| 276. The Arts and Their Mission: Lecture VI
09 Jun 1923, Dornach Tr. Lisa D. Monges, Virginia Moore Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| For to understand color is to understand a component part of the world. Kant once said: Give me matter, and out of it I shall create a world. Well, you could have given him matter endlessly without his ever being able to make a world out of it. |
| 276. The Arts and Their Mission: Lecture VI
09 Jun 1923, Dornach Tr. Lisa D. Monges, Virginia Moore Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Today I would like to examine certain other aspects of our subject. I have often dealt with the genius of language, and you know from my book Theosophy that we refer to real spiritual entities when we speak of spiritual beings in an anthroposophical context. Thus “genius of language” designates the spiritual entity behind any specific language, an entity with whom man can become familiar and through whom he can receive, from the spiritual world, strength to express his thoughts which, at the outset, are present in his earthly self as a dead heritage from that higher world. It is, therefore, appropriate for anthroposophical students to seek, in the formation of language, a meaning which is independent of man because rooted in the spirit. I have already drawn attention to the peculiar way the German language designates the beautiful and its opposite. We speak of the opposite of the beautiful (das Schoene) as the ugly or hateful (das Haessliche). Were we to denote the beautiful in the same way we would call it—since the opposite of hate is love—the lovely or loving. As it is, we make a significant difference. In German the word beautiful (das Schoene) is related to shining (das Scheinende). The beautiful shines; brings its inner nature to the surface. It is the distinguishing quality of the beautiful not to hide itself, but to carry its essence into outer configuration. Thus beauty reveals inwardness through outer form; a shining radiates outward into the world. If we were to speak, in this sense, of beauty's opposite, we would call it the concealed or non-radiant, that which holds back its being, refusing to disclose it in any outer sheath. To put it another way, “the beautiful” designates something objective. If we were to treat its opposite just as objectively, we would have to speak of concealment, of something whose outer aspect belies what it really is. But here subjectivity enters, for we cannot love what conceals itself, showing a false countenance; we must hate it. In this way the ugly calls up quite a different emotional reaction than the beautiful; we do not respond to it out of the same recesses of our nature. Thus the genius of language reveals itself. And we should ask: When in the broadest sense we strive for the beautiful in art, what is our goal? The very fact that the German word for “beautiful” proceeds outward (as its opposite suggests a remaining within our emotions, our hate) means that the beautiful bears a relation to the spiritual outside us. For what shines? What we apprehend with our senses does not need to shine for us; it exists. It is the spiritual that shines, radiating into the sensory, proclaiming its being even in the sensory. By speaking objectively of the beautiful, we take hold of it as a spiritual element which reveals itself in the world through art. The task of art is to take hold of the shining, the radiance, the manifestation, of that which as spirit weaves and lives throughout the world. All genuine art seeks the spirit. Even when art wishes to represent the ugly, the disagreeable, it is concerned, not with the sensory-disagreeable as such, but with the spiritual which proclaims its nature in the midst of unpleasantness. If the spiritual shines through the ugly, even the ugly becomes beautiful. In art it is upon a relation to the spiritual that beauty depends. Proceeding from this truth, let us consider one of the arts: painting. Recently we dealt with it insofar as it reveals the spiritual-essential through shining color. In ancient times man, by surrendering in the right way to the genius of language, showed his inner knowledge of color in his vocabulary. When an instinctive clairvoyance prevailed, he felt that metals revealed their inner natures in their colors, therefore gave them, not earthly names, but names connecting them with the planets. Otherwise people would have felt ashamed. For man looked upon color as a divine-spiritual element bestowed upon earthly substances only in the sense of our recent lectures. Perceiving the gold in gold's color, he saw not merely the earthly in that metal but the sun proclaiming itself from the cosmos in its gold color. Indeed, from the very start man saw something transcending the earthly in the colors of earthly objects. But it was only to living things that particular colors were ascribed, for living things approach the spirit in such a way that the spiritual shines forth. Animals were felt to have their own colors because in them the spirit-soul element manifests directly. In ancient times, when man's artistic sense was not outward but inward, he painted not at all. To paint a tree green is not true painting for the reason that however well one imitates