth centuries one would have been able to give the account quite differently. The following might then have been found in a certain chapter, e.g., of Outline of Occult Science. An idea would have been called up, to begin with, of the Beings who may be designated as the Beings of the First Hierarchy: Seraphim, Cherubim, Thrones. The Seraphim would have been characterised as Beings with whom there is no subject and object, with whom subject and object are one and the same, Beings who would not say: Outside me are things—but: The world is, and I am the World, and the World is I. Such Beings know only of themselves, and this knowledge of themselves is for them an inner experience of which man has a weak reflection when he has the experience of being filled, shall we say, with a glowing enthusiasm. It is, you know, quite difficult to make the man of today understand what is meant by “glowing enthusiasm.” Even in the beginning of the nineteenth century men knew better what it is than they do today. In those days it could still happen that some poem or other was being read aloud and the people were so filled with enthusiasm—forgive me, but it really was so—that present-day man would say they had all gone out of their minds. They were so moved, so warmed! Today people freeze up just when you expect them to be “enthused.” Now it was lifting this element of enthusiasm, this rapture of the soul that came naturally especially to the men of Middle and Eastern Europe—it was by lifting it into consciousness, by making it alone the complete content of consciousness, that men came to form an idea of the inner life of the Seraphim. Again as a bright, clear element in consciousness, full of light, so that thought turns directly into light, illuminating everything—such an idea did men form of the element of consciousness of the Cherubim. And the element of consciousness of the Thrones was conceived as sustaining, bearing the worlds in Grace. There you have one such sketch. I could go on speaking of it for a long time. For the moment I only wanted to show you that in those days one would have tried to describe the Seraphim, Cherubim and Thrones in the true qualities of their being. And then one would have gone on to say: the Choir of Seraphim, Cherubim and Thrones works together, in such wise that the Thrones found and establish a kernel; the Cherubim let their own light-filled being stream forth from this centre or kernel; and the Seraphim enwrap the whole in a mantle of warmth and enthusiasm that rays far out into cosmic space. [Footnote: Drawings were made on the blackboard, with coloured chalks.] All the drawing I have made is Beings: in the midst the Thrones; in the circumference around them the Cherubim; and, outermost of all, the Seraphim. All is essential Being, Beings who move and weave into one another, do, think, will, feel in one another. All is of the very essence of Being. And now, if a being having the right sensitiveness were to take its path through the space where the Thrones have in this manner established a kernel and centre, where the Cherubim have made a kind of circling around it and the Seraphim have, as it were, enclosed the whole—if a being with the required sensitiveness were to come into this realm of the activity of the First Hierarchy, it would feel warmth in varying differentiations—here greater warmth, there less; but it would all be an experience of soul, and yet at the same time physical experience in the senses; that is to say, when the being felt itself warm in soul, the feeling would be actually the feeling you have when you are in a well-warmed room. Such a united building-up by Beings of the First Hierarchy did verily once take place in the Universe; it formed what we call the Saturn existence. The warmth is merely the expression of the fact that the Beings are there. The warmth is nothing more than the expression of the fact that the Beings are there. A picture will perhaps make clearer to you what I mean. Let us suppose you have an affection for a certain human being. You feel his presence gives you warmth. But now someone comes along who is frightfully abstract and says: “The person himself doesn't interest me, I will imagine him absent; the warmth he sheds around him, that alone is what interests me.” Or suppose he doesn't even say “The warmth he sheds around him is all that interests me.” Suppose he says: “The warmth is all that interests me.” He talks nonsense, of course, you will see that at once; for if the man is not there who sheds the warmth, then the warmth is not there either. The warmth is in any case only there when the man is there. In itself it is nothing. The man must be there, if the warmth is to be there. Even so must Seraphim, Cherubim and Thrones be there; if the Beings are not there, neither is the warmth. The warmth is merely the revelation of Seraphim, Cherubim and Thrones. Now in the time of which I speak, everything was exactly as I have described it. Men spoke of Elements. They spoke of the Element of Warmth, and by the Element of Warmth they understood Cherubim, Seraphim, Thrones—and that is the Saturn existence. The description went further. It was said: Seraphim, Cherubim, Thrones—these alone have the power to bring forth something of the nature of Saturn, to place it into the Cosmos. The highest Hierarchy alone is capable of placing such an existence into the Cosmos. But when this highest Hierarchy had once placed it there and a new world-becoming had taken its start, then the evolution could go on further. The Sun, as it were, that is formed of Seraphim, Cherubim and Thrones could carry evolution further. And it came to pass in the following manner. Beings of the Second Hierarchy, Kyriotetes, Dynamis, Exusiai, Beings that had been generated by the Seraphim, Cherubim and Thrones, press into the space that has been formed through the working of Seraphim, Cherubim and Thrones, that has been fashioned to Saturn warmth. Thither entered younger, cosmically younger Beings. And how did these cosmically younger Beings work? Whereas the Cherubim, Seraphim and Thrones reveal themselves in the Element of Warmth, the Beings of the second Hierarchy form themselves in the Element of Light. Saturn is dark; it gives warmth. And now within the dark world of the Saturn existence arises that which can arise through the working of the Sons of the First Hierarchy, through Exusiai, Dynamis and Kyriotetes. What is it that is able now to arise within the Saturn warmth? The penetration of the Second Hierarchy signifies an inner illumination. The Saturn Warmth is inwardly shone through with light and at the same time it becomes denser. Instead of only the Warmth Element there is now also Air. And in the revelation of Light we have the entry of the Second Hierarchy. You must clearly understand that it is in very deed and truth Beings who thus press their way into the Saturn existence. One who had the requisite power of perception would see the event as a penetration of Light; it is Light that reveals the path of the Beings. And wherever Light occurs, there occurs too, under certain conditions, shadow, darkness, dark shadow. Through the Penetration by the Second Hierarchy in the form of Light, shadow also comes to pass. What is shadow? It is Air. And indeed until the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries men knew what Air is. Today men know only that air consists of oxygen, nitrogen and so forth. When that is said, it is very much as if someone were to say about a watch that it consisted of glass and silver. He would be saying nothing at all about the watch. And nothing at all is said about Air as a cosmic phenomenon when we say that it consists of oxygen and nitrogen. We say very much, on the other hand, if we know: Air comes forth from the Cosmos as the shadow of Light. In actual fact we have, with the entry of the second Hierarchy into the Saturn warmth, the entry of Light and we have too the shadow of Light, Air. And when we have this we have Sun. Such is the way one would have had to speak in the thirteenth and twelfth centuries. And what follows after this? The further evolution comes about through the working of the Sons of the Second Hierarchy—Archai, Archangels, Angels. The Second Hierarchy have accomplished the entry of the Element of Light, Light that has drawn after it its shadow, the darkness of Air—not the indifferent, neutral darkness that belongs to Saturn, the darkness that is simply absence of Light, but the darkness that is wrought out as the antithesis of Light. And now to this Element of Light the Third Hierarchy—Archai, Archangels, Angels—add through their own nature and being a new Element, an Element that is like our human desire, like our impulse to strive after something, to long for something. Thereby the following comes to pass. Let us suppose an Archai or Archangel Being enters, and comes upon an Element of Light, encounters, as it were, a place of Light. In this place of Light the Being receives, through its receptivity for the Light, the urge, the desire for darkness. The Angel Being bears Light into darkness—or an Angel Being bears darkness into Light. These Beings are mediators, messengers between Light and Darkness. It follows from this that what previously has only shone in Light and drawn after it its shadow, the darkness of Air, begins now to shine in colour, to glow in a play of colour. Light begins to appear in darkness, darkness in light. The Third Hierarchy create colour out of light and darkness. Here we may find a connection with something that is historical, with something that is to be found in written document. For in the time of Aristotle men still knew, when they contemplated in the Mysteries, whence colours come; they knew that the Beings of the Third Hierarchy have to do with colour. Therefore Aristotle, in his colour harmony, showed that colour signifies a working together of Light and Darkness. But this spiritual element in man's thought, whereby he knew that behind Warmth he has to see Beings of the First Hierarchy, behind Light and its shadow Darkness, Beings of the Second Hierarchy, and behind the iridescent play of Colour he has to see in a great cosmic harmony, Beings of the Third Hierarchy—this spiritual element in man's thought has been lost. And nothing is left for man today but the unhappy Newtonian Theory of Colour. The Initiates continued to smile at Newton's theory till the eighteenth century, but in that time it became an article of faith for professional physicists. One must indeed have lost all knowledge of the spiritual world when one can speak in the sense of Newton's Theory of Colour. If one is still inwardly stimulated by the spiritual world, as was the case with Goethe, then one resists it. One places before men the truth of the matter, as Goethe did, and attacks with might and main. For Goethe never censured so hardly as when he had to censure Newton, he went for him and his theory hammer and tongs! Such a thing is incomprehensible nowadays, for the simple reason that in our time anyone who does not recognise the Newtonian Theory of Colour is a fool in the eyes of the physicists. But things were different in Goethe's time. He did not stand alone. True, he stood alone as one who spoke openly on the matter; but there were others who really knew, even as late as the end of the eighteenth century, whence colour comes, who knew with absolute certainty how colour wells up from within the Spiritual. But now we must go further. We have seen that Air is the shadow of Light. And as, when Light arises, under certain conditions we find the dark shadow, so when colour is present and works as a reality—and it can do so, for when it penetrates into the Air-element, it flames up in this Air, works in it, in a word is something, is no mere reflection but a reality flashing and sparkling in the Air-element—when this is so, then under certain conditions we get pressure, counter-pressure, and out of the real Colour there comes into being the fluid, the Element of Water. As, for cosmic thinking, the shadow of Light is Air, so is Water the reflection, the creation of Colour in the Cosmos. You will say: No, that I cannot understand! But try for once really to grasp Colour in its true meaning. Red—surely you do not think that red is, in its essence, the neutral surface it is generally regarded as being? Red is something that makes an attack upon you.—I have often spoken of this.—You want to run away from red; it thrusts you back. Blue-violet, on the other hand, you want to run after! It runs away from you all the time; it grows deeper and ever deeper. Everything is contained in the colours. The colours are a world, and the soul element in the world of colour simply cannot exist without movement; we ourselves, if we follow the colours with soul-experience, must follow with movement. People gaze open-eyed at the rainbow. [Footnote: A sketch of a rainbow was made on the blackboard with chalks of the colours as seen in the sky: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet.] But if you look at the rainbow with a little imagination, you may see there elemental Beings. These elemental Beings are full of activity and demonstrate it in a very remarkable manner. Here (at yellow) you see some of them streaming forth from the rainbow, continually coming away out of it. They move across and the moment they reach the lower end of the green they are drawn to it again. You see them disappear at this point (green). On the other side they come out again. To one who views it with imagination, the whole rainbow manifests a streaming out of spirit and a disappearing of it again within. It is like a spiritual dance, in very deed a spiritual waltz, wonderful to behold. And you may observe too how these spiritual Beings come forth from the rainbow with terrible fear, and how they go in with invincible courage. When you look at the red-yellow, you see fear streaming out, and when you look at the blue-violet you have the feeling: there all is courage and bravery of heart. Now picture to yourselves: There before me is no mere rainbow! Beings are coming out of it and disappearing into it—here anxiety and fear, there courage ... And now, here the rainbow receives a certain thickness and you will be able to imagine how this gives rise to the element of Water. In this watery element spiritual Beings live, Beings that are actually a kind of copy of the Beings of the Third Hierarchy. There is no doubt about it: if we want to get near the men of real knowledge in the eleventh, twelfth and thirteenth centuries, we must understand these things. Indeed we cannot even understand the men of still later times, we cannot understand Albertus Magnus, if we read him with the knowledge we have today. We must read him with a manner of knowledge that takes account of the fact that spiritual things like these were still a reality for him: only then shall we understand how he expresses himself, how he uses his words. Thus we have, as a reflection of the Hierarchies, first Air and then Water. The Hierarchies themselves dive in, as it were—the second Hierarchy in the form of Light, the third Hierarchy in the form of Colour. And with this latter event the Moon existence is attained. And now we come to the Fourth Hierarchy. (I am telling it, you remember, as it was thought of in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries.) We today do not speak of the Fourth Hierarchy; but men still spoke in that way in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries. What is this Fourth Hierarchy? It is Man. Man himself is the fourth Hierarchy. But by the Fourth Hierarchy was not meant the two-legged being that goes about the world today, ageing year by year! To the true man of knowledge of those times, present-day man would have appeared as something very strange. No, in those times they spoke of original Man, of Man before the Fall, who still bore a form that gave him power over the Earth, even as the Angels and Archangels and Archai had power over the Moon existence, the second Hierarchy over the Sun existence and the first Hierarchy over the Saturn existence. They spoke of Man in his original Earthly existence and then they were right to speak of him as the Fourth Hierarchy. And with this Fourth Hierarchy came—as a gift it is true, of the higher Hierarchies, but the higher Hierarchies have held it only as a possession they did not themselves use but guarded and kept—with the Fourth Hierarchy came Life. Into the world of Colour, into the iridescent world of changing colour, of which I have only been able to give you the merest hints and suggestions, came Life. You will say: Then did nothing live before this time? My dear friends, you can understand how it is from the human being himself. Your Ego and your astral body have not life, and yet they exist, they have being. That which is of the soul and the spirit does not need life. Life begins only with your etheric body. And the etheric body is something external, it is of the nature of a sheath. Thus only after the Moon existence and with the Earth existence does Life enter into the domain of that evolution to which our Earth belongs. The world of moving, glancing colour is quickened to life. And now not only do Angels and Archangels and Archai experience a longing desire to carry Darkness into Light, and Light into Darkness, thereby calling forth the play of colour in the planet; now a desire becomes manifest to experience this play of colour as something inward, to feel it all inwardly; when Darkness dominates Light, to feel weakness, laziness; when Light dominates Darkness, to feel activity. For what is happening really, when you run? When you run, Light predominates over Darkness in you; when you sit and are lazy and indolent, then Darkness predominates over Light. It is a play of Colour, an activity of Colour, not physical, but of the soul. Colour permeated with Life, in its iridescence streamed-through with Life—that is what appeared with the coming of the Fourth Hierarchy, Man. And in this moment of cosmic becoming, the forces that became active in the play of colour began to build contours, began to fashion forms. Life, as it rounded off and moulded the colours, called into being the hard, fast form of the crystal. And we have come into Earth existence. Such things as I have been describing to you were fundamental truths for the mediaeval alchemists and occultists, Rosicrucians and others, who flourished—though history tells us little of them—from the ninth and tenth on into the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, and of whom stragglers are to be found as late as the eighteenth and even the beginning of the nineteenth century—always however in these later times regarded as strange and eccentric people. Only with the entry of the nineteenth century did this knowledge become entirely hidden. Only then did men come to acquire a conception of the world that led them to a point of view which I will indicate in the following way. Imagine, my dear friends, that here we have a man. Suppose I cease to have any interest in this man, but I take his clothes and hang them on a coat-hanger that has a knob here above like a head. From now on I take no further interest in the man and I tell myself: There is the man! What does it matter to me what can be put into these clothes? That, the coat-hanger with the clothes, is the man! This is really what happened with the Elements. It does not interest us any longer that behind Warmth or Fire is the First Hierarchy, behind Light and Air the Second Hierarchy, behind what we call Chemical Ether or Colour Ether and Water the Third Hierarchy, and behind the Life Element and Earth the Fourth Hierarchy, Man.—The peg, the hanger and on it the clothes.—That is all! There you have the first Act of the drama. The second Act begins with Kant! One has there the hanger and the clothes hanging on it, and one begins to philosophise in true Kantian fashion as to what the “thing-in-itself” of these clothes may be. And one comes to a realisation that the “thing-in-itself” of the clothes cannot be known. Very clever, very clever indeed! Of course, if you first take away the man and have only the coat-hanger with the clothes, you can philosophise over the clothes, you can make most beautiful speculations! You can either philosophise in Kantian fashion and say: “The ‘thing-in-itself’ cannot be known,” or in the fashion of Helmholtz and think to yourself: “But these clothes, they cannot of themselves have forms; there is nothing really there but tiny, whirling specks of dust, tiny atoms, which hit and strike each other and behold, the clothes are held in their form!” Yes, my friends, that is the way thought has developed in recent times. It is all abstract, shadowy. And yet we live today in this way of thinking, in this way of speculating; it gives the stamp to our whole natural-scientific outlook. And when we do not admit that we think in this atomistic way, then we do it most of all! For we are very far from admitting that it is quite unnecessary to dream of a whirling dance of atoms, and that what we have rather to do is to put back the man into the clothes. This is however the very thing which the renewal of Spiritual Science must try to do. I wanted to indicate to you today, in a number of pictures, the nature and manner of thinking in earlier centuries and what is really contained in the older writings, although it has become obscure. The very obscurity, however, has led to incidents that are not without interest. A Norwegian scientist of today has reprinted a passage from the writings of Basilius Valentinus and has interpreted it in terms of modern chemistry. He could not possibly say otherwise than that it is nonsense, because this is what it appears to be if, in the modern sense, one thinks of a chemist standing in a laboratory, making experiments with retorts and other up-to-date apparatus. What Basilius Valentinus really gives in this passage is a fragment of embryology, expressed in pictures. That is what he gives—a fragment of embryology. According to the modern mode of thought it seems to indicate a laboratory experiment, which then proves to be nonsense. For you will not expect to reproduce the real processes of embryology in a retort—unless you be like the mediaevally minded Wagner of Goethe's Faust. It is time that these things were understood. And in connection with the great truths of which I was able to speak during the Christmas Foundation Meeting, I shall have more to say concerning the spiritual life and its history during the last few centuries. |
| 233a. Rosicrucianism and Modern Initiation: The Time of Transition