her, nature is still the essential thing; nature is still more beautiful, more vital; it needs no copy. A real painter never imitates. He uses an object as a recipient or focus of the sun, or to observe a color reflex in that object's surroundings, or to catch, above it, an interweaving of light and darkness. In other words, the thing painted is merely an inducement. For example, we never paint a flower standing in front of a window; we paint the light which, shining in at the window, is seen through the flower. We paint the sun's colored light; catch the sun. In the case of a person, this can be done still more spiritually. To paint a human forehead the way one believes it should look is nonsense; this is not painting. But to observe how the sun rays strike that forehead, how color shows up in the ensuing radiance, how light and darkness intermingle, to capture with one's paint brush all that interplay: this is the task of the painter. Seizing what passes in a moment, he relates it to the spiritual. If, with a sense for painting, we look at an interior view, the matter of most importance is not the figure or figures therein. I once accompanied a friend to an exhibition where we saw a painting of a man kneeling before an altar, his back toward us. The painter had given himself the task of showing how sunlight falling through a window struck the man's back. My friend remarked that he would much rather see a front view. Well, this was only material, not artistic, interest. He wanted the painter to show the man's character, and so forth. But one is justified in doing this only if one expresses all perceptions through color. If I wish to paint a human being sick in bed with a certain disease, and study his facial color in order to apprehend how illness shines through the sensory, this may be artistic. If I want to show, in totality, the extent to which the whole cosmos manifests in the human flesh color, this may also be artistic. But if I try to imitate Mr. Lehman as he sits here before me, I will not succeed; moreover, this is not the task of art. What is artistic is how the sun illumines him, how light is deflected through his bushy eyebrows. Thus for a painter the important thing is how the whole world acts upon his subject; and his means of holding fast to a transitory moment are light and darkness, the whole spectrum. In times not so long ago one could not imagine a presentation of Mary, the Mother of God, without a face so transfigured it had passed beyond the ordinary human state; a face overcome by light. One could not imagine her clothed otherwise than in a red garment and blue cloak, because only so is the Mother of God placed rightly into earthly life; the red garment depicting all the emotions of the earthly, the blue cloak the soul element which weaves the spiritual around her; the face permeated and transfigured by spirit, overcome by light as a revelation of the spirit. We do not, however, properly and artistically take hold of these truths if we stop with what I have just described. For I have translated the artistic into the inartistic. We feel them artistically only if we create directly out of red and blue and the light by experiencing the light, in its relationship to colors and darkness, as a world in itself. Then colors speak their own language, and the Virgin Mary is created out of them. To achieve this one must live with color; color must become emancipated from the heavy matter opposing its innermost nature. Palette colors are alien to true painting in that, when used on a plane surface, they have a down-dragging effect. One cannot live with oil-based colors, only with fluid colors. When a painter puts fluid colors upon a plane, color—owing to the peculiar relationship between man and color—springs to life; he conceives out of color; a world arises out of it. True painting comes into being only if he captures the shining, revealing, radiating element as something living; only if he creates what is to be formed on the plane out of this element. For to understand color is to understand a component part of the world. Kant once said: Give me matter, and out of it I shall create a world. Well, you could have given him matter endlessly without his ever being able to make a world out of it. But out of the interplaying medium of color a world of sorts can indeed be created, because every color has direct relationship with something spiritual. In the face of present-day materialism, the concept and activity of painting have—except for the beginnings made by impressionism and, still more, by expressionism—been more or less lost. For the most part modern man does not paint, he imitates figures with a kind of drawing, then colors the surface. But colored surfaces are not painting for the reason that they are not born out of color and light and darkness. We must not misunderstand things. If somebody goes wild and just lays on colors side by side in the belief that this is what I call “overcoming drawing,” he is mistaken. By “overcoming drawing” I do not mean to do away with drawing, but to let it rise out of the colors, be born from the colors. Colors will yield the drawing; one simply has to know how to live in colors. Living so, an artist develops an ability—while disregarding the rest of the world—to bring forth works of art out of color itself. Look at Titian's “Ascension of Mary.” This painting stands at the boundary line of the ancient principle of art. The living experience of color one finds in Raphael and, more especially, in Leonardo da Vinci, has departed; only a certain tradition prevents the painter from totally forsaking the living-in-color. Experience this “Ascension of Mary.” The green, the red, the blue, cry out. Now take the details, the individual colors and their harmonious interaction, and you will feel how Titian lived in the element of color and how, in this instance, he really created out of it all three worlds. Look at the wonderful build-up of those worlds. Below, he has created out of color the Apostles experiencing the event of Mary's ascension. One sees in the colors how these men are anchored to the earth; colors which convey, not heaviness in the lower part of the painting, only a darkness which fetters the watching ones to earth. In the color-treatment of Mary one experiences the intermediate realm. A dull darkness from below connects her feet and legs with the earth; while, above her, light preponderates. This third and highest realm receives her head and radiates above it in full light, lifting it up. Thus are set forth, through inner color experience, the three stages of lower realm, middle realm, and the heights where Mary is being received by God the Father. To understand this picture we must forget everything else and look at it solely from the standpoint of color, for here the three stages of the world are derived from color not intellectually but artistically. True painting takes hold of this world of effulgent shining, of splendid manifestation in light and darkness and color, in order to contrast what is earthly-material with the artistic. But the artistic is not permitted to reach the spiritual. Otherwise it would be not “shine” but wisdom. For wisdom is no longer artistic, wisdom leads into the formless and therefore undepictable realm of the divine. With artistry like Titian's in “The Ascension of Mary,” we feel, on beholding the reception of Mary's head by God the Father, that now we must go no further in the treatment of light; we must halt. For we have reached the limit of the possible. To carry it further would be to fall into the intellectualistic, the inartistic. We must not make one stroke beyond what is indicated by light, rather than contour. The moment we insist on contour, we become intellectualistic, inartistic. Near the top this picture is in danger of becoming inartistic. The painters immediately after Titian fell prey to this danger. Look at the depiction of angels right up to the time of Titian. They are painted in heavenly regions. But look how carefully the painters avoided leaving the realm of color. Always you can ask yourself in regard to these angels of the pre-Titian age, and of Titian too: Couldn't they be clouds? If you cannot do that, if there is no uncertainty about existence, being, or semblance, shine, if there is an attempt fully to delineate the essence of the spiritual, artistry ceases. In the seventeenth century it was otherwise, for materialism affects the presentation of the spiritual. Now angels began to be painted with all kinds of foreshortenings, and one can no longer ask: Couldn't that be clouds? When reason is active, artistry dies. Again, look at the Apostles below: one has a feeling that in this “Ascension of Mary” only Mary is really artistic. Above, there is the danger of passing into the formlessness of pure wisdom. If one attains the formless one attains, in a certain sense, the zenith of the artistic. One has dared to press forward boldly to the abyss where art ceases, where the colors disappear in light, and where, if one were to proceed, one could only draw. But drawing is not painting. Thus the upper part of the picture approaches the realm of wisdom. And the more one is able to express, in the sensory world, this wisdom-filled realm, and the more the angels might be taken for billowy clouds shimmering in light, the greater the art. Proceeding from the bottom of the picture to the really beautiful, to Mary herself rising into the realm of wisdom, we see that Titian was able to paint her beautifully because she has not yet arrived at, but only soars up toward, the realm of wisdom; and we feel that, were she to rise still higher, she must enter where art ceases. Below stand the Apostles. Here the artist has tried to express their earth-fettered character. But now a different danger threatens. Had he placed Mary further down, he could not have depicted her inward beauty. If Mary were to sit among the Apostles, she could not appear as she does as a kind of balance between heaven and earth; she would look different. She simply does not fit among the Apostles with their brownish tones. Not only are they subject to earthly gravity; something else has entered: the element of drawing takes hold. This you can see in Titian's picture. Why is it so? Well, brown having already left the realm of color, it cannot express Mary's beauty; something not belonging entirely to the realm of the beautiful would be injected. If Mary stood or sat among the Apostles and were colored as