06 Jan 1924, Dornach Tr. Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| The idea shows itself in a significant manner, it is still, shall we say, human in character. Later, in Kant, in du Bois-Reymond, you will find expressed in them: “Man cannot cross the boundaries of knowledge.” |
| 233a. Rosicrucianism and Modern Initiation: The Time of Transition
06 Jan 1924, Dornach Tr. Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
I spoke to you yesterday of the special form in which the results of research in the realm of spiritual knowledge were communicated in the Middle Ages. This form was, so to speak, the last Act before a door was shut for the evolution of the spirit of man, a door that had been open for many centuries and given entrance by way of natural gift and faculty into the spiritual world. The door was shut when the time came for man, so far as his instinctive faculties were concerned, to be placed out-side the kingdom of the divine-spiritual Will that ruled over him. From that time forward he had to find in his own inmost being, in his own will, the possibility to evolve conscious freedom in the soul. All the great moves of evolution, however, take place slowly, gradually, step by step. And the experience that had been attained by the pupil when the teacher led him up into the Ether-heights and down into the deep clefts of the Earth—even in those times it was no longer possible in the form it had taken in the ancient Mysteries—this experience was now, in later times, directly connected with an experience of Nature (though not with Nature on the Earth's surface itself) which came to man in a more unconscious form. Think for a moment how it was with those persons who strove after knowledge about the year 1200 and on through the following century. They heard tell how, only a short time before, pupils were still able to find teachers, like the one of whom I told you yesterday; but they themselves were directed to human thinking as the means of attaining knowledge. In the succeeding time of the Middle Ages we can see this human thinking developing and spreading, asserting itself in an impressive manner. It sets out on new paths with inner zeal, with sincere and whole-hearted devotion, and these paths are followed by large circles of knowledge-seekers. What we may truly call the knowledge of the Spiritual, that too continued its way. And after a few centuries we come to the time when Rosicrucianism proper was founded. Rosicrucianism is connected with a change that took place in the whole spiritual world in respect of man. I shall best describe the change by giving you once again a picture. Mysteries in the old sense of the word were no longer possible in the time of which I have been speaking. There were however men who yearned for knowledge in the sense of the ancient Mysteries, and who experienced hard and heavy conflicts of soul when they heard how in the past men had been led up to the mountain and down to the clefts of the Earth, and had thus found knowledge. They developed all possible inner methods, they made all possible inner efforts in order to rouse the soul within them, that it might after all yet find the way. And he who is able to see such things can find in those times, as we said just now, not places of the Mysteries, but gatherings of knowledge-seekers who met together in an atmosphere warmed through and through with the glow of piety. What appears later as Rosicrucianism, sound and genuine Rosicrucianism, as well as the debased and charlatan kinds, comes in reality from men who gathered together in this simple way and sought so to temper their souls that genuine spiritual knowledge might yet be able to arise for them. In such a gathering, that took place in most unpretentious surroundings, the simple living-room of a kind of manor house, a few persons were once met, who, through certain exercises half thoughtful and meditative in character, half of the nature of prayer, done in common by them all, had developed a mystical mood in which all shared. It was the same mystical mood of soul that was cultivated in later times by the so-called “Brothers of the Common Life,” and later still by the followers of Comenius and by many other Brotherhoods. In this small circle, however, it showed itself with a peculiar intensity, and whilst these few men were there gathered together, making devotion, so to say, of their ordinary consciousness, of their whole intellect, in this intense mystical atmosphere of soul, it happened that a being came to them, not a being of flesh and blood like the teacher whom the pupil met and who led him to the mountains and to the clefts of the Earth, but a being who was only able to appear in an etheric body in this little company of men. This being revealed himself as the same who had guided the pupil about the year 1200. He was now in the after-death state. He had descended to these men from the spiritual world; they had drawn him thither by the mood of soul that prevailed in them—mystical, meditative, pious. My dear friends, in order that no misunderstanding may arise, let me expressly emphasise that there is there no question of any mediumistic power. The little company who were gathered there would have looked upon any use—or any sanctioning—of mediumistic powers, as deeply sinful; they would have been led to do so by certain ideas belonging to old and honoured tradition. Just in those very communities of which I am telling you, mediumship and all that is related to it was regarded not merely as harmful but as sinful—and for the following reason. These persons knew that mediumship goes together with a peculiar constitution of the physical body; they knew that it is the physical body that gives the medium his spiritual powers. But the physical body they looked upon as “fallen,” and information that came by the help of mediumship they could not but regard under all circumstances as acquired by the help of Ahrimanic or Luciferic powers. In those times, things like this were still clearly and exactly known. And so we have not to think of anything mediumistic in this connection. There was the mood of mysticism and meditation, and that alone. And it was the enhancing and strengthening of this mood through fellowship of soul, that, so to speak, enchanted into the circle, but of his own free-will, that disembodied human being, purely spiritual, and yet at the same time human. The being spoke to them thus, in a deeply solemn manner:—“You are not altogether prepared for my appearance but I am among you discarnate, without physical body, forasmuch as a time has come when for a short period of Earth existence the Initiate of olden times is unable to appear in a physical body. The time will come again when he can do so, when the Michael period begins. But I am come to reveal to you that the inner being of man nevertheless remains unchanged, that the inner being of man, if it holds itself aright, can yet find the way to the divine-spiritual existence. For a period of time, however, the human intellect and understanding will be so constituted that it will have to be suppressed in order for that which is of the Spirit to be able to speak to the human soul. Therefore remain in your mystic and pious mood of soul ... You have received from me, all of you together, the picture, the imagination. I have, however, been able to give you no more than a mere indication of that which will come to fulfilment within you; you will go on further and find a continuation of what you have here experienced!” And now, three from the number gathered there together, were chosen, to the end that they might establish a special union with the spiritual world, once more not at all through any kind of mediumistic powers but through a development of that mystic, meditative, pious mood of soul. These three, who were guarded and protected by the rest of the circle, closely and intimately cared for by the others, experienced from time to time a kind of absence of mind. They were at these times, in their external bodily nature, wonderfully lovely and beautiful, they acquired a sort of shining countenance, shining like the sun, and they wrote down, in symbols, revelations which they received from the spiritual world. These symbolic revelations were the first pictures by which the Rosicrucians were shown when it behoved them to know of the spiritual world. The revelations contained a kind of philosophy, a kind of theology and also a kind of medicine. And the remarkable thing was that the others (it seems to me as though the others were four in number, so that the whole was a company of seven), after the experience they had with their brothers, beholding how their eyes shone like the sun and how their countenances were bright and radiant—these other four were able to give again in ordinary language what was conveyed in the symbols. The brothers whose destiny it was to bring the symbols from the spiritual world, could only write down the symbols, they could only say, when they returned again into their ordinary consciousness: “We have been among the stars, and have found the old teachers of the secret knowledge.” They could not themselves turn the symbolic pictures that they drew, into ordinary human speech. The others could and did. And this is the source of a great deal of knowledge that passed over into the literature of theology, more particularly such as was philosophical in character (not the theology of the Church but rather of the laity) and into the literature of medicine. And what was thus received from the spiritual world in symbols was afterwards communicated to small groups that were organised by the first Rosicrucians. Again and again, in the time from the thirteenth to the fifteenth centuries, there was still the possibility in certain very small groups for experiences of this nature. Revelations came frequently to men from the spiritual world in this or some similar way. But those who had to translate what was thus revealed in pictures were not always capable of doing it quite faithfully. Hence the want of clarity in the philosophy of this period. One has to discover for oneself what it really means, by seeking for it again in the world of the Spirit. For those however who have had knowledge of this kind of revelation received from the spiritual world, it has always been possible to link on to such revelations. But picture to yourselves, my dear friends, what strange feelings must gradually have come over these men, who had to receive the very highest knowledge—for what was given to them was so accounted—from a direction that was growing more and more foreign, almost uncanny, to them; for they could no longer see into the world out of which the secrets came to them; ordinary consciousness could not reach so far. It can readily be understood that such things easily led to charlatanism and even to fraud. Indeed at no time of human evolution have charlatanism and the highest and purest of revelation stood so close to one another as in this period. It is difficult to distinguish the true from the false—so much so that many regard the whole of Rosicrucianism as charlatan. One can understand this, for the true Rosicrucians are extra-ordinarily hard to find among the charlatans, and the whole matter is all the more difficult and problematic for the reason that one has always to bear in mind that the spiritual revelation comes from sources which in their real quality and nature remain hidden. The small circles gathered by the first Rosicrucians grew to a larger brotherhood, who always went about unrecognised, appearing here and there in the world, generally with the calling of a physician, healing the sick, and at the same time spreading knowledge as they went. And it was so that in regard to very much of this knowledge, the spreading of it was not without a certain embarrassment, inasmuch as the men who carried it on were not able to speak of the connection in which they stood to the spiritual world. But now something else was developed in this pursuit of spiritual knowledge and spiritual research, something that is of very great beauty. There were the three brethren and the four. The three are only able to attain their goal when the four work together with them. The two groups are absolutely interdependent. The three receive the revelations from the spiritual world, the four are able to translate them into ordinary human language. What the three give would be nothing but quite unintelligible pictures, if the four were not able to translate them. And again, the four would have nothing to translate, if the three did not receive their revelations, in picture form, from the spiritual world. This gave rise to the development within such communities of an inner brotherhood of soul, a brotherhood in knowledge and in spiritual life, which in some circles of those times was held to be among the very highest of human attributes. Such small groups of men did indeed learn to know through their striving the true worth of brotherhood. And gradually they came more and more to feel how the evolution of humanity towards freedom is such that the bond between men and Gods would be completely severed were it not kept whole by such brotherhood, where the one looks to the other, where the one is in very truth dependent on the other. We have here a picture of something in the soul which is wonderfully beautiful. And much that was written in those days possesses a certain charm which we only understand when we know how this atmosphere of brotherhood which permeated the spiritual life of many circles in Europe in those times, shed its radiant light into the writings. There is however another mood that we find in those who are striving for knowledge, and this mood began gradually to pervade their whole endeavours and made people anxious. If in those times one did not approach the sources of spiritual revelation, ultimately it was so that one could no longer know whether these revelations were good or evil. And a certain anxiety began to be felt in regard to some of the influences. The anxiety spread later over large circles of people, who came to have fear, intense fear of all knowledge. The development of the mood of which I speak may be particularly well studied in the examples of two men. One is Raimund of Sabunda, who lived in the fifteenth century, being born about 1430. Raimund of Sabunda is a remarkable man. If you study carefully what remains to us of his thought, then you will have the feeling: This is surely almost the very same revelation that was communicated in full consciousness about the year 1200 by the teacher who took his pupil to the mountain tops and to the chasms of the Earth! Only in Raimund of Sabunda of the fifteenth century, it is all given in a vague, impersonal style, philosophical in character, theological too and medical. The truth is that Raimund of Sabunda had also received his revelations by way of the genuine Rosicrucians, that is to say, by the path that had been opened by the great Initiate of the twelfth century, whose work and influence I described to you yesterday, and who continued to inspire men from out of the spiritual world, as I have been relating to you today. For the revelation that afterwards came through Rosicrucianism, as I have often described to you, came originally from this great Initiate and those who were with him in the spiritual world; the mood and feeling of the whole teaching was set by him. Anxiety, however, was at this time beginning to take hold of men. Now Raimund of Sabunda was a bold, brave spirit, he was one of those men who can value ideas, who understand how to live in ideas. And so, although we notice in him a certain vagueness due to the fact that the revelations have their source after all in the spiritual world, yet in him we find no trace of anxiety or fear in regard to knowledge. All the more striking is another and very characteristic example of that spiritual stream: Pico della Mirandola, who also belongs to the fifteenth century. The short-lived Pico della Mirandola is a very remarkable figure. If you study deeply the fruits of his thought and contemplation, you will see how the same initiative I have just described is everywhere active in them, due to the continuation of the wisdom of that old Initiate by way of the Rosicrucian stream. But in Pico della Mirandola you will observe a kind of shrinking back before this knowledge. Let me give you an instance. He established how everything that happens on Earth—stones and rock coming into being, plants living and growing and bearing fruit, animals living their life—how all this cannot be attributed to the forces of the Earth. If anyone were to think: There is the Earth, and the forces of the Earth produce that which is on the Earth, he would have quite a wrong notion of the matter. The true view, according to Pico della Mirandola, is that up there are the Stars and what happens in the Earth is dependent on the Stars. One must look up to the Heavens, if one wants to understand what happens on Earth. Speaking in the sense of Pico della Mirandola we should have to say: You give me your hand, my brother man, but it is not your feeling alone that is the cause why you give me your hand, it is the star standing over you that gives you the impulse to hold out your hand to me. Ultimately everything that is brought about has its source in the Heavens, in the Cosmos; what happens on Earth is but the reflection of what happens in the Heavens. Pico della Mirandola gives expression to this as his firm conviction, and yet at the same time he says: But it is not for man to look up to these causes in the stars, he has only to take account of the immediate cause on Earth. From this point of view Pico della Mirandola combats—and it is most characteristic that he does so—the Astrology that he finds prevalent. He knows well that the old, real, and genuine Astrology expresses itself in the destinies of men. He knows that; it is for him a truth. And yet he says: one should not pursue Astrology, one should look only for the immediate causes. Note well what it is we have before us here. For the first time we are confronted with the idea of “boundaries” to knowledge. The idea shows itself in a significant manner, it is still, shall we say, human in character. Later, in Kant, in du Bois-Reymond, you will find expressed in them: “Man cannot cross the boundaries of knowledge.” The idea is said to rest on an inner necessity. That is not the case with Pico della Mirandola in the fifteenth century. He says: “What is on Earth has undoubtedly come about through cosmic causes. But man is called upon to forgo the attainment of a knowledge of these cosmic causes; he has to limit himself to the Earth.” Thus we have in the fifteenth century, in such a markedly characteristic person as Pico della Mirandola, voluntary renunciation of the highest knowledge. My dear friends, we have here a spiritual event in the history of culture of the greatest imaginable importance. Men made the resolve: We will renounce knowledge! And that which comes to pass externally in such a person as Pico della Mirandola has once more, in very deed and fact, its counterpart in the Spiritual. It was again in one of those simple gatherings of Rosicrucians that in the second half of the fifteenth century, on the occasion of a ritual arranged for this very purpose, man's Star-knowledge was in deeply solemn manner offered up in sacrifice. What took place in that ritual, which was enacted in all the solemnity proper to such a festival, may be expressed as follows.