they are, it would be a great offense. I am now speaking only of this picture and do not maintain that when standing on earth Mary must be in every instance, artistically speaking, an offense. But in this picture it would be a blow in the face if Mary stood below. Why? Because if she stood there colored like the Apostles we would have to say that the artist presented her as virtuous. This is the way he presents the Apostles; we cannot conceive of them otherwise than looking upward in their virtue. But this for Mary would he inappropriate. With her, virtue is so self-evident that we must not express it. It would be like presenting God as virtuous. If something is self-evident, if it has become the being itself, we must not express it in mere outer semblance. Therefore Mary soars up into a region beyond all virtues, where we cannot say of her, through colors, that she is virtuous, any more than we can say of God that He is virtuous. He may, at most, be virtue itself. But this is an abstract, philosophical statement having nothing to do with art. With the Apostles, however, the artist succeeded in representing, through his color treatment, virtuous human beings. They are virtuous. Let us look at how the genius of language reflects this truth. Tugend (virtue, in German) is related to taugen (to be fit, in German). To be fit, to be able to cope with something morally, is to be virtuous. Goethe speaks of a triad: wisdom, semblance and power. Art is the middle term: semblance, the beautiful; wisdom is formless knowledge; virtue is power to carry out worthwhile things effectively.1 Since ancient times this triad has been revered. Once, years ago, a man said to me—and I could appreciate his point of view—that he was sick and tired of hearing people speak of the true, the beautiful and the good, for anyone in search of an idealistic expression mouthed the phrase. But in ancient times these realities were experienced not externally but with complete soul participation. Thus in the upper region of Titian's picture we see wisdom not yet transcendent, radiating artistically because of the way it is painted. In the middle, beauty; below, virtue, that which is fit. What is the inner nature of the fit? Here is manifest the genius, the profundity, of the languages active among men. If we proceeded in an exterior way we might be reminded of a certain hunchback who went to church and listened to a priest describing quite externally how everything in the world is good and beautiful and fit. Waiting at the church door, the hunchback asked the priest: You said the idea of everything is good—have I, too, a good shape? The priest replied: For a hunchback you have a very good shape. If things are considered as externally as this, we shall never penetrate to the depths. In many fields modern observation proceeds so. Filled with external characteristics and definitions, men do not know that their ideas turn round and round in circles. In respect to virtue it is not a question of fitness for just anything, but of fitness for something spiritual, so that a person places himself into the spiritual world as a human being. Whoever is a complete human being by reason of his bringing the spiritual not merely to manifestation but to full realization through his will is—in the true sense—virtuous. Here we enter a region which lies within the human and religious, but no longer within the artistic, sphere, and least of all within the sphere of the beautiful. Everything in the world contains a polarity. Thus we can say of Titian's picture: Above Mary he is in danger of passing beyond the beautiful, there where he reaches the abyss of wisdom. Below, he comes to the brink of the other abyss. For as soon as a painter represents the virtuous, meaning that which man realizes through his own being, out of the spiritual, he again leaves behind the beautiful, the artistic. The virtuous human being can be painted only by characterizing virtue in its outer appearance, let us say by contrasting it with vice. But an artistic presentation of virtue as such is no longer possible. Where in our age do we not forsake the artistic? Simple life conditions are reproduced crudely, naturalistically, without any relation to the spiritual, and without this relation there is no art. Hence the striving of impressionism and expressionism to return to the spiritual. Though in many cases clumsy, tentative, exploratory, it is better than the inartistic copying of a model. Furthermore, if one grasps the concept of the artistically-beautiful, one can deal with the tragic in its artistic manifestations. The human being who acts in accordance with his thoughts, who lives his life intellectualistically, can never become really tragic. Nor can the human being who leads an entirely virtuous life. The only tragic person is one who in some way leans toward the daimonic, that is to say, toward the spiritual, whether in a good or bad sense. Today in this age when man is in the process of becoming free, daimonic man, that is man under the influence of tutelary spirits, is an anachronism. That man should outgrow the daimonic and become free is the whole meaning of the fifth post-Atlantean age. But as he progresses in freedom the possibility of tragedy diminishes and finally ceases. Take ancient tragic characters, even most of Shakespeare's: they have a daimonism which leads to the tragic. Wherever man had the appearance of the daimonic-spiritual, wherever the daimonic-spiritual radiated and manifested through him, wherever he became its medium, tragedy was possible. In this sense the tragic will have to taper off now; a free mankind must rid itself of tutelary spirits. This it has not yet done. On the contrary, it is more and more falling prey to such forces. But the great task and mission of the age is to pull human beings away from the daimonic towards freedom. The irony is that the more we get rid of the inner daimons which make us tragic personalities, the less do we get rid of external ones. For the moment modern man enters into relation with the outer world, he encounters something of the nature of daimons. Our thoughts must become freer and freer. And if, as I say in The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity, thoughts become will impulses, then the will also becomes free. These are polaric contrasts in freedom: free thoughts, free will. Between lies that part of human nature which is connected with karma. And just as once upon a time the daimonic led to tragedy, so now the experiencing of karma can lead to inmost tragedy. Tragedy will flourish when man experiences karma. As long as we live in our thoughts we are free. But the words with which we have clothed our thoughts, once spoken or written, no longer belong to us. What may happen to a word I have uttered! Having absorbed it, somebody else surrounds it with different emotions and sensations, and thus the word lives on. As it flies through the world it becomes a power proceeding from man himself. This is his karma. Because it connects him with the earth, it may burst in on him again. Even the word which leads its own existence because it belongs not to us but to the genius of language may create the tragic. Just in our present time we see mankind at the inception of tragic situations through an overestimation of language, of the word. Peoples wish to separate themselves according to language, and their desire provides the basis for the gigantic tragedy which during this very century will break in upon the earth. This is the tragedy of karma. If past tragedy is that of daimonology, future tragedy will be that of karma. Art is eternal; its forms change. And if in everything artistic there is some relationship to the spiritual, you will understand that with the artistic we place ourselves, creatively or through enjoyment, in the spirit world. A real artist may create his picture in a lonely desert. He does not worry about who will look at his picture or whether anybody at all will look at it, for he creates within a divine-spiritual community. Gods look over his shoulder; he creates in their company. What does he care whether or not anybody admires his picture. A person may be an artist in complete loneliness. Yet he cannot become one without bringing, by means of his creation, something spiritual into the world, so that it lives in the spirituality of the world. If one forgets this basic connection, art becomes non-art. To create artistically is possible only if the work has a relationship to the world. Those ancient artists who painted pictures on the walls of churches were conscious of this fact; they knew that their murals stood within earth life insofar as this is permeated by the spirit; that they guided believers. One can hardly imagine anything worse than painting for exhibitions. It is horrible to walk through a picture or sculpture gallery where completely unrelated subjects appear side by side. Painting lost meaning when it passed from something for church or home to an isolated phenomenon. If we paint or view a picture in a frame, we can imagine ourselves looking out through a window. But to paint for exhibitions—this is beyond discussion. An age which sees value in exhibitions has lost its connection with art. By this can be seen how much waits to be done in culture if we would find our way back to the spiritual-artistic. Exhibitions must be overcome. Of course some individual artists detest exhibitions. But today we live in an age when the individual cannot achieve very much unless his judgment grows out of a world-conception permeating fully free human beings; just as world-conceptions permeating people in less free ages led to the rise of genuine cultures. Today we have no real culture. Only a spiritual world-conception can build up true culture, the indubitably artistic.
|
| 293. The Study of Man: Lecture V
26 Aug 1919, Stuttgart Tr. Daphne Harwood, Helen Fox Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| First of all it says dogmatically: we look out upon the world that is round about us, and within us there lives only the mirrored image of this world. And so it comes to all its other deductions. Kant himself is not clear as to what is in the environment which man perceives. For reality is not within the environment, nor is it in phenomena: only gradually, through our own winning of it, does reality come in sight, and the first sight of reality is the last thing we get. |
| 293. The Study of Man: Lecture V
26 Aug 1919, Stuttgart Tr. Daphne Harwood