—Men stood before a kind of altar and said: “We resolve now to feel ourselves responsible not for ourselves alone nor our community, nor our nation, nor even only for the men of our time; we resolve to feel ourselves responsible for all men who have ever lived on Earth, to feel that we belong to the whole of mankind. And we feel that mankind has deserted the rank of the Fourth Hierarchy and has descended too deeply into matter” (for the Fall into Sin was understood in this sense) “and in order that man may be able to return to the rank of the Fourth Hierarchy, may be able to find for himself in freedom of will what in earlier times Gods have tried to find for him and with him, let now the higher knowledge be offered up for a season!” And certain Beings of the spiritual world, who are not of human kind, who do not come to Earth in human incarnation, accepted the sacrifice in order to fulfil therewith certain purposes in the spiritual world. It would take us too far to speak of these here; we will do so another time. But the impulse to freedom was thereby made possible for man from out of the spiritual world. I tell you of this ritual in order to show you how everything that takes place in the external life of the physical senses has its spiritual counterpart; we have only to look for it in the right place. For it can happen that such a celebration, enacted—I will not say in this instance, with full knowledge, but enacted by persons who stand in connection with the spiritual world—may have very deep meaning; from it can radiate impulses for a whole culture or a whole stream of civilisation. Whoever wants to know the fundamental colouring and tone of a particular epoch of time must look for that source in the Spiritual whence spring the forces that stream through this epoch of time. In the years that followed, whatever came into being of a truly spiritual nature, was an echo of this creative working from out of the unknown spiritual worlds. And side by side with the external materialism that developed in the succeeding centuries, we can always find individual spirits who lived under the influence of that renunciation of the higher knowledge. I should like to give you a brief description of a type of man who might be met with from the fifteenth century onwards through the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries. You might find him in some country village as a herb-gatherer for an apothecary, or in some other simple calling. If one takes an interest in special forms and manifestations of the being of man as they show themselves in this or that individuality, then one may meet and recognise such a person. At first he is extraordinarily reserved, speaks but little, perhaps even turns away your attention from what you are trying to find in him by talking in a trivial manner, on purpose to make you think it is not worth while to converse with him. If, however, you know better than to look merely at the content of the words a man says, if you know how to hear the ring of the words, how to listen to the way the words come out of a man, then you will go on listening to such a one, despite all discouragement. And if out of some karmic connection he receives the impression that he really should speak to you, then he will begin to speak, carefully and guardedly. And you will make the discovery that he is a kind of wise man. But what he says is not earthly wisdom. Neither is there contained in it much of what we now call spiritual science. But they are warm words of the heart, far-reaching moral teachings; nor is there anything sentimental about his way of uttering them, he speaks them rather as proverbs. He might say something like this. “Let us go over to yonder fir-tree. My soul can creep into the needles and cones, for my soul is everywhere. From the cones and needles of the fir-tree, my soul sees through them, looks out into the deeps and distances of the worlds beyond; and then I become one with the whole world. That is the true piety, to become one with the whole world. Where is God? God is in every fir-cone. And he who does not recognise God in every fir-cone, he who sees God somewhere else than in every fir-cone—he does not know the true God.” I want only to describe to you how these men spoke, men that you might find in the way I have described. Such was their manner of speaking. And they might go on to say more. “Yes, and when one creeps into the fir-cones and into the needles of the fir-tree, then one finds how the God rejoices over the human beings in the world. And when one descends deep down into one's own heart, into the abysses of the innermost of man's nature, there also one finds the God; but then one learns to know how He is made sad through the sinfulness of men.” In such wise spake these simple sages. A great number of them possessed—to speak in modern language—“editions” of the geometrical figures of the old Rosicrucians. These they would show to those who approached them in the right way. When however they spoke about these figures—which were no more than quite simple, even poor, impressions—then the conversation would unfold in a strange manner. There were many people who, although they took interest in the unpretentious wise man before them, were at the same time overcome with curiosity as to what these strange Rosicrucian pictures really meant, and asked about them. But they received from these wise men, who were often regarded as eccentric, no clear and exact answer; they received only the advice: If one attains the right deepening of soul, then one can see through these figures, as through a window, into the spiritual world. The wise men would give as it were a description of what they themselves had been able to feel and experience from the figures rather than any explanation or interpretation of them. And often it was so, that when one had heard these expressions of feeling in connection with the figures, one could not put them into thought at all; for these simple sages did not give thoughts. What they gave, however, had an after-working that was of immense significance. One left these men, not only with warmth in one's soul, but with the feeling: I have received a knowledge that lives in me, a knowledge I can by no means enclose in thoughts and concepts. That was one of the ways in which, during this period from the fourteenth, fifteenth to the end of the eighteenth century, the nature of the Divine and the nature of the Human, what God is and what Man is, was taught and made known to man through feeling. We cannot quite say, without words, but we can say, without ideas, although not on that account without content. In this period much intercourse went on among men by means of a silencing of thought. No one can arrive at a true conception of the character of this period who does not know how much was brought to pass in those days through this silencing of thought, when men interchanged not mere words but their very souls. I have given you, my dear friends, a picture of one of the features of that time of transition when freedom was first beginning to flourish among men. I shall have more to say on this from many aspects. For the moment, taking my start from all that took place at the Christmas Foundation Meeting, I wanted here to add something further to what was given then. |
| 219. Man and the World of Stars: Rhythms of Earthly and Spiritual Life. Love, Memory, the Moral Life
15 Dec 1922, Dornach Tr. Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Assume for a moment that the cosmic nebula of Kant and Laplace, with its mechanical forces and mechanical laws, did actually constitute the beginning of Earth-existence; assume that from these whirling nebulae, through the working of neutral laws of Nature, the kingdoms of earthly existence had come into being, and finally Man. |
| 219. Man and the World of Stars: Rhythms of Earthly and Spiritual Life. Love, Memory, the Moral Life
15 Dec 1922, Dornach Tr. Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Let us recall what I have been telling you about man's experiences between death and a new birth. The various descriptions have enabled us to realize that this life—above all in its main period, about the middle of the time between death and rebirth—is such that man lives in communion with the Beings referred to in the book Occult Science as the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies. This life of man in communion with those higher Beings is comparable with the life he has here, when in the physical body, in communion with the beings of the three kingdoms of Nature. Basically speaking, everything in his earthly environment belongs to one of the three kingdoms of Nature—to the mineral or the plant or the animal kingdom, or indeed the physical human kingdom, which in this particular connection can be taken as belonging to the animal kingdom. Man has his senses, and through his sense-impressions he lives in communion with the beings of the three kingdoms of Nature. What unfolds in his life of feeling between birth and death, in so far as it is the outcome of experiences arising from his environment, is also related to these three kingdoms of Nature. The same applies to what comes from the will, namely, human action. Thus between birth and death man is interwoven with what his senses convey to him from the three kingdoms of Nature. In like manner between death and a new birth, in the time indicated above, man lives within the higher realms, among the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies. This life together with the Beings of the Hierarchies is, in reality, all action, perpetual activity. We have heard how the spirit-seed of the physical body is produced in cooperation with these higher Beings. Here on Earth, when we perceive or connect ourselves with the entities belonging to the three kingdoms of Nature, we feel outside them. But there is a condition between death and a new birth when we find ourselves wholly within the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies; we are entirely given up to them. That is one of the conditions in which we then live.—Let us picture it clearly.—Here on the Earth, when, for example, we pick a flower, the fact is correctly described by saying, ‘I pick the flower.’ But if this way of speaking were applied to our life together with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies, the facts would not then be correctly expressed. When we do something in connection with these Beings, we must say: the other Being acts in us. Thus we are in a condition which compels us all the time not to call the activity—in which of course we ourselves partake—our own activity, but the activity of the Beings of the Hierarchies in us. We have in very truth a cosmic consciousness. Just as here we feel heart, lungs and so on, to be within us, so do we then feel the world to be within us, but it is the world of the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies. Everything that takes place is the outcome of an activity in which we, too, are involved; but to describe the facts correctly we should have to say: such and such a Being of the Higher Hierarchies is acting in us. Now the condition thus described is only one of the conditions obtaining between death and a new birth. We could not be men in the true sense if we lived in this one condition only. In the spiritual world between death and rebirth we should no more be able to bear this condition only, than here on Earth we could bear inbreathing without exhaling. The condition I have just described must alternate with another, which consists in our obliterating through our cosmic consciousness all thinking and feeling about the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies, obliterating too all will that works in this way in us from the Beings of the Hierarchies. Thus we may say that there are times during the life between death and a new birth when we find ourselves filled through and through with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies and their radiance. We feel them within ourselves. But there is another condition, in which we have first suppressed and then obliterated altogether, this consciousness of the Higher Beings manifesting in us. Then—to use earthly terms—we are ‘out of our body’—the condition is of course entirely spiritual but let us put it in this way: we are out of our body. In this condition we know nothing of the world that lives within us, but we have as it were ‘come to ourselves.’ We no longer live in the other Beings of the Hierarchies but we live wholly in ourselves. Between death and a new birth, we should never have consciousness of ourselves if we lived only in the one condition. Just as here on Earth, inbreathing must alternate with out-breathing, or sleeping with waking life, so between death and a new birth there must be rhythmic alternation between the inner experience of the whole world of the Hierarchies within us, and a condition in which we have come to ourselves. Now in a certain sense all earthly life is an outcome of what we have experienced in pre-earthly existence between death and a new birth. As you will remember, I have told you how even such faculties in man's earthly life as walking, speaking, and thinking are transformations of certain activities in pre-earthly existence. Today we will turn our attention more specifically to the life of soul. What we experience in pre-earthly existence in working together with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies leaves in us a heritage for our earthly life, a faint shadow of this communion with the Hierarchies. If between death and a new birth we had no such community of life with the Beings of the Hierarchies, we could not unfold, here on Earth, the power of love. The power of love we unfold here on Earth is of course only a faint reflection, a shadow of our communion with the Spirit-Beings of the Higher Hierarchies between death and a new birth, but it is a reflection of that communion. That here on the Earth we are able to unfold human love, sympathetic understanding for another human being, is due to the fact that between death and a new birth we are able to live in communion with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies. Spiritual-scientific vision enables us to perceive what happens to those who in previous earthly lives acquired little aptitude—we shall presently speak of how it is acquired—for living together during the appropriate period after death with the Beings of the Hierarchies, in certain states entirely given up to them. Such men here on Earth are incapable of unfolding love in which there is real strength, incapable of unfolding that all-embracing love which comes to expression in the power to understand other men. We may say with truth: it is among the Gods, in pre-earthly existence, that we acquire the gift for observing our fellow-man, to perceive how he thinks and how he feels, to understand him with inner sympathy. If we were deprived of this intercourse with the Gods—for so indeed it may be called—we should never be capable of unfolding here on Earth that insight into other human beings which alone makes earthly life a reality. When in this connection I speak of love, and especially of all-embracing human love, you must think of love as having this real and concrete meaning; you must think of it as signifying a genuine, intimate understanding of the other man. If to the all-embracing love of humanity, this understanding of one's fellow-man is added, we have everything that constitutes human morality. For human morality on Earth—if it is not merely expressed in empty phrases or fine talk or in resolutions not afterwards carried out—depends upon the interest one man takes in another, upon the capability to see into the other man. Those who have the gift of understanding other human beings will receive from this understanding the impulses for a social life imbued with true morality. So we may also say: everything that constitutes moral life in earthly existence has been acquired by man in pre-earthly existence; from his communion with the Gods there has remained in him the urge to unfold, in the soul at any rate, community on Earth as well. And it is the development of a life where the one man together with the other fulfils the tasks and the mission of the Earth—it is this alone that in reality leads to the moral life on Earth. Thus we see that love, and the outcome of love—morality—are in very truth a consequence of what man has experienced spiritually in pre-earthly existence. Now let us think of the other condition in the life between death and rebirth, when man's consciousness of communion with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies has been dimmed, when, as in earthly sleep, the impressions from the environment are silenced, when deliberate communion with the higher Beings ceases and man ‘comes to himself.’ This condition too has a consequence, an echo, a heritage, here in earthly life—and this heritage is the faculty of Memory. The possibility for us to have experiences at a definite moment and then after a lapse of time to draw forth from the depth of our being something that brings pictures of these experiences into our consciousness—this faculty of memory that is so necessary in our earthly life, is a faint reflection, a shadow, of our independent state of life in the spiritual world. Here on Earth we should only be able to live in the passing moment instead of in our whole past life as far back as a few years after birth, if between death and a new birth we were not able to emerge, as it were, from universal life and be entirely alone, alone in ourselves. While we are asleep here on Earth, our physical and etheric bodies lie in the bed; our astral body and our Ego are outside the physical and the etheric bodies and are then in a position to experience—unconsciously, it is true—the environment of soul and spirit. Man is unconscious between going to sleep and waking. Nevertheless, as I have already said, he does indeed have experiences during sleep, some of which I have also described. But they do not enter the field of consciousness, and in earthly life this is a necessary state of things. What is the reason for it? If from the time of going to sleep to that of waking we were to experience what we do in fact experience in our Ego and in our astral body, so strongly and intensely as to be able to bring it into consciousness, then every time on waking we should want to impress into the physical and etheric bodies too, what we experienced in sleep; we should want to make our physical and our etheric bodies into something different from what they are. One who has knowledge of what is experienced between going to sleep and waking, must accustom himself to an act of renunciation. He must be able to say to himself: ‘I will refrain from the desire to press what I experience with my Ego and my astral body during sleep into the physical and etheric bodies, for in earthly life these bodies could not stand it.’ It is quite possible to speak in a grotesque way about these things—indeed they can be made to seem almost comical, although what is said is meant very seriously. During sleep man does in fact experience images of the Cosmos. Because of this he is continually being tempted, as an outcome of his sleep, to give himself, for example, a different countenance. If that which does not, in fact, come to his consciousness were to do so, he would always be wanting to change his face, for the face he actually has would be reminding him all the time of former earthly lives, of sins in former earthly lives. In the morning, before waking, there is actually a strong urge in man to do to the physical body something that is like dressing it in clothes. One who has knowledge of this must consciously refrain from giving way to the urge; otherwise he would fall into a completely disorganized condition; he would perpetually be trying to change his whole organism, especially if in one respect or another it happens to be not quite healthy, or something is wrong with it. But during life between death and a new birth we experience so consciously that this consciousness leads to the forming and shaping of our next physical body. If this were left to ourselves alone, we should not shape the physical body in accordance with our karma. In reality, however, we form it together with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies, the Beings who watch over our karma. And so we get the eyes, the nose, and so forth, which in all probability we should not, if it were left to us, have given to ourselves. For there are certain times between death and a new birth when we are intensely egoistic—precisely at those times when the consciousness of our connection with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies has been dimmed. Our experiences are then so strong and intense that out of the forces they contain the physical body can be formed; and we do in fact form it. This is an experience of such intensity that it has in it the seed of actual creation. Then, through the very fact that it is much weakened in earthly life, it takes effect partly as earthly love and partly as the faculty of remembrance, as memory. Here on Earth, the fact that we feel ourselves within an Ego, depends upon memory. If we lived only in the present and had no memories, our Ego would have no inner coherence. In fact, as I have often said, we should not be able to feel ourselves in a strongly marked Ego at all. You can understand how memory as an earthly, shadowlike faculty comes into being. It comes into being through the fact that in pre-earthly existence in the spiritual world, a faculty of tremendous power is present—the faculty whereby in those periods when we ‘come to ourselves’ we prepare our body according to the instructions received from the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies, when, in the other state of existence, we live in union with them. This faculty is at work, to begin with as a formative force, in our body. In the child, as long as it has no consciousness leading to memory—i.e. in the earliest period of childhood—this stronger creative force still enters into and works with the forces of growth. Then something that is finer, more rarefied, is as it were separated out from these stronger forces—and this is the human faculty of memory. The fact that here on Earth too, man lives primarily in himself, is again connected with this faculty of memory. Memory is also very much connected with human egoism on the one side and, on the other, with human freedom. Freedom will become a reality in a human being in whose life on Earth there is a true echo of what is experienced in pre-earthly existence as a kind of rhythm: namely, feeling oneself united with the Beings of the Hierarchies, freeing oneself, entering into union again, and so on. Here on Earth the experiences come to expression, not as a rhythm, but as two co-existing human faculties: the faculty of love and the faculty of memory. But a certain heritage from this rhythm in pre-earthly existence can remain with man. If this is so, then in earthly life too, the true relationship will be established in him between memory and love. He will be able on the one side to develop understanding, loving understanding of other men. And on the other side, from his experience of the world together with other human beings, his own re-collective thinking will contribute to his own development, to the strengthening of his own nature. A true relationship of this kind can remain as a legacy of the rhythm that is an essential in pre-earthly existence. But the true relationship may also be upset. It may, for instance, be that a man is willing to be guided only by what he himself has experienced. This trait is greatly accentuated when a man has little interest in what others experience, little faculty of looking into the hearts and minds of others, when his interest is confined almost entirely to what gradually accumulates in his own store of memories. This again is intimately connected with his Ego, and so egoism is intensified. Such a man gets ‘out of gear’ with himself, because the true relationship existing between death and rebirth is lacking in him; a certain rhythm is not there. And at the same time, when a man takes interest only in what piles up in his own soul, when he is concerned all the time with himself alone, then he becomes increasingly unfit—if I may put it so—for the experiences between death and a new birth. By being interested only in himself, a man shuts himself off in a certain respect from communion with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies. A man in whom love and memory are rightly interrelated evolves the feeling of true human freedom instead of egoistic introspection. For in another respect this feeling of human freedom too is an echo of the emergence from communion with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies between death and a new birth. The feeling of freedom is the healthy aftermath of that emergence; egoism is the morbid aftermath. And as the life together with the Beings of the Higher Hierarchies between death and a new birth is the basis of man's morality on Earth, so the necessary emergence from life in communion with them is at the same time the basis on Earth for the immorality of men, for their severance from one another, for actions on the part of the one that cut across the actions of the other, and so forth. For this is at the root of all immorality. So you see it is necessary for man to be mindful that what can appear here on the Earth as something injurious, has a definite significance for the higher worlds. On the Earth too it is the case that the air we inhale is healthy, while the air we exhale is unhealthy, capable of begetting illness, for in effect we exhale carbonic acid. So too, that which underlies immorality here on the Earth is something that is necessary for our experience in the spiritual world. These connections must be studied because, in effect, morality and immorality cannot really be explained in the light of earthly conditions. Anyone who attempts such explanations will inevitably be on the wrong track. For through the fact that man is moral or the reverse, he relates himself, in his life of soul, to a supersensible world. And we may say: By directing men's minds to the study of this relationship to a spiritual world, anthroposophical Spiritual Science has made it possible, for the first time, to acquire a basis for understanding the moral. To a view of the world that will only acknowledge the validity of science dealing with the world of Nature, the moral can only consist in illusions arising from processes of Nature which are supposed to take their course in man as well. Assume for a moment that the cosmic nebula of Kant and Laplace, with its mechanical forces and mechanical laws, did actually constitute the beginning of Earth-existence; assume that from these whirling nebulae, through the working of neutral laws of Nature, the kingdoms of earthly existence had come into being, and finally Man. If that were so, man's moral impulses would be mere dreams. For everything he calls moral would pass away when, again in accordance with mechanical laws, the Earth had reached her end. No vindication of the reality of the moral life can ever arise from such a world-view if followed honestly to its conclusions. Vindication of the moral can only result when, as in anthroposophical Spiritual Science, those realms of existence are revealed where the moral is as much a reality as the world of Nature is a reality here in the life between birth and death. As plants grow and blossom here, between death and a new birth certain activities unfold when man is among the Gods. These activities are the moral element in its reality, the reality of the moral element. In that realm the moral has reality, whereas on the Earth there is only a reflection of that reality. But man, we must remember, belongs to both worlds. Hence for him, if he can perceive these facts in the light of Spiritual Science, the moral world has reality—but knowledge of this reality can never be derived from physical existence. Here you have one reason why it is necessary for man to acquire understanding of Spiritual Science. Without Spiritual Science he could not really be honest with his knowledge. He could not honestly ascribe reality to the moral world, because he is not willing to investigate the realm where that reality lies. It is of tremendous importance to understand such a sentence as this in the right way. But there is still another respect in which I want to emphasize how necessary the knowledge attainable through Spiritual Science is to man. Here again we shall have to turn to the realities of another world. Already when we achieve Imaginative Knowledge—the knowledge that enables us to live in the etheric world instead of in the physical world, so that instead of physical things we perceive the activities (for activities they are) in the ether—already when this is achieved, three-dimensional Space as it is on Earth falls away from our field of experience. To speak of a three-dimensional space has no meaning, for we are then living in Time. Hence from from other standpoints I have spoken of the etheric body as a Time-organism. I have said, for example, that here, in the spatial organism, we have the head and, let us say, the leg; and if we sting or cut our leg the head will feel it. Spatially, in this spatial body, one organ is connected with the others. So in the time-body which consists in processes—processes in which everything lying in the deeper foundations of our human nature between birth and death are involved—every detail is connected with every other. You will remember that in lectures on Education I have said that if at a certain age in childhood we have learnt to have reverence, this power of reverence is transformed in later years into a power of gentleness and blessing which can be conveyed to other men. On the other hand, those who in childhood were never able to revere in the true way cannot unfold this power to bless in later life. As in the spatial organism the foot or the leg is connected with the head, so youth is connected with old age, and old age with youth. It is only for external physical vision that the world flows in the one direction, from the past into the future. For higher vision there is also the reverse stream, from the future into the past. It is into this stream, as I have described, that we enter after death, journeying backwards. In the time-organism everything is interconnected. If the spatial organism as a whole is to be in order, you cannot remove essential organs from it. You cannot, for instance, remove any considerable part of your face without ruining the whole organism. Similarly you cannot remove anything belonging to man that takes its course in time. Imagine that in the spatial organism, at the place where your eyes are situated there were some quite different growth—instead of eyes, some kind of tumor. Then you could not see. As the eyes are situated at a definite place in the spatial organism, so in the time-organism—and I now mean not only the time-organism between birth and death but the time-organism in man that reaches beyond all births and deaths—in this time-organism is incorporated everything that exists between birth and death and in this life develops through concepts, ideas, mental pictures, of a spiritual world. And what thus develops are the eyes for beholding supersensible existence. If between birth and death no knowledge of the supersensible world is developed, this will mean blindness in the life in the supersensible world between death and a new birth, just as the absence of eyes means blindness in the spatial organism. Man passes through death even if on Earth he acquires no knowledge of the supersensible world; but he enters then into a world where he sees nothing, where he can only grope his way about. This is the agonizing experience that is the natural corollary of the materialistic age for one who has true insight into Initiation-Science today. He sees how men on Earth lapse into materialism; but he also knows what this lapse means for the spiritual life. He knows that it means eradication of the eyes, that in the existence awaiting them after death, men will only be able to grope their way about. In olden times, when there was instinctive knowledge of the supersensible world, men passed through the gate of death able to see. That old, instinctive supersensible knowledge is now extinct. Today, spiritual knowledge must be consciously acquired—spiritual knowledge, I say, not clairvoyance. As I have always emphasized, clairvoyance too can be attained, but that is not the essential here. The essential thing is that what is discovered through clairvoyant research shall be understood—as it can be understood—by ordinary human reason, healthy human reason. Clairvoyance is needed to investigate these things, but it is not needed for acquiring the faculty of sight in the supersensible world after death. And anyone who declares that ordinary knowledge acquired through healthy human reason does not give him eyes for supersensible existence but that for this he needs clairvoyance—anyone who speaks like this might just as well declare that man cannot think unless his eyes do the thinking. As little as in physical life the eyes need think, as little does knowledge of the supersensible worlds need clairvoyance for the purposes I have indicated today. Naturally, there would be no supersensible knowledge on Earth if there were no clairvoyance; but even the seer must make intelligible in the ordinary way what he sees in the supersensible. However powerful a man's clairvoyant faculty might be in earthly life, however clear his vision of the spiritual world, if he were too easy-going to bring into the form of logical, intelligible ideas what he sees in the spiritual world, he would still be blinded in the spiritual world after death. What constitutes the great suffering for one who has insight into modern Initiation-Science is that he must admit: materialism makes men blind when they pass through the gate of death. And here again is something showing that it is of significance for the whole of cosmic existence whether man today inclines to supersensible knowledge or not. The time when it is essential for him to do so has arrived; the very progress of humanity depends upon man acquiring supersensible knowledge. |
| 220. Anthroposophy and Modern Civilization
14 Jan 1923, Dornach Tr. Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Then in one's dream one comes to the limit of one's dream. And beyond the dream is what Kant calls the “Thing in itself,” and one cannot approach the thing in its reality. Edouard von Hartmann, that acute thinker, often spoke of this kind of dreaming with relation to reality. |
| 220. Anthroposophy and Modern Civilization
14 Jan 1923, Dornach Tr. Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Today I should like to continue the theme which we have studied in the last two lectures. Firstly, it is a question of realising those impulses in evolution which have led to the spiritual life of our present age, so that we can see on the one side the Anthroposophical view of the world as a necessity, but on the other hand can fully understand that this Anthroposophical view of the world must find its enemies. Naturally I shall not now enter into the special characteristics of this or that opponent, perhaps that is comprehensible at the present time. Indeed, I want to deal with our theme as generally as possible because it is not essential for the moment to fix our minds on our opponents. Rather it is essential for us at present to understand that if the Anthroposophical Society is to exist as a Society, it must become fully aware of its position in the spiritual life of the day. Also, the Society itself must contribute something towards its own consolidation. Therefore, I am not going to say anything particularly new today. Only a few weeks ago I emphasised the fact that consolidation of the Anthroposophical Society is an absolute necessity. So first of all, it has to become clear to us how Anthroposophy is placed in modern civilisation, a civilisation which, as regards Europe and America, really only goes back to the time which we have so often, discussed, the time of the 4th Post-Christian century. Now this 4th Post-Christian century lies right in the middle of the 4th Post-Atlantean epoch of time, and I have often pointed out that the spreading of Christianity,—the whole mood by which Christianity was grasped in the early years of the first three or four centuries of Christian evolution—was essentially different to the mood later on in time. Today we think that following history backwards, we can study the previous epoch, that we can go back to the Middle Ages, then to the events we call the Wanderings of the Peoples. Further back we come to the Roman Empire, passing through that we come to Greece, and then we imagine that we can feel the same atmosphere in this Greece as we can feel in the time of the Roman Emperors or in later European history. But that is not the case. In reality there lies a deep cleft between that which can still be placed with a certain vividness before the consciousness of modern man, namely, his journey back to Rome; but a deep cleft exists between this and that which took place as life in ancient Greece. Let us bring an outline of this before our souls. If we study the Greece of Pericles or Plato, or of Phidias, or even the Greece of Sophocles and Aeschylus, we find that their basic mood of soul goes back to a Mystery civilisation, to an ancient spirituality. And, above all things, this Greece had still much in itself of what I characterised yesterday as a living experience of absolutely real processes in man's inner being, and which I described as the salt, sulphur and mercury processes. We must be quite clear that Greek thought and Greek feeling came close to the feeling of man, whereas that later age,—from the 4th Post-Christian century onwards—already began to get ready for that which came about in the way described in my last two lectures, in which I showed how Man himself was lost for human nature, for human consciousness. I also told you that these three personalities, Bruno, Jacob Boehme and, in a certain connection also Lord Bacon, struggled for a knowledge of man's nature, but that it was impossible for their striving really to approach the Being of Man. If, however, we go further back, from Rome to Greece, then this alienation of man's nature—any talk or an alienation of man's nature—ceased to have any sense, because the ancient Greek knew himself as a human being standing in the cosmos. The Greek had no idea of that concept of nature which came about later, that concept of nature which finally culminated in the seizing of the mechanism of nature. One might say of the ancient Greek:—That he saw the clouds, the rain falling, the clouds ascending and all that comes out of the world as fluid; then when with especial vividness looking into himself with his still sharply concrete vision, he saw the circulation of his blood, he did not feel a very great distinction between the rising and falling of water in Nature and the movement of his own blood. The Greek could still grasp something of `the world in man and man in the world.' These things cannot be taken too deeply, because they lead into a mood of soul which only exists in fragments of the external history. One should not forget how, in the 4th Post-Christian century, evolution took the form of destroying everything which remained of the ancient clairvoyant civilisation. Certainly, modern humanity knows something of this, because of all the information which has been dug up, but one should not forget how that which later gave the impulse to Western civilisation really arose on the relics of ancient Hellenism, of that widespread Hellenism which not only existed in the South of Europe, but even passed over into Asia. Again, one should not forget that between the middle of the 4th and middle of the 5th centuries after Christ, countless temples were burnt, having an infinitely significant pictorial content, a precious content with reference to everything developed by Hellenism. Our modern humanity, proceeding only according to external documents, does not realise this anymore. But one should recall the words of an author of that time, when he wrote in one of his letters:—“This age is passing to its downfall. All those holy places to be found in the open country, and for the sake of which the labourers worked in every field, are being destroyed. Where can the countrymen now find joy for their work?” One can hardly conceive today how much was destroyed between the middle of the 4th and the middle of the 5th century after Christ, Now the destruction of those external monuments was part of the effort to exterminate spiritual life in Greece, and this, as you know, was given its most bitter blow by the closing of the Schools of Philosophy in Athens in the year 529. Yes, one can look back into ancient Rome, but one cannot look back into ancient Greece through external history. And it is indeed true that very many things in Western civilisation have come down to us, through the Benedictine Orders, but we must not forget that even the holy Benedict himself founded the Mother Church of the Benedictine Order on the site of an old heathen Temple which had been destroyed. All that had to disappear first, and it did disappear. Now, with normal human feelings, it is difficult to understand why such an impulse for destruction passed over the whole of the South of Europe, Asia Minor and North Africa at that time. It only becomes comprehensible when one is convinced that the consciousness of mankind in that age was entirely different. I have often mentioned a sentence which is quite incorrect:—“Nature,—or one may say, the world, makes no leaps,” but in history such leaps do occur and the soul mood of civilised humanity in the 2nd and 3rd centuries after Christ was quite different to the soul mood of today. But now I should like to draw your attention to something which may make it clearer to you as to how this transformation really occurred. You see, today we must say when we speak of the interchange between waking and sleeping, that the physical and etheric bodies remain in the bed, while the ego and astral bodies go outside. The soul and spirit go out of the physical and etheric bodies. Now at a certain time in ancient India this was not true; just the opposite would have been correct. Then one would have said that in sleep the soul and spirit of man go deeper into his physical body, more into his physical body. Now this fact is almost unnoticed, and I must point out to you how, for instance, when the Theosophical Society was founded, the people who founded it had heard some of the spiritual truths from India, and what they heard they made their own property. Now they heard this fact, of the ego and astral body going out. Of course, because the Indians said it then, (i.e. when the Theosophical Society was founded) naturally that was in the 19th century, and in India what is real can be often observed. But when these same people of the Theosophical Society tell us that this is primeval Indian wisdom, it is pure nonsense, because the ancient Indian would have said just the opposite: That the soul and spirit go deeper into the physical body when man sleeps. Which was the case in ancient times. Now in a certain sense a consciousness of this was existing in Greece, a consciousness of the fact that in sleep the soul and spirit seize the physical body more than in waking, and that this lies in the evolution of mankind. Now today, because we have to describe things out of our direct spiritual perception, we must describe the following as correct:—The ancient Wise Men, and even the people of Greece, had an instinctive dreamy clairvoyance. And we can describe it so from our modern standpoint, but for those people it was not dreamy. They felt in their condition of clairvoyance as if they were just waking up, they felt themselves especially awake. And so, their consciousness existed with a greater intensity when they perceived the world in those magnificent pictures which I described to you in my last lectures. But they knew that when they pressed down into the inner part of their being and at the same time saw that which occurs in man, that that which they beheld were world processes, because man is in the world. And they knew then that in their time man dived still deeper into his physical body, and in deep sleep their consciousness became dim twilight, even unconsciousness. And these people ascribed to the Influence of their physical body that which embraces the soul and leads it over into sin. And it was just from this point of view that the ancient consciousness of sin arose. If we exclude the Jewish form of sin, the consciousness of sin leads back into heathendom, and it proceeded from the consciousness of the diving down into the physical body which does not leave the soul free enough to live in the spiritual world. But considering all that I am describing to you, it must be said:—that ancient humanity had a consciousness of the fact that he was a spiritual being, and as a spiritual being, lived in a physical body, but it never occurred to him. to call that MAN which he saw as physical body. Why, the very word MAN itself leads back to some such meaning as “The Thinker.” Not to something which is to be seen with a more or less red or white face, with two arms and two legs. That was not a man! Man was a being who dwelt as a spiritual soul in that dwelling house of the physical body. And a consciousness of this spiritual psychic man, existing in the wonderful, plastic, artistic forms in Greece, passed over into the sphere of Art, and into the general Greek civilisation. And even if the external temples, even if the cult became infinitely decadent in many connections, one must still say that in all the divine images and temples which were destroyed, much existed that points to this ancient soul mood. And I might add that the ancient spiritual psychic consciousness of humanity was shown with tremendous power in the form of everything destroyed in those centuries. Now if with that consciousness—not of the following incarnation when the consciousness was changed—but if a Mystery Initiate of that early Greek age came to us with the same consciousness which he then had, he would say:—”You modern human beings, you are all asleep,” Indeed he would say:—“You modern men are sleeping through everything. We were awake, we woke up in our bodies. We woke up as spiritual beings in our bodies; we knew that we were human beings, because in our bodies we could distinguish ourselves from the body. What you call waking, for us is sleeping, because whereas you wake up and direct your attention to the external world and explain something about the external world, all the time you are asleep with regard to your own human nature. You are asleep, we were awake.” That is what he would say, and from a certain point of view he should be quite right. We wake up from our moment of waking until we go to sleep, as we say, when we are in our physical bodies as spiritual human beings. But then we know nothing of ourselves, we are asleep with regard to ourselves. When, however, we are in the world outside us, we are asleep—and that is the time from sleeping to waking up. Thus, it is that we must learn to wake with the same intensity as that with which the ancient humanity were awake in their bodies. That is, modern man must learn to be awake outside his body when he is really in the external world. From this you can see that we are dealing with a transition. As humanity, we have all gone to sleep compared with the ancient waking condition, but now we are in just that period when we have to be wakened up into a new waking state. What is the aim of Anthroposophy in this connection? Anthroposophy wants to be, Anthroposophy is nothing else than something which points out to you that man must learn to wake up outside of himself. And so, Anthroposophy comes along and shakes up modern humanity, the modern humanity which that ancient Initiate would have called a sleeping humanity, Anthroposophy shakes it up, hut they do not want to wake. Anthroposophy often feels like Gallus beside the sleeper Stickl. (A reference to the Christmas Play just performed). Anthroposophy points out that the birds in the forest are singing. “Let them sing” says the present generation, “the birds have tiny heads and have soon had their ration of sleep.” Then Gallus goes on: “But the heavens are creaking,” Stickl (who is half asleep), “Let them go on creaking, they are old enough.” Of course, it is not said in the same words, but Anthroposophy says:—“The spiritual world wants to break through! Get up while the light of the spirit is shining.” The answer is:—“Let it go on shining, it is old enough.” My dear friends, really it is so. Anthroposophy wants to awaken the sleepers, because that is just what is demanded of modern civilisation—an awakening—but humanity wants to sleep, and to go on sleeping! I might say of Jacob Boehme—because he went right into the racial wisdom, and of Giordano Bruno, because he stands in a spiritual community which at that time had preserved so much from ancient times—that in them there lived a memory of the ancient waking condition. In Lord Bacon there really lived the impulse for the justification of this new sleeping. That is, as I might put it, a still deeper explanation than we were able to give in the two preceding lectures and is the characteristic of our age. Now with reference to the grasping of his own human nature, man of the present day cannot be awake as was humanity in ancient times, because man today does not press deep down into his physical body as ancient humanity did when asleep; because today when man goes to sleep he goes out of himself, but he must learn to come out of his physical body in a waking condition, for only thereby will he be in a position to realise himself again in his human nature. But this impulse to continue asleep is still growing. “Stickl, the carters are cracking their whips in the street.” “Well, let them go on cracking, they have not far to go.” It is du Bois Raymond, not Gallus, who says;—“Man has limits of knowledge, he cannot enter into the phenomena, the secrets of nature, he must limit himself.” But Anthroposophy says;—“We must strive yet further and further; the call for spirituality is already resounding.” “Well” says du Bois Raymond, “let it go on sounding, it won't be so very long before Natural Science will have come to the end of earthly days and therewith to the end of the discovery of all the secrets of nature.” My dear friends, in many a relationship one thus finds a justification for the sleep of humanity today, because all talk of the limit of knowledge is a justification for sleep instead of a justification for a penetration into one's knowledge of human nature. And our present humanity can find ways enough of going to sleep. Even of this we have often spoken in our lectures. Today people only want to listen to things which can be put before them in images, in pictures. That is why the cinema is liked so much., but it is not popular when the listeners are asked to work with their heads. And so it is today that people want to go on dreaming of world secrets, but do not want to co-operate actively with those world secrets by means of energetic thinking. But that is just the path of awakening—one begins to wake up in one's thinking, because it is thought which first of all seeks to evolve into activity. That is the reason why in my “Philosophie der Freiheit” decades ago I pointed to this kind of thinking with such energy. And now I should like to remind you of something else. I should like you to call to mind many a dream which you have had, and I should like to ask you whether you have never had a dream in which you have done something of which you would have been ashamed if you had done it in the daytime,—if you ever did by day what you did in the dream. Well, perhaps there are many sitting here who have never had such a dream, but at any rate they could let other people tell them of such an experience, because many people have dreamt of things they would never repeat in their waking lives, because they would be ashamed. My dear friends, apply that to our great sleep today—which we call the great sleep of present civilisation—where people really are letting themselves dream of all kinds of cosmic secrets, Anthroposophy comes along and says:—“Stickl, get up!” Anthroposophy wants to wake the people, they ought to wake! I can give you this assurance,—Many of the things that have been done in this civilisation would never have been done if humanity had been awake. That really is the case. You will say:—Who is going to believe that? Well, the dreamer pursuing his little business in his dreams, does not bother himself as to how that is really going to look when he is awake, but unconsciously the feeling exists somewhere in his soul that one really dare not do such things if one were awake. I do not mean this in a pedantic or a commonplace way, I just mean that many of the things which one considers today as being quite in order would look differently if one were really awake in one's soul. And an unholy anxiety prevails in the soul because of this, especially in science. (If one were awake one could no longer comfortably dissect first a liver and next a brain.) One would be terribly ashamed of many methods of investigation if one were awake Anthroposophically. How can one ask people using such methods to wake up without any further reason? One notices many extraordinary apologies which exist for sleeping. And now I want you to think of something else. What an immense pleasure a dreamer has when he dreams something which actually happens, say a couple of days later. You must have noticed yourselves the tremendous joy of a superstitious dreamer when his dream actually happens; and it often happens, and they all have this tremendous joy. In our present civilisation dreamers calculate by Newton's laws of gravitation, by formulae which have been worked out by mathematicians, and they have calculated that Uranus has a definite path in the heavens. But that path does not agree with the formulae and therefore they go on dreaming; certain disturbances must exist owing to a planet as yet undiscovered. When this did happen, and when Dr. Gall really discovered Neptune, the vision was fulfilled. Now this is just what is so often brought forward today as a justification of the methods of Natural Science. The existence of Neptune was calculated in a dream and later the dream really happened. It is just like a person dreaming of something which later on takes place. Then there is the case of Mendaleff, who even calculated elements out of his periodic system. But this dream of a curse is not quite so difficult, because when such a periodical system is discovered and one place in it is empty, then it is easy enough to fill up that place and to mention a few properties. Here we have the fulfilment of a vision by the same methods as when a sleeper dreams of something which actually takes place a couple of days later, and which, he then calls a verification of the fact. And today people say that in this way the affair can be proved. One has to understand how radically our modern civilisation has become the civilisation of sleepers and how necessary an awakening is for humanity. At the same time this tendency to sleep in our present age has to be seen very clearly by those who have received an urge from Spiritual Science towards waking. Such a moment must occur as sometimes in a dream when the dreamer knows “I am dreaming,” and in the same way humanity ought to have a special feeling for a strong expression which was once used by that energetic philosopher J.G. Fichte. Fichte said “The world which is spread out before mankind is a dream and all that man thinks about the world is a dream about a dream,” Of course one must not fall into anything like the philosophy of Schopenhauer, because, after all you are not doing very much for a human being when you characterise everything in front of him as a dream. It is not one's task merely to say:—“one dreams,” that is not quite enough. But that is all that many people of the present want to prove:—Man dreams and cannot do anything else but dream. Then in one's dream one comes to the limit of one's dream. And beyond the dream is what Kant calls the “Thing in itself,” and one cannot approach the thing in its reality. Edouard von Hartmann, that acute thinker, often spoke of this kind of dreaming with relation to reality. And Edouard von Hartmann makes it clear that everything which man has in his consciousness is a dream by the side of the Thing in Itself, of which man knows nothing, but which lies at the basis of his dream. So that Hartmann, who drives everything to extremes, speaks of the `real' table, in contrast to the table which we have before us in our sensations. The table we have in our consciousness is a dream, and behind that stands the table in its reality. Hartmann distinguishes between the table as appearance and the table in itself; between the chair in appearance and the chair in itself. But he is not fully conscious that finally the chair of which he is speaking had something to do with the chair in itself, because if you take the chair as appearance one cannot very well sit down on it. Even a dreamer has to have a bed to lie on. And so all this talk of “the Thing in Itself” can only be a preparation for something else. For what? For waking up, my dear friends. And so it is not a question of seeing the world as a dream, but, as soon as we have the idea:—That is a dream!—we must do something we must wake up; and this waking up already begins with an energetic grasping of one's own thinking. It begins with active thinking, and from that point one comes to other things. Now you see, what I have characterised—this impulse for awakening—is a necessary impulse for the present time. Certainly that which as Anthroposophy can be presented to the world; but however, when an Anthroposophical Society becomes a Society, then that Society must represent a reality. Then every single person who lives in the Anthroposophical Society should feel it as a reality, and he must be deeply permeated by the will to awake, and not, as is so often the case, feel insulted if one says to him:—“Stickl, stand up.” This is very necessary. And it is something which I should like to repeat in a few words. The misfortune (i.e. the burning of the Bau) which has met us should above all be an awakening call to the Anthroposophical Society to do something that is a reality. This real Being—which I have characterised at the end of the Christmas Congress—this real Being (Wesen) which one can feel since that time as “the living stream from man to man within the Anthroposophical Society” that must exist, a living stream from one to the other. A certain lack of love has often appeared in the newest phases of our Society instead of a mutual trust, and if this lack of love gets the upper hand then the Anthroposophical Society must crumble. You see, our building brought many wonderfully beautiful qualities in the different Anthroposophists to the surface, but side by side with them there had to be an invigoration of the Society itself. Many of these beautiful qualities were named during our course of lectures which were given during the building of the Bau, and on the night of the burning of the Bau, but those beautiful qualities require guidance, and above all things this is necessary:—That anyone who has anything to do within the Society should not carry into it those things, which today are so customary outside it. And above all things, that each one who does anything for the Society should do it with real personal interest and participation. It is this personal interest, this personal share that one misses when people do one thing or another for our Society. My dear friends, no service for the Society—and that means anything done in the Society by one person for another—nothing can be trivial. The tiniest service rendered becomes valuable through its standing in the service of something great. That is so often forgotten, and the Society must really see this with the greatest and highest satisfaction, at a time when such a staggering blow demands the cultivation of these most beautiful qualities in the members. But at the same time, it should not be forgotten that in the industrious and patient accomplishment of everyday things, much which is necessary is overlooked. These are things which must not be undervalued when one sees Anthroposophy finding its enemies in the world around it. The fact that an enemy (Gegenschaft} is there, must not be overlooked, rather must it be grasped out of the very objective course of evolution itself. And I have often been astonished, and have said so publicly, at the lack of interest when opposition, taking its roots in objective untruth, develops around us. We must really place ourselves as positive defenders of Anthroposophy when it comes to a question of objective untruth. And at the same time, we must be able to raise ourselves to an understanding of the fact that Anthroposophy can only exist in an atmosphere of truth. We must develop a feeling of what it really means when so much untruth and so much objective calumny is brought against Anthroposophy. And for this we also need a real inner life. So you see, my dear friends we have a splendid opportunity for awakening ourselves. And if we can only reach the awakening in this sphere, then the impulse for awakening will spread itself out over other things. But if we see everyone asleep while the flames of untruth are making themselves felt everywhere, then we must not be surprised when even Stickl goes on sleeping? So that which I should like to characterise today, both in great things and also in tiny things is:—“Think, feel and meditate about this awakening.” So many today long for esotericism while these calumniations are hailing on our windows. Well, my dear friends, esotericism is there. Take hold of it. But, above all things, the will to awake is esoteric in our Society, and this will to awake must take its place within the Anthroposophical Society. Then the will to awake within the Society will be a point from which the awakening of the whole present civilisation will radiate. |
| 220. The Case for Anthroposophy: Introduction
Owen Barfield |
|---|
| And he suggests that the only reason why Brentano himself could not take the logically indicated second step (which must have carried him in the direction of anthroposophy) was that at the very outset of his philosophical career, following Emanuel Kant, he had irrevocably nailed his colours to the back of the Cartesian guillotine, by accepting the axiom that concepts without sensory content are “empty”. |
| 220. The Case for Anthroposophy: Introduction
Owen Barfield |
|---|
by Owen Barfield The prolonged historical event now usually referred to as “the scientific revolution” was characterised by the appearance of a new attitude to the element of sense perception in the total human experience. At first as an instinct, then as a waxing habit, and finally as a matter of deliberate choice, it came to be accepted that this element is, for the purposes of knowledge, the only reliable one; and further that it is possible, and indeed necessary, to isolate, in a way that had not hitherto been thought possible, this one element from all the others that go to make up man’s actual experience of the world. The word “matter” came to signify, in effect, that which the senses can, or could, perceive without help from the mind, or from any other source not itself perceptible by the senses. Whereas hitherto the perceptible and the imperceptible had been felt as happily intermixed with one another, and had been explored on that footing, the philosopher Descartes finally formulated the insulation of matter from mind as a philosophical principle, and the methodology of natural science is erected on that principle. It was by the rigorous exclusion from its field, under the name of “occult qualities”, of every element, whether spiritual or mental or called by any other name, which can only be conceived as non-material, and therefore non-measurable, that natural knowledge acquired a precision unknown before the revolution—because inherently impossible in terms of the old fusion; and, armed with that precision (entitling it to the name of “science”), went on to achieve its formidable technological victories. It is the elimination of occult qualities from the purview of science that constitutes the difference between astrology and astronomy, between alchemy and chemistry, and in general the difference between Aristotelian man and his environment in the past and modern man and his environment in the present. When two mutually dependent human relatives are separated, so that, for the first time, one of them can “go it alone”, there may be drawbacks, but it is the advantages that are often most immediately evident. By freeing itself from the taint of “occult qualities”, that is, by meticulously disentangling itself from all reference, explicit or implicit, to non-material factors, the material world, as a field of knowledge, gained inestimable advantages. We perhaps take them for granted now; but the men of the seventeenth century—the members of the Royal Society for instance had a prophetic inkling of what the new liberty promised. You have only to read some of their pronouncements. For them it was an emotional as well as an intellectual experience. “Bliss was it in that dawn to be alive ...” But when two people separate, so that one of them can go it alone, it follows as a natural consequence that the other can also go it alone. It might have been expected, then, that, by meticulously disentangling itself from all reference, explicit or implicit, to material factors, the immaterial, as a field of knowledge, would also gain inestimable advantages. That is what did not happen. But it will be well to state at once that it is nevertheless precisely this correlative epistemological principle that is the basis of Rudolf Steiner’s anthroposophy. It belongs to the post-Aristotelian age for the same reason that natural science does; but in the opposite way. Thus, the parallel terms, “spiritual science” and “occult science”, which he also used, do not betoken a fond belief that the methodology of technological1 science can be applied to the immaterial. The methodology of technological science is, rightly, based on the exclusion of all occult qualities from its thinking. The methodology of spiritual science is based on an equally rigorous exclusion of all “physical qualities” from its thinking. That is one of the things I hope this book will help to make clear. What did happen was well expressed by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, when he pointed out in his Aids to Reflection that Descartes, having discovered a technical principle, which “as a fiction of science, it would be difficult to overvalue”, erroneously propounded that principle as a truth of fact. (The principle in question was the necessity of abstracting from corporeal substance all its positive properties, “in order to submit the various phaenomena of moving bodies to geometrical construction”.) And of course the same point has since been made by A. N. Whitehead and others. But Coleridge could also point prophetically, in another place,2 to
The necessity for such a revolution, he said, arises from the fact that, for self-conscious man, although to experience a world of corporeal substance as existing quite apart from his thinking self is “a law of his nature,” it is not ‘;a conclusion of his judgment”. That this is indeed the case hardly needs arguing today, since it has become the discovery of technological science itself. Whether we go to neurology or to physics, or elsewhere, we are confronted with the demonstrable conclusion that the actual, macroscopic world of nature—as distinct from the microscopic, submicroscopic and inferred world of physical science—is (as, for instance, the biologist, Professor Marjorie Grene, puts it in her book The Knower and the Known) “mediated by concepts as well as presented through the senses”. What is remarkable is the rapidity with which the presence of this Trojan Horse in the citadel of its methodology was detected by technological science itself, as it was progressively realised that everything in nature that constitutes her “qualities” must be located on the res cogitans, and not the res extensa, side of the Cartesian guillotine. But this is as much as to say that those qualities are, in the technological sense, “occult”; and it could be argued without much difficulty that any science which proposes to enquire into them must also be “occult”—unless it is content to do so by extrapolating into the psyche a theoretical apparatus applicable, by definition, only to subject-matter that has first been sedulously dehydrated of all psyche. Yet this last is the approach which the methodology of natural science, as we have it, renders inevitable. If you have first affirmed that the material world is in fact independent of the psychic, and then determined to concentrate attention exclusively on the former, it does not make all that difference whether or no you go to the behaviouristic lengths of explicitly denying the existence of psyche. Either it does not exist or, if it does exist, it is occult and must be left severely alone. In any case you have withdrawn attention from it for so long that it might as well not be there, as far as you are concerned. For the purpose of cognition, it will gradually (as the author puts it on page 77) has “petered out”. Moreover this continues to be the case even after the failure of science to eliminate psyche from the knowable world has become evident. The demonstrative arguments of a Coleridge, a Whitehead, a Michael Polanyi are perforce acknowledged; but the acknowledgment remains an intellectual, not an emotional experience. The Trojan Horse certainly does seem to be there, and in rather a conspicuous way; but the necessary traffic-diversions can be arranged, and it is much less embarrassing to leave it standing in the market-place than to get involved. There is however one experience inseparable from the progress of natural science, which is apt to be an emotional as well as an intellectual one. And that is the fact that the exclusion of the psychic, as such, from matter of science entails recognition of the limits of science. This is, of course, the opposite experience from the one that enthralled the scientists of the seventeenth century. They rejoiced in a conviction that all the boundaries had gone and the prospects opened up to human knowledge had become limitless. Whereas, more and more as the nineteenth century progressed, it was the opposite that was stressed. “Ignorabimus.” We shall never know. There are limits beyond which, in the very nature of things, the mind can never pass. One of the things heavily stressed by Steiner (in Section I and again more specifically in Section III) is the significance, from the point of view of anthroposophy, of precisely this experience, and not so much in itself as for what it may lead to. The more monstrous and menacing the Horse is felt to be, towering there and casting its shadow over the centre of the town, the more ready we may be to begin asking ourselves whether there may not perhaps be something alive inside it. This experience can be an emotional, and indeed a volitional one, because it involves a frustrating, if suppressed, conflict between the scientific impulse, which is a will to know and a refusal to acknowledge boundaries except for the purpose of overthrowing them—and the scientific tradition, followed for the last three hundred years, which has ended in itself erecting boundaries that claim to be no less absolute than the old theological ones it did overthrow. In developing his contention that the shock of contact with these self-imposed limits of knowledge may itself be the necessary first step towards breaching them, the author refers in particular to two German writers, F. T. Vischer and Gideon Spicker. It would be a mistake to conclude from this, or from the nineteenth century idiom of the quotations, that the theme is out of date. The boundaries are still there and are still felt. The substance is the same, whether it is Gideon Spicker pointing out that every one, without exception, starts from an unproven and unprovable premise, namely the necessity of thinking. No investigation ever gets behind this necessity, however deep it may dig. It has to be simply and groundlessly accepted ... or Bertrand Russell, in Human Knowledge: Its Scope and Limits, conceding that the foundation, on which the whole structure of empirical science is erected, is itself demonstrably non-empirical: If an individual is to know anything beyond his own experiences up to the present moment, his stock of uninferred knowledge must consist not only of matters of fact, but also of general laws, or at least a law, allowing him to make inferences from matters of fact ... The only alternative to this hypothesis is complete scepticism as to all the inferences of science and common sense, including those which I have called animal inference. The abiding question is, how we choose to react to the boundaries. We may, with Russell and the empiricists, having once conscientiously “shown awareness” of them, proceed henceforth to ignore them and hope, so to speak, that they will go away; or, with the linguistic philosophers, we may flatly decline to look at them; or we may wrap ourselves in the vatic “silence” of a Heidegger or a Wittgenstein or a Norman O. Brown to be broken only by paradox and aphorism, or fall in behind the growing number of distinguished enthusiasts for metaphor, symbol and myth; or, with the scientific positivists, we may resign ourselves to the conviction that there is really no difference between knowledge and technology; we may even perhaps attempt some new definition of knowledge along the lines of the groping relativism, or personalism, of Karl Popper or of Michael Polanyi. But how far all of these are from the vision that was engendered by the scientific impulse in its first appearance among men! Steiner, as will be seen, advocates a different response, and one which, it seems to me, is more in accord with the fateful impulse itself, however it may differ from the methodology and the tradition which that impulse has so far begotten. At intervals through the ensuing pages the reader will encounter a passing reference to, and sometimes a quotation from, the German philosopher and psychologist, Franz Brentano. Here too he may be inclined to form a hasty judgment that the book is unduly “dated” by them. But here too it is the substance that matters, and that is far from being out of date. What that substance is, it is hoped, may be sufficiently gathered from the book itself. Brentano is however so little known to English readers that I have thought it best to omit from the translation that part of it which amounts to an exegesis of his psychology. There remain two points to which I wish to draw attention here. In a short section entitled “Direction of the Psychic from the Extra-psychic in Brentano” (also omitted) the author briefly capitulates the former’s refutation of a certain influential and still widely accepted psychological fallacy: namely, that the degree of conviction with which we treat a proposition as “true” (and thus, the existential component in any existential judgment) depends on the degree of intensity—the “passion”3—with which we feel it. This, says Brentano, is based on an impermissible analogy (“size”) between the psyche itself on the one hand and the world of space on the other. If conviction really depended on intensity of feeling, doctors would be advising their patients against studying mathematics, or even learning arithmetic, for fear of a nervous breakdown. What it in fact depends on, adds Steiner, is an inner intuition of the psyche neither similar nor analogous, but corresponding in its objectivity, to the psyche’s outer experience of causality in the physical world. And this experience is considered elsewhere in the book, for instance in Sections VII and VIII. The other point concerns Brentano’s relation to the present day. It is not always the philosopher whose name is best known and whose works are still read, whose influence is most abiding. Brentano was the teacher of Edmund Husserl, who acknowledged that teaching as the determining influence in his intellectual and vocational life; and without the Phenomenology of Husserl, with its stress on the “intentionality” or “intentional relation” in the act of perceiving, there is some doubt whether Existentialism would ever have been born. Thus, while from a superficial point of view the relation to Brentano, which certainly pervades the book as a whole, may be felt as a dating one, for anyone at all acquainted in detail with the history of western thought it can have the consequence of bringing it almost modishly up to date. Steiner’s Von Seelenrätseln (of which what follows is a partial translation) is not a systematic presentation of the philosophical basis of anthroposophy. For that the reader must go to his The Philosophy of Freedom, or Goethe’s Theory of Knowledge, or Truth and Science;4 and perhaps especially the last. The Foreword to Von Seelenrätseln does in fact describe it as a Rechtfertigung—vindication—of anthroposophical methodology, but my choice of a title for these extracts came from the impression I had myself retained of its essential content after reading the whole and translating a good deal of it. Steiner’s Von Seelenrätseln was published in 1917, the year of Brentano’s death; and its longest section (here omitted) amounts, as its title, Franz Brentano (Ein Nachruf), suggests, to an obituary essay. Steiner had always, he says in a Foreword, been both an admirer and an assiduous reader of Brentano and had long been intending to write about him. The main body of the essay is thus a patient and detailed exposition, supported by quotations, of Brentano’s psychology, in which the word “judgment” is used to name that intentional relation between the psyche and the extra-psychic, or physical world, which enables it either to reject a representation as subjective or to accept it as objective. This “judgment” is an exclusively psychic activity, and must be sharply distinguished as such from both representations and feelings. As the essay proceeds, Steiner makes it clear that he sees Brentano’s emphasis on intentionality as a first step in the direction of that psychological elimination of “physical qualities”, to which I have already referred. And he suggests that the only reason why Brentano himself could not take the logically indicated second step (which must have carried him in the direction of anthroposophy) was that at the very outset of his philosophical career, following Emanuel Kant, he had irrevocably nailed his colours to the back of the Cartesian guillotine, by accepting the axiom that concepts without sensory content are “empty”. Is this why today, although we have a philosophical and an ethical existentialism, and now even an existential psychology, we have as yet no existential epistemology? This essay is immediately preceded by a lengthy response in detail to a chapter in a then recently published book by Max Dessoir, and that in its turn by the introductory essay entitled Anthropology and Anthroposophy, which also forms the opening section of the book now presented to English readers. The arguments against including Max Dessoir über Anthroposophie seemed to me to be the same, only a good deal stronger than those against including the Brentano obituary. Steiner felt bound to go into Dessoir’s chapter in some detail, because it echoed irresponsibly a number of flagrant misunderstandings, or misrepresentations, of anthroposophy that were current in Germany at the time. Briefly, Dessoir’s arguments are all based on the assumption that anthroposophy ignores the principles of natural science and must collapse as soon as it is confronted with them; whereas Steiner’s real argument is, as he himself formulates it in the Foreword, that “either the grounds for there being such a thing as anthroposophy are valid, or else no truth-value can be assigned to the insights of natural science itself”. What he disputed was not facts, but hypotheses which have come to be treated as facts. I have omitted the Foreword; but the argument, so formulated, is sufficiently apparent from the rest of the book. The remainder of Von Seelenrätseln consists of eight Commentary Notes (Skizzenhafte Erweiterungen) of varying lengths, each referring specifically to a different point in the text, but each bearing a title and all of them quite capable, it seems to me, of standing on their own. Seven of them appear here as Sections II to VIII, and I have already borrowed from the eighth (Diremption of the Psychic from the Extra-psychic in Brentano) for the purposes of this Introduction. We are left with a book rather less than half the length of the original and requiring, if only for that reason, a different title; but still with a book which I have thought it important to make available, as best I can, in the English tongue; and that not only for the general reasons I have already suggested, but also for a particular one with which I will conclude. One of the Commentary Notes (Section VII) stands on rather a different footing, is perhaps even in a different category, from the others. At a certain point in the Brentano obituary Steiner quotes from a previous book of his own a passage in which he compares the relation between the unconscious and the conscious psyche to that between a man himself and his reflection in a looking glass. In which case the notion that the actual life of the soul consists of the way it expresses itself through the body, would be as fantastic as that of a man, regarding himself in a mirror, who should suppose that the form he sees there has been produced by the mirror. Whereas of course the mirror is the condition, not the cause, of what he sees. In the same way, the ordinary waking experience of the psyche certainly is conditioned by its bodily apparatus; but “it is not the soul itself that is dependent on the bodily instruments, but only the ordinary consciousness of the soul”. Now Section VII is, in form, a Note on this sentence; and it is somewhat odd that Steiner should have chosen a “Note” for the purpose to which he applied it. For he made it the occasion of his first mention (after thirty years of silent reflection and study) of the principle of psychosomatic tri-unity. Moreover it is still the locus classicus for a full statement of that same “threefold” principle, which, as every serious student of it knows, lies at the very foundation of anthroposophy, while at the same time it runs like a twisted Ariadne’s thread through nearly every matter selected for scrutiny. Even those readers, therefore, who are already too well convinced to feel that any “case” for anthroposophy is needed so far as they are concerned, will probably be glad to have it available in book form and in the English language. It has once before been translated—in 1925 by the late George Adams—but his version was only printed in a privately circulated periodical and has been out of print for more than forty years. It hardly needs adding that this Note in particular will repay particularly careful study. But there is one aspect of it, and of the doctrine it propounds, to which I feel impelled to direct attention before I withdraw and leave the book to speak for itself. If Section I is the statement, Section VII strikes me as a particularly good illustration, of the true relation between Steiner’s anthroposophy and that natural science which the scientific revolution has in fact brought about. Although he criticises, and rejects, a certain conclusion which has been drawn from the evidence afforded by neurological experiments, Steiner does not attack the physiology developed since Harvey’s day; still less does he ignore it; he enlists it. It is not only psychologically (for the reason already given) but also technologically that the scientific revolution was a necessary precondition of anthroposophical cognition. And this has a bearing on an objection of a very different order that is sometimes brought against it. I was myself once asked: What is there in Steiner that you do not also find in Jacob Boehme, if you know how to look for it? The content of Section VII (here called “Principles of Psychosomatic Physiology”) could never have come to light in the context of an Aristotelian physiology, a physiology of “animal spirits”, for example, and of four “elements” that were psychic as well as physical and four “humours” that were physical as well as psychic, no-one quite saw how. If your need is to know, not only with the warm wisdom of instinctive intelligence, but also with effective precision, you must first suffer the guillotine. Only after you have disentangled two strands of a single thread and laid them carefully side by side can you twist them together by your own act. The mind must have learnt to distinguish soma absolutely from psyche before it can be in a position to trace their interaction with the requisite finesse; and this applies not only to the human organism, but also to nature as a whole. It is the case that there is to be found in anthroposophy that immemorial understanding of tri-unity in man, in nature and in God, and of God and nature and man, which had long permeated the philosophy and religion of the East, before it continued to survive (often subterraneously) in the West in the doctrines of Platonism, Neo-Platonism, Hermetism, etc.; true that you will find it in Augustine, in pseudo-Dionysius, in Cusanus, in Bruno, in William Blake and a cloud of other witnesses, of whom Boehme is perhaps the outstanding representative. It would be surprising if it were not so. What differentiates anthroposophy from its “traditional” predecessors, both methodologically and in its content, is precisely its “post-revolutionary” status. It is, if you are that way minded, the perennial philosophy; but, if so, it is that philosophy risen again, and in a form determined by its having risen again, from the psychological and spiritual eclipse of the scientific revolution. To resume for a moment the metaphor I adopted at the outset of these remarks, it is because the two blood-relations were wise enough to separate for a spell as “family”, that they are able to come together again in the new and more specifically human relationship of independence, fellowship and love. Just how badly is it needed, a genuinely psychosomatic physiology? That is a question the reflective reader will answer for himself. For my own part, to select only one from a number of reasons that come to mind, I doubt whether any less deep-seated remedy will ultimately avail against a certain creeping-sickness now hardly less apparent from the Times Literary Supplement than in the Charing Cross Road; I mean the increasingly simian preoccupation of captive human fancy with the secretions and the excretions of its own physical body. A few final words about the translation. I have varied slightly the order in which the Sections are arranged and in most cases have substituted my own titles for those in the original. The German word Seele feels to me to be much more at home in technical as well as non-technical contexts than the English soul; and this is still more so with the adjective seelisch, for which we have no equivalent except soul—(adjectival). It is not however somewhat aggressively technical, as psyche is. I have compromised by using psyche and psychic generally but by no means universally. Habits of speech alter fairly quickly in some areas of discourse. Coleridge apologised for psychological as an “insolens verbum”. The same might possibly have been said of psyche in 1917, but hardly, I think, today and still less tomorrow. The mental or intelligential reference of Geist—operating towards exclusion, even from the sub-conscious imagination, of “physical qualities”—is more emphatic than that of spirit; and once again this is even truer of Geistig and spiritual. I doubt if much can be done about this; but I have sought to help a little by rather infrequently Englishing Geistig and Geist—(adjectival) as noetic. The distinctively English mind and mental sometimes appear to a translator of German as a sort of planets in the night sky of vocabulary and I have here and there adopted them both in seelisch and in Geistig contexts. And then of course there were those two thorns in the flesh of all who are rash enough to attempt translating philosophical or psychological German—Vorstellung and vorstellen. This is a problem that would bear discussing at some length. But it must suffice to say that I have mainly used representation and represent (after considering and rejecting presentation and present) occasionally substituting, where the context seemed to demand it, idea and ideation. The very meaning feels to me to lurk somewhere between the English terms—which is a good reason for using them both. Other usages are based on similar considerations and reflection. As to any habitual reader of Steiner who may suspect that I have taken too many liberties, I can only assure him that, as far as I know, I have at least had no other motive than a keen desire to do the fullest possible justice to thought-laden sentences written by an Austrian in 1917, but being read (as I hope) by an Anglo-Saxon in and after 1970.
|
| 28. The Story of My Life: Chapter XIV
Tr. Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| I should now have been extremely glad to be questioned orally on something which was related to the Seven Books of Platonism; but no question related to this; all were drawn from the philosophy of Kant. [ 9 ] I have always kept the image of Heinrich von Stein deeply imprinted on my heart; and it would have given me immeasurable pleasure to have met the man again. |
| 28. The Story of My Life: Chapter XIV
Tr. Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] For an indeterminate length of time I again faced a task that was given me, not through any external circumstance, but through the inner processes of development of my views of life and the world. To the same cause was due the fact that I used for my doctor's examination at the University of Rostock my dissertation on the endeavour after “an understanding of human consciousness with itself.” External circumstances merely prevented me from taking the examination in Vienna. I had official credit for the work of the Realschule, not of the Gymnasium, though I had completed privately the Gymnasium course of study, even tutoring also in these courses. This fact barred me from obtaining the doctor's degree in Austria. I had grounded myself thoroughly in philosophy, but I was credited officially with a course of study which excluded me from everything to which the study of philosophy gives a man access. [ 2 ] Now at the close of the first phase of my life a philosophical work had fallen into my hands which fascinated me extraordinarily – the Sieben Bücher Platonismus 1 of Heinrich von Stein, who was then teaching philosophy at Rostock. This fact led me to submit my dissertation to the lovable old philosopher, whom I valued highly because of his book, and whom I saw for the first time in connection with the examination. [ 3 ] The personality of Heinrich von Stein still lives in my memory – almost as if I had spent much of my life with him. For the Seven Books of Platonism is the expression of a sharply stamped philosophical individuality. Philosophy as thought-content is not taken in this work as something which stands upon its own feet. Plato is viewed from all angles as the philosopher who sought for such a self-supporting philosophy. What he found in this direction is carefully set forth by Heinrich von Stein. In the first chapters of the book one enters vitally and wholly into the Platonic world conception. Then, however, Stein passes on to the breaking into human evolution of the Christ revelation. This actual breaking in of the spiritual life he sets forth as something higher than the elaboration of thought-content through mere philosophy. [ 4 ] From Plato to Christ as to the fulfilment of that for which men have striven – such we may designate the exposition of von Stein. Then he traces further the influence of world conceptions of Platonism in the Christian evolution. [ 5 ] Stein is of the opinion that revelation gave content from without to human strivings after a world-conception. There I could not agree with him. I knew from experience that the human being, when he comes to an understanding with himself in vital spiritual consciousness, can possess the revelation, and that this revelation can then attain to an existence in the ideal experience of man. But I felt something in the book which drew me on. The real life of the spirit behind the ideal life, even though in a form which was not my own, had set in motion an impulse toward a comprehensive exposition of the history of philosophy. Plato, the great representative of an ideal world which was fixed through its fulfilment by the Christ impulse – it is the setting forth of this which forms the content of Stein's book. In spite of the opposition I felt toward the book, it came closer to me than any of the philosophies which merely elaborate a content out of concepts and sense-experiences. [ 6 ] I missed in Stein also the consciousness that Plato's ideal world had its source in a primal revelation of the spiritual world. This (pre-Christian) revelation, which has been sympathetically set forth, for example, in Otto Willmann's Geschichte des Idealismus2 does not appear in Stein's view. He sets forth Platonism, not as the residue of ideas from the primal revelation, which then recovers in Christianity and on a higher level its lost spiritual form; he represents the Platonic ideas as a content of concepts self-woven which then attained life through Christ. [ 7 ] Yet the book is one of those written with philosophical warmth, and its author a personality penetrated by a deep religious feeling who sought in philosophy the expression of the religious life. On every page of the three-volume work one is aware of the personality in the background. After I had read this book, and especially the parts dealing with the relation of Platonism to Christianity, over and over again, it was a significant experience to meet the author face to face. [ 8 ] A personality serene in his whole bearing, in advanced age, with mild eyes that looked as if they were made to survey kindly but penetratingly the process of evolution of his students; speech which in every sentence carried the reflection of the philosopher in the tone of the words – just so did Stein stand before me when I visited him before the examination. He said to me: “Your dissertation is not such as is required; one can perceive from it that you have not produced it under the guidance of a professor; but what it contains makes it possible that I can very gladly accept you.” I should now have been extremely glad to be questioned orally on something which was related to the Seven Books of Platonism; but no question related to this; all were drawn from the philosophy of Kant. [ 9 ] I have always kept the image of Heinrich von Stein deeply imprinted on my heart; and it would have given me immeasurable pleasure to have met the man again. Destiny never again brought us together. My doctor's examination is one of my pleasant memories, because the impression of Stein's personality shines out beyond everything else pertaining to it. [ 10 ] The mood in which I came to Weimar was tinged by previous thorough-going work in Platonism. I think that mood helped me greatly to take the right attitude toward my task on the Goethe and Schiller archives. How did Plato live in the ideal world, and how Goethe? This occupied my thoughts on my walk to and from the archives; it occupied me also as I went over the manuscripts of the Goethe legacy. [ 11 ] This question was in the background when at the beginning of 1891 I expressed in some such words as the following my impression of Goethe's knowledge of nature “It is impossible for the majority of men to grasp the fact that something for whose appearance subjective conditions are necessary may still have objective significance and being. And of this very sort is the ‘archetypal plant.’ It is the essential of all plants, objectively contained within them; but if it is to attain to phenomenal existence the human spirit must freely construct it.” Or these other words: that a correct understanding of Goethe's way of thinking “admits of the possibility of asking whether it is in keeping with the conception of Goethe to identify the ‘archetypal plant’ or ‘archetypal animal’ with any physically real organic form which has appeared or will appear at any definite time. To this question the only possible answer is a decisive ‘No.’ The ‘archetypal’ plant is contained in every plant; it may be won from the plant world by the constructive power of the spirit; but no single individual form can be said to be typical.3 [ 12 ] I now entered the Goethe-Schiller Institute as a collaborator. This was the place into which the philology of the end of the nineteenth century had taken over Goethe's literary remains. At the head of the Institute was Bernhard Suphan. With him also, I may say, I had a personal relationship from the very first day of the Weimar phase of my life. I had frequent opportunities to be in his home. That Bernhard Suphan had succeeded Erich Schmidt, the first director of the Institute, was due to his friendship with Herman Grimm. [ 13 ] The last descendant of Goethe, Walther von Goethe, had left Goethe's literary remains as a legacy to the Grand-duchess Sophie. She had founded the archives in order that the legacy might be introduced in appropriate manner into the spiritual life of the times. She naturally turned to those personalities of whom she had to assume that they might know what was to be done with the Goethe literary remains. [ 14 ] First of all, there was Herr von Loeper. He was, so to speak, foreordained to become the intermediary between Goethe scholars and the Court at Weimar to which the control of the Goethe legacy had been entrusted. For he had attained to high rank in the Prussian household administration, and thus stood in close relation with the Queen of Prussia, sister of the Grand-duchess of Saxe-Weimar; and, besides, he was a collaborator in the most famous edition of Goethe of that time, that of Hempel. [ 15 ] Loeper was an unique personality, a very congenial mixture of the man of the world and the recluse. As an amateur, not as a professional, had he come to be interested in “Goethe research.” But he had attained to high distinction in this. In his opinions concerning Goethe, which appear in such beautiful form in his edition of Faust, he was entirely independent. What he advanced he had learned from Goethe himself. Since he had now to advise how Goethe's literary remains could best be administered, he had to turn to those with whom he had become familiar as Goethe scholars through his own work with Goethe. [ 16 ] The first to be considered was Herman Grimm. It was as an historian of art that Herman Grimm had become concerned with Goethe; as such he had delivered lectures on Goethe at the University of Berlin, which he then published as a book. But he might well look upon himself as a sort of spiritual descendant of Goethe. He was rooted in those circles of the German spiritual life which had always been conscious of a living tradition of Goethe, and which might in a sense consider themselves bound in a personal way with him. The wife of Herman Grimm was Gisela von Arnim, the daughter of Bettina, author of the book, Goethe's Correspondence with a Child. [ 17 ] Herman Grimm's judgments about Goethe were those of an historian of art. Moreover, as an historian of art he had grown into scholarship only so far as this was possible to him under the standards of a personally coloured relationship to art as a connoisseur. [ 18 ] I think that Herman Grimm could readily come to an understanding with Loeper, with whom he was naturally on friendly terms by reason of their common interest in Goethe I imagine that, when these two discussed Goethe, the human interest in the genius came strongly to the fore and scholarly considerations fell into the background. [ 19 ] This scholarly way of looking at Goethe was the vital thing in William Scherer, professor of German literature at the University of Berlin. In him both Loeper and Grimm had to recognize the official Goethe scholar. Loeper did so in a childlike, harmless fashion; Herman Grimm with a certain inner opposition. For to him the philological point of view which characterized Scherer was really uncongenial. [ 20 ] With these three persons rested the actual direction in the administration of the Goethe legacy. But it nevertheless really slipped entirely into the hands of Scherer. Loeper really thought nothing about this further than to advise and to share from without as a collaborator in the task; he had his fixed social relationships through his position in the household of the Prussian King. Herman Grimm thought just as little about it. He could only contribute points of view and right directions for the work by reason of his position in the spiritual life; for the directing of details he could not take responsibility. [ 21 ] Quite different was the thing for William Scherer. For him Goethe was an important chapter in the history of German literature. In the Goethe archives new sources had come to light of immeasurable value for this chapter. Therefore, the work in the Goethe archives must be systematically united with the general work of the history of literature. The plan arose for an edition of Goethe which should take a philologically correct form. Scherer took over the intellectual supervision; the direction of the archives was left to his student Erich Schmidt, who then occupied the chair of modern German literature at Vienna. [ 22 ] Thus the work of the Goethe Institute received its stamp. Not only so, but also everything that happened at the Institute or by reason of this. All bore the mark of the contemporary philological character of thought and work. [ 23 ] In William Scherer literary-historical philology strove for an imitation of contemporary natural-scientific methods. Men took the current ideas of the natural sciences and sought to form philological and literary-historical ideas on these as models. Whence had a poet derived something? How had this something been modified in him? These were the questions which were placed at the foundations of a history of the evolution of the spiritual life. The poetic personalities disappeared from view; instead there came forward views as to how “material” and “motif” were evolved by the personalities. The climax of this sort of view was reached in Erich Schmidt's extended monograph on Lessing. In this Lessing's personality is not the main fact but an extremely painstaking consideration of the motifs of Minna von Barnhelm, Nathan, and the like. [ 24 ] Scherer died young, shortly after the Goethe Institute was established. His students were numerous. Erich Schmidt was called from the Goethe Institute to Scherer's position in Berlin. Herman Grimm then arranged so that not one of the numerous students of Scherer should have the direction of the Institute, but instead Bernhard Suphan. [ 25 ] As to his post before this time, he had been teaching in a Gymnasium in Berlin. At the same time he had undertaken the editing of Herder's works. Through this he seemed marked as the person to take direction also of the edition of Goethe. [ 26 ] Erich Schmidt still exercised a certain influence; through this fact Scherer's spirit still continued to rule over the Goethe task. But the ideas of Herman Grimm came forward in stronger fashion, if not in the manner of work yet in the personal relationships within the Goethe Institute. [ 27 ] When I came to Weimar, and entered into a close relationship with Bernhard Suphan, he was a man sorely tried in his personal life. His first and second wives, who were sisters, he had seen buried at an early age. He lived now with his two children in Weimar, grieving over those who had left him, and not feeling any happiness in life. His sole satisfaction lay in the good will which the Grand-duchess Sophie, his profoundly honoured lady, bore to him. In this respect for her there was nothing servile: Suphan loved and admired the Grand-duchess in an entirely personal way. [ 28 ] In loyal dependence was Suphan devoted to Herman Grimm. He had previously been honoured as a member of the household of Grimm in Berlin, and had breathed with satisfaction the spiritual atmosphere of that home. But there was something in him which prevented him from getting adjusted to life. One could speak freely with him about the highest spiritual matters, yet something bitter would easily come into the conversation, something arising from his experiences. Most of all did this melancholy dominate in his own mind; then he would help himself past these experiences by means of a dry humour. So one could not feel warm in his company. He could in a moment grasp some great idea quite sympathetically, and then, without any transition, fall immediately into the petty and trivial. He always showed good will toward me. In the spiritual interests vital within my own soul he could take no part, and at times treated them from the view-point of his dry humour; but in the direction of my work in the Goethe Institute and in my personal life he felt the warmest interest. [ 29 ] I cannot deny that I was often painfully disturbed by what Suphan did, the way in which he conducted himself in the management of the Institute, and the direction of the editing of Goethe; I never made any secret of this fact. Yet, when I look back upon the years which I passed with him, this is outweighed by a strong inner interest in the fate and the personality of the sorely tried man. He suffered in his life, and he suffered in himself. I saw how in a certain way, with all the good aspects of his character and all his capacities, he sank more and more into a bottomless brooding which rose up in his soul. When the Goethe and Schiller archives were moved to the new building erected in Ilm, Suphan said that he looked upon himself in relation to the opening of this building like one of those human victims who in primitive times were walled up before the doors of sacred buildings to sanctify the thing. He had really come gradually to fancy himself altogether in the role of one sacrificed on behalf of something with which he did not feel that he was wholly united. He felt that he was a beast of burden working at this Goethe task with which others with higher intellectual gifts might have been occupied. In this mood I always found him later whenever I met him after I had left Weimar. He ended his life by suicide in a mood of depression. Besides Bernhard Suphan, there was engaged at the Goethe and Schiller Institute at the time of my entrance Julius Wahle. He was one of those called by Erich Schmidt. Wahle and I were intimates from the time of my first sojourn at Weimar; a heartfelt friendship grew up between us. Wahle was working at the editing of Goethe's journals. Eduard von der Hellen worked as Keeper of the Records, and also had the responsibility of editing Goethe's letters. [ 30 ] On Goethe's works a great part of the German “world of Germanists” was engaged. There was a constant coming and going of professors and instructors in philology. One was then much in company with them during their longer or shorter visits. One could get vitally into the circle of interests of these persons. [ 31 ] Besides these actual collaborators in the Goethe task the archives were visited by numbers of persons who were interested in one way or another in the rich collections of manuscripts of other German poets. For the Institute gradually became the place for collecting the literary remains of many poets. And other interested persons came also who at first were less interested in manuscripts than in simply studying in the library contained within the rooms of the Institute. There were, moreover, many visitors who merely wished to see the treasures there. [ 32 ] Everybody who worked at the Institute was happy when Loeper appeared. He entered with sympathetic and amiable remarks. He requested the material he needed for his work, sat down, and worked for hours with a concentration seldom to be seen in anyone. No matter what was going on around him, he did not look up. If I were seeking for a personification of amiability, I should choose Herr von Loeper. Amiable was his Goethe research, amiable every word he uttered to anyone. Especially amiable was the stamp his whole inner life had taken from the fact that he seemed to be thinking of one thing only: how to bring the world to a true understanding of Goethe. I once sat by him during the presentation of Faust in the theatre. I began to discuss the manner of presentation, the dramatic qualities. He did not hear at all what I said. But he replied: “Yes, this actor often uses words and phrases that do not agree with those of Goethe.” Still more lovable did Loeper appear to me in his “absentmindedness.” When in a pause I chanced to speak of something which required a reckoning of duration of time, Loeper said: “Therefore the hours to 100 minutes; the minutes to 100 seconds ...” I stared at him, and said: “Your Excellency, 60.” He took out his watch, tested it, laughed heartily, counted, and said: “Yes, yes, 60 minutes, 60 seconds.” I often observed in him such instances of absent-mindedness. But over such proofs of Loeper's unique temper of mind I myself could not laugh, for they seemed to me a significant by-product – and also charming in their effect – of the personality so utterly free from pose, unsentimental, I might say gracious, in its earnestness. He spoke in rather sprawling sentences, almost without modulation; but one heard through the colourless speech a firm articulation of thought. [ 33 ] Spiritual purpose entered the Institute when Herman Grimm appeared. From the standpoint from which I had read – while still in Vienna – his book on Goethe, I felt the deepest sympathy with his type of mind. And when I was able to meet him for the first time in the Institute, I had read almost everything that had come from his pen. Through Suphan I was soon afterwards brought into much more intimate acquaintance with him. Then, while Suphan was once absent from Weimar and he came for a visit to the Institute, he invited me to luncheon at his hotel. I was alone with him. It was plainly agreeable to him to see how I could enter into his way of viewing the world and life. He became communicative. He spoke to me of his idea of a Geschicte der Deutsche Phantasie 4 which he had in mind. I then received the impression that he would write such a book. This did not come to pass. But he explained to me beautifully how the contemporary stream of historic evolution has its impulse in the creative fantasy of the folk, which in its temper takes on the character of a living, working supersensible genius. During this luncheon I was wholly filled with the expositions of Herman Grimm. I believed that I knew how the supersensible spiritual works through man. I had before me a man whose spiritual vision reached as far as the creative spiritual, but who would not lay hold upon the actual life of this spiritual, but remained in the region where the spiritual expresses its life in man in the form of fantasy. Herman Grimm had a special gift for surveying greater or lesser epochs of the history of the mind and of setting forth the period surveyed in precise, brilliant, epigrammatic characterization. When he described a single personality – Michelangelo, Raphael, Goethe, Homer – his representation always appeared against the background of such a survey. How often have I read his essays in which he characterized in his striking glances the Greek and Roman cultures and the Middle Ages. The whole man was the revelation of unified style. When he fashioned his beautiful sentences in oral speech I had the feeling: “This may appear just so in one of his essays”; and, when I read an essay of his after having become acquainted with him, I felt as if I were listening to him. He permitted himself no laxity in oral speech, but he had the feeling that in artistic or literary presentation one must remain the same person who moved about in everyday life. But Herman Grimm did not roam around like other men even in everyday life. It was inevitable for him to lead a life possessed of style. [ 34 ] When Herman Grimm appeared in Weimar, and in the Institute, then one felt that the plan of the legacy was, so to speak, united with Goethe by secret spiritual threads. Not so when Erich Schmidt came. He was bound to these papers that were preserved in the Institute, not by ideas, but by the historic-philological methods. I could never attain to a human relation with Erich Schmidt. And so all the great respect shown him by all those who worked at the Institute as Scherer philologists made practically no impression upon me. [ 35 ] Those were always pleasant moments when the Grand-duke Karl Alexander appeared in the Institute. An inwardly true enthusiasm – though manifested in a fashionable bearing – for everything pertaining to Goethe was a part of the nature of this man. Because of his age, his long connection with much that was important in the spiritual life of Germany, and because of his attractive lovableness he made a satisfying impression. It was a pleasing thought to know that he was the protector of the Goethe work in the Institute. [ 36 ] The Grand-duchess Sophie, owner of the Institute, one saw there only on special festival occasions. When she had anything to say, she caused Suphan to be summoned. The collaborating workers were taken to her to be presented. But her solicitude for the Institute was extraordinary. She herself personally made all the preliminary preparations for the erection of a public building in which the poetic legacies might be worthily housed. [ 37 ] The heir of the Grand-duke also, Carl August, who died before he became Grand-duke, came often to the Institute. His interest in everything there going on was not profound, but he liked to mingle with us collaborators. This interesting himself in the requirements of the spiritual life he viewed rather as a duty. But the interest of the heiress, Pauline, was full of warmth. I was able many times to converse with her about things which pertained to Goethe, poetry, and the like. As regards its social intercourse the Institute was between the scientific and artistic circles and the courtly circle of Weimar. From both sides it received its own colouring. Scarcely would the door have closed after a professor when it would reopen to admit some princely personage who came for a visit. Many men of all social positions shared in what went on in the Institute. At bottom it was a stirring life, stimulating in many relationships. [ 38 ] Immediately beside the Institute was the Weimar library. In this resided as chief librarian a man of a childlike temperament and unlimited scholarship, Reinhold Köhle. The collaborators at the Institute often had occasion to resort there. For what they had in the Institute as literary aid to their work was here greatly augmented. Reinhold Köhle had roved around with unique comprehensiveness in the myths, fairy-tales, and sagas; his knowledge in the field of linguistic scholarship was of the most admirable universality. He knew where to turn for the most out-of-the-way literary material. His modesty was most touching, and he received one with great cordiality. He never permitted anyone to bring the books he needed from their resting-places into the work-room of the archives where we did our work. I came in once and asked for a book that Goethe used in connection with his studies in botany, in order to look into it. Reinhold Köhle went to get the old book which had rested somewhere on the topmost shelves unused for decades. He did not come back for a long time. Someone went to see where he was. He had fallen from the ladder on which he had to climb to attend to the books. He had broken his thigh. The noble and lovable person never recovered from the effect of the accident. After a lingering illness this widely known man died. I grieved over the painful thought that his misfortune had happened while he was attending to a book for me.
|
| 127. The Mission of the New Spirit Revelation: The Relationship Between Theosophy and Philosophy
28 Mar 1911, Prague Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| How did it come about that this concept, which appears in a certain refined way in Kant, rather coarsely in Schopenhauer, but then is described astutely by the most diverse epistemologists of the 19th century, was able to gain such significance? |
| 127. The Mission of the New Spirit Revelation: The Relationship Between Theosophy and Philosophy
28 Mar 1911, Prague Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
A special consideration of the lectures on “Occult Physiology” Following the public lectures “How to Refute Theosophy?” and “How to Defend Theosophy?” and following the reflections that I have given in the lecture cycle on “Occult Physiology” over the past few days, “Occult Physiology”, a number of questions may arise, and there is a need to communicate a little with the honored audience about these questions, which have been touched upon here. The two public lectures were primarily aimed at showing how, on the basis of spiritual science or theosophy, one must be very aware of the possible objections that may arise, and how the occultist and on the other hand, it should be clear to you from the lectures how to defend the Theosophical truths in the face of the opponents' weighty objections. However, it is precisely from the realization of the difficulties that arise for Theosophy that every Theosophist should feel the need for the greatest possible accuracy and precision in the presentation of the Theosophical truths. Those who, out of a realization of the corresponding connections, have to represent these things are well aware of this, but despite all that has been emphasized in public lectures, they inevitably come into conflict with those who stand on the ground of today's science. Therefore, as strange as it may seem, Theosophy requires, on the one hand, the most exact and precise logical formulation for clothing the truths brought down from the higher worlds, and on the other hand, no less for the mere ordinary reasonableness. And anyone who sets himself this task of formulating precisely and exactly logically, and for this purpose avoids everything that might be a mere filler in a sentence or merely rhetorical embellishment, very often feels how easily he can be misunderstood, simply because in our time there is not everywhere the same intense need to accept the truths put forward just as exactly and precisely as they are expressed. Even in its scientific endeavors, humanity in our time is not yet accustomed to taking things exactly. If one takes what is said quite exactly, then not only must one not change anything in the sentences, but one must also pay close attention to the boundaries that are included in the formulations. We have a suitable example of this, which came up recently during a question and answer session. The question was asked: If dream consciousness is only a kind of pictorial consciousness, how is it then that certain subconscious actions, such as night wandering, can be carried out from this dream consciousness? The questioner has not taken into account, as I mentioned at the time, that the sentence that the contents of dream consciousness are pictorial does not mean that they are only pictorial, but that, of course, since only one side of the horizon of dream consciousness has been characterized from only one side, it followed from the very nature of this characterization that just as our daytime actions follow from our daytime consciousness, so too certain actions of a less conscious nature could follow from the pictorial consciousness of the dream. It should be said without charge that not listening carefully is one of the main reasons why so many misunderstandings are brought to Theosophy and its representation today. Such misunderstandings are not only brought by the opponents of Theosophy, but also to a large extent by those who profess this Theosophical worldview. And perhaps a large part of the blame for the misunderstandings that the outside world has of spiritual science lies in the fact that even within the theosophical circles, so much is sinned in the direction just described. If we now look around at the sciences that are recognized in our time, we might perhaps have the general feeling that Theosophy has the greatest affinity with the various branches of philosophy. Such an assertion would be absolutely correct, and one could actually assume from the nature of the matter that the closest possibility of understanding the theosophical insights would be on the side of philosophy. But precisely there, other difficulties arise. Philosophy, as it is cultivated today, one might say everywhere, has become a kind of specialized science to a much greater extent than it was relatively recently. It has become a specialized science and, if we look at its practical work today and do not get involved in individual theories, it works essentially in abstract regions. And there is not much inclination to lead philosophy back to a concrete conception of the actual. Indeed, there are even difficulties in the way philosophy is practiced today if one wants to embrace the world of the actual with this philosophical endeavor. The epistemology that has been developed with great ingenuity in the second half of the 19th century and up to the present day in the most diverse directions has come about mainly because these difficulties in penetrating from the abstract heights of thinking, of the concept, down to the facts were felt. Now, in lectures such as this series on “Occult Physiology”, Theosophy is needed everywhere to penetrate directly into our actual world with what it has to give as supersensible contents of consciousness. If I may speak in trivial terms, I would like to say: Theosophy is not as fortunate as today's philosophy, which dwells in abstract regions and which would not be very inclined to include in its considerations such concepts as, let us say, blood or liver or spleen, that is, contents of the actual. It would shrink from making the transition from its abstract concepts to the concrete events and things that directly and actually approach us. Theosophy is more daring in this respect and can therefore very easily be regarded as a spiritual activity that boldly and unjustifiably builds a bridge from the most spiritual to the most factual. Now it must be interesting to ask oneself why philosophers find it so difficult to approach Theosophy. Perhaps precisely because philosophy avoids building this bridge. For Theosophy itself, this fact is in a sense fatal, extraordinarily so. For one very often encounters resistance to the Theosophical insights, especially when one wants to work through them logically. It is precisely on the philosophical side that one encounters resistance in this regard. And it has even happened very often that one encounters less resistance when one, so to speak, gleefully tells people sensational observations from the higher worlds. They often forgive this relatively easily, because, firstly, these things are “interesting” and, secondly, people say to themselves: Well, since we cannot see into these worlds, we are not called upon to make any judgment about them. Now, however, the aim of Theosophy is to bring everything that can be found in the higher worlds down to a rational level of understanding. The facts, if they can truly be regarded as such, are found through supersensible research in the supersensible worlds. In our time, however, the form of presentation should be such that everything is clothed in strictly logical forms and that, wherever it is already possible today, it is pointed out how the most actual external processes can already provide us with confirmations everywhere for what we can assert from spiritual research. In this whole process of bringing down the knowledge of the spiritual world, of clothing it in logical or other rational forms and presenting it in a form that meets the logical needs of our time, there now exists, one might say, a truly extraordinary source of misunderstanding. Take the complicated things that were said in these lectures on “Occult Physiology,” which can only be applied with restrictions and with precise indications of the limits. Take the very complicated things in the immensely mobile and variable world of the spiritual, and compare this world of the spiritual in all its variability, in the difficulty of encompassing something coming down to us from spiritual worlds with rough conceptual contours, compare it with the ease with which any external fact can be characterized through an experiment or through sensory observation and described in a logical style! Now, however, throughout our philosophy today, there is a tendency to take no account whatever when defining and describing concepts other than those derived from the world that lies before us as the sensual world. This is particularly noticeable in philosophy when it is compelled, for example in the ethical field, to find a different origin for the basic concepts than those derived from the external perception of the physical world. We find – and this could easily be demonstrated, but of course only through detailed explanations from contemporary philosophical literature – that in everything that is dealt with in philosophy today, the definitions of terms are so rough because, when it comes to conceptualized content, basically the only consideration is the perceptual world that exists around us, and it is only on the basis of this that concepts are formed. Is there any evidence that in philosophy, when the most elementary concepts arise, the content of consciousness is also obtained from a different source than from the world of sensory perception? — In short, contemporary philosophy lacks the possibility of coming to an understanding of theosophy because it cannot tie in with its theories with concepts such as we use in our theosophical discussions. In philosophical literature, the horizon of consciousness has been defined in such a way that when concepts are formed, only the external world of perception is taken into account, and not the kind of content that comes from a different source than that of sensory perception. Theosophy, however, must arrive at its concepts in a completely different way; it must ascend to supersensible knowledge and bring its concepts down from the supersensible. But it must also delve into the realm of reality and must govern the philosophical concepts gained from observation of the sensual world. If we want to visualize this schematically, then on the one hand we have concepts in philosophy that are gained through external perception, and on the other hand we have concepts that are gained from the supersensible through spiritual perception. And if we think of the field of concepts through which we communicate, we have to say: If theosophy is to be considered justified, then our concepts must be taken from both sides, on the one hand from sensory perception, on the other hand from spiritual perception, and these two sides must meet in the field of our concepts. Concepts gained through external perception (philosophy) + concepts gained through supersensible perception (theosophy) = conceptual field Particularly in theosophical expositions, there is a need for the concepts brought down from the spiritual world to meet with the philosophical concepts. This means that our concepts can be connected everywhere to the concepts that are gained from the world of external sensory perception. Our present-day epistemologies are more or less almost exclusively constructed from the point of view that the concepts are taken only from one side. I do not want to say that there are no epistemologies where something supernatural is admitted as the origin of the concepts. But wherever something is to be proved positively, the examples are characterized by the fact that the concepts are taken only from the left side (scheme), that is, from the side on which the concepts are gained from the sensual-physical world of perception. This is also quite natural because [in philosophy] spiritual facts are not recognized as such. The possibility is simply not considered that spiritual facts, which are brought down from the spiritual worlds, can be conceptualized in the same way that the facts of the physical world are conceptualized. This circumstance has led to the fact that Theosophy, when it wants to communicate with philosophy, finds almost no prepared ground on the side of philosophy and that in philosophy the way in which concepts are used in Theosophy cannot easily be understood. One might say: When dealing with the world of outer sensory perception, it is easy to give concepts clear contours. Here, things themselves have clear contours, clear boundaries, and one is easily able to give concepts clear contours as well. If, on the other hand, one is confronted with the spiritual world, which is mobile and variable in itself, then much must often first be gathered together and restrictions or extensions made in the concepts in order to be able to characterize to some extent what is actually to be said. The theory of knowledge as it is pursued today is least of all suited to engage with such concepts as they are used in Theosophy. Because, in order to define the terms, the reasons for the definitions — consciously or unconsciously — are only taken from one side, and so, without really knowing it, something is mixed into all the terms that are formed that leads to epistemological terms that are not at all useful for explaining or elucidating anything in Theosophy. The concept, as it is supplied by the so-called non-theosophical world, is simply unsuitable as an instrument for characterizing what is brought down from the spiritual world through Theosophy. Now there is one such concept in particular that is a terrible troublemaker in the field of epistemology. I know very well that it is not perceived as such at all, but it is a troublemaker. If we disregard all the finer nuances that have emerged so astutely in the course of the 19th century, this is where the epistemological problem is formulated that one says: How does the I, with its content of consciousness - or, if you will, without speaking of the I -, how does our content of consciousness come to be related to a reality by us? These trains of thought have more or less – with the exception of certain epistemological trends in the 19th century – led to an epistemology that repeatedly perceives it as a great difficulty to see the possibility of how the trans-subjective or transcendental, that is, that which lies outside our consciousness, can enter our consciousness. I will admit that this only roughly characterizes the problem of knowledge. But the difficulties are essentially characterized by the fact that one says: How can that which is subjective content of consciousness somehow approach being, reality? How can it be related to reality? For we must be clear about the fact that even if we presuppose a trans-subjective reality lying outside our consciousness, that which is within our consciousness cannot directly approach this reality. We therefore have – so it is said – the content of consciousness within us, and we can ask ourselves: how do we have the possibility, from this content of consciousness, to penetrate into being, into reality, which is independent of our consciousness?— An important contemporary epistemologist has characterized this problem with a concise expression: The human ego, in so far as it encompasses the horizon of consciousness, cannot leap over itself, for it would have to leap out of itself if it were to leap into reality. But then it would be in reality and not in consciousness. — It seems clear to this epistemologist, then, that nothing can be said about the relationship between the content of consciousness and real reality. Many years ago, in my epistemological writings, I was concerned, first of all, with establishing this problem of knowledge – which is also fundamental in Theosophy – and then with removing the difficulties that arise from such a formulation as the one just described. In doing so, however, something very strange could happen. For example, at the time when what I want to talk about took place, there were philosophers who started from the premise, very similar to Schopenhauer's, that “the world is my idea.” That is to say, that which is given in consciousness is initially only the content of our imagination. The question then arises as to how to build a bridge from the imagination to that which is outside the imagined, to trans-subjective reality. Now, for anyone who is not fascinated by statements that have supposedly been made in this field, but approaches the matter impartially, a question is immediately posed, and in the face of a large amount of epistemological literature, namely that which was written in the seventies and in the first half of the eighties, one must ask: If anything is “my idea” and if this idea itself is supposed to be more than something lying within the content of consciousness, if it is supposed to have validity for itself, then this means that something is said which, basically, must not lie before the starting point of epistemology, but something that can only be established after these much more important epistemological basic questions have been discussed. For we must first ask ourselves: Why are we at all allowed to call something that arises in us as content of consciousness “my idea”? Do we have the right to say: What appears on my horizon of consciousness is my idea? Epistemology certainly does not have the right to start from the judgment that what is given is my idea, but rather, if it really goes back to its first beginnings, it has the duty to first justify that what appears is the subjective content of consciousness. Of course, there are several hundred objections to what has just been said, but I don't think it's possible to hold on to a single one of them for long if you approach the matter with an open mind. But I did experience that a well-known and important philosopher gave me a very peculiar answer when I pointed out this dilemma to him and wanted to explain that it should first be examined whether it is epistemologically justified to characterize the imagination as something unreal. He said: “That is self-evident, it is already in the definition of the word ‘imagination’ that we place something in front of us that is not real.” He could not understand - so ingrained were these ideas, which have grown over the centuries - that with this first definition, something completely unfounded is placed. If we want to make any kind of statement at all within the scope of the world in which we find ourselves – whereby I ask you to understand the words “the world in which we find ourselves” as the world as we experience it in our everyday lives – , for example, that what is given as the world is an “idea”, then we must realize that it is not at all possible to make such a statement without that which we call our thinking activity, without thoughts and concepts. I do not want to say anything about the fact that such a statement is actually a “judgment” in formal logic. In the moment when we begin at all not to leave anything as it appears before us, but to make a statement about it, we intervene with our thinking in the world that is around us. And if we are to have any right to intervene in the world, to define something as “subjective,” then we must be aware that that which defines something as being called subjective must itself not be subjective. Because if we assume that we have the sphere of subjectivity here (a circle is drawn on the board and the word “subjectivity” is written above it) and, from there, we make the statement, for example, that A is subjective, is “my idea” or whatever, then this statement itself is subjective. Subjectivity  The conclusion from this is not that we may accept this statement, but the conclusion must be that such a conclusion must not be drawn, because such a statement would cancel itself out. If a subjectivity can only be established from within itself, then that would be a self-abrogating statement. If the statement “A is subjective” is to have any meaning, then it must not proceed from the sphere of subjectivity, but from a reality outside of subjectivity. That is to say, if the “I” is to be at all in a position to say that something has a subjective character, for example, if something is “my idea”, if the “I” is to have the right to call something subjective, then it must not be within the sphere of subjectivity itself, but must make this observation from outside the sphere of subjectivity. Thus we must not trace the statement that something is subjective back to the ego, which itself is subjective.*) But this provides a way out of the sphere of subjectivity, in that we realize that we could not make any statement about what is subjective and what is objective, and would have to refrain from even the very first steps of thinking about it at all, if we did not stand in such a relationship to subjectivity and objectivity that both have an equal share in us. This leads us to recognize – which I cannot expand on further now – that our ego cannot be taken only subjectively, but is more comprehensive than our subjectivity. We have the right, from a given content, that is, from something objective, to distinguish that which is subjective. We are initially confronted with the different terms “objective”, “subjective” and “transsubjective”. “Objective” is, of course, different from “transsubjective” [gap in the transcripts]. Now the question is – once we have established these prerequisites – whether we are able to remove the stumbling block that is one of the most important obstacles in epistemology, namely the question of whether or not the whole extent of our self can be found within subjectivity. For if the ego must also partake of objectivity, the question “Can something enter the sphere of subjectivity?” takes on a completely different form. As soon as one can describe the ego as participating in the sphere of objectivity, the ego must have qualities within it that are similar to those of the objective; something from the sphere of objectivity must also be found in the ego. In other words, we may now assume a relationship between the objective and the subjective that differs significantly from the view that nothing can pass from the trans-subjective to the subjective. If one says that nothing can pass over to the subjective, then, firstly, one has defined the subjective in epistemological terms as self-contained, and, secondly, one has used a concept that is only valid for a certain sphere of reality, but cannot be valid for the whole of reality. This is the concept of the “thing in itself”. This concept plays a major role for many epistemologists; it is like a net in which philosophical thinking catches itself. However, one does not realize that this concept applies only to a certain sphere of reality and that it ceases to have validity where this sphere ceases. In the material, for example, the concept applies. I would like to recall the example of the seal and sealing wax. If you take a seal on which the name “Miller” is engraved and press it into hot sealing wax, then you can rightly say: Nothing of the matter of the seal can come over into the sealing wax. - There you have something where the non-transferability applies. But it is different with the name “Müller”; it can flow completely into the sealing wax. And if the wax could speak and wanted to emphasize that none of the material of the seal had flowed into it, it would still have to admit that what matters, namely the name “Müller,” had come across completely. So we have gone beyond the sphere where the concept of the “thing in itself” had any justification. How did it come about that this concept, which appears in a certain refined way in Kant, rather coarsely in Schopenhauer, but then is described astutely by the most diverse epistemologists of the 19th century, was able to gain such significance? It is, if you look at the whole thing more closely, because what people work out in concepts depends on the whole way they think. Only in an age in which all concepts have to be characterized in such a way that they are always formed by external perception could such a concept as that of the “thing in itself” arise. But concepts derived from outer perception alone are not suitable for characterizing the spiritual. If it were not for the fact that a disguised, one might say thoroughly masked, materialism has been introduced into the theory of knowledge — for that is the crucial point: a materialism that is really not easy to recognize has been introduced into the theory of knowledge - then one would realize that a theory of knowledge that is to apply to the spiritual realm must also have concepts that are not formulated in this crude style, such as the concept of the “thing in itself.” For the spiritual, where one cannot speak of an outside and an inside in the same sense, it must be clear that we need more subtle concepts. I could only sketch this out, because otherwise I would have to write a whole book, which would be very thick and would also have to have several volumes because I would have to connect metaphysical areas to the history of philosophy and to epistemology. But you can see that it is quite understandable that this kind of thinking, because it arises from deeply masked prejudices, is unusable for everything that reaches into the spiritual world. I have spoken to you for an hour now only about this most abstract concept. I have tried to make the matter understandable and I am absolutely clear about the fact that the objections, which are clearly before my mind, can of course arise in many other minds as well. If it had been a different meeting, it might have required a special justification to deceive one's listeners, as it were, by speaking in the most abstract — or, as some might believe, the most complicated — terms instead of the usual factual material that is expected. Well, in the course of our theosophical work, we have seen time and again that theosophy also has the good thing that one develops the duty to recognize within the theosophical movement, and that with it, little by little, a naughty concept is overcome that exists everywhere else, a very naughty concept that says: This is something that goes beyond my horizon, that I don't want to deal with, that is not interesting to me! For some who deal with fundamental philosophical questions and who know from experience the sometimes sparsely attended lectures on epistemology, it may be surprising that here in our movement so many people, who, according to the judgment of this or that epistemologist, are “most thorough dilettantes” in the field of epistemology, come to a meeting to listen to such a topic. In some places we have had an even larger audience, especially at philosophical lectures that were interspersed with theosophical lectures. But if you look at the situation more thoroughly, you may say that this is precisely one of the best testimonies for the theosophists. The theosophists know that they should listen to all the objections that can be raised without prejudice. They remain calm in the face of such objections, for they know full well that, although it is possible and legitimate to raise objections to research in the supersensible worlds, they also know that much of what is initially called illogical may ultimately turn out to be very logical after all. The theosophist also learns to consider it his duty to accept knowledge into his soul, even if it takes effort to deal with epistemology and logic. For in this way he will increasingly be able not only to listen to general theosophical expositions, but also to work seriously with logical concepts and conceptual classifications in theosophy. The world will have to become familiar with the idea that philosophy in its broadest sense will be reborn within the theosophical movement. Zeal for philosophical rigor, for thorough logical conceptualization, will gradually, if I may use the word, take root within the Theosophical movement. By which I do not mean to say that the results in this respect, on close inspection, are not already very satisfactory. We will still have to view this with modesty, but we are on the way to achieving this goal. The more we acquire the good will for intellectual endeavor, for scientific conscientiousness, for philosophical thoroughness, the more we will be able to use theosophical work not only to pursue our own personal goals, but also to achieve goals for humanity. Some things are only at the stage of the very first volition today. But it is evident that in the will that is applied to knowledge, there is already something like an ethical self-education that is achieved through the interest we take in Theosophy. And soon there will be no lack of that. If there are no obstacles other than those that already exist today, the outside world will not be able to deny Theosophy the recognition that the Theosophist does not strive for easy satisfaction of his soul's longings, but that in Theosophy a serious striving for philosophical thoroughness and conscientiousness is manifested, not mere dilettantism. This striving will be particularly suited to sharpening people's philosophical conscience. If we do not accept the theosophical teachings as dogmas, but understand what Theosophy can be as a real power in our soul, then it can be the fuel for the human soul to increasingly grasp the hidden powers within it and to lead it to an awareness of its destiny. Therefore, within our Theosophical movement, we want to promote this zeal for thorough logic and epistemology, and so, by standing firmer on the ground of our physical world, we learn to look up ever more clearly and without raptures and nebulous mysticism to the spiritual worlds, whose content we want to bring down and insert into our physical world view. Whether we want to do this depends solely on whether we can ascribe a real mission to Theosophy in the earthly existence of humanity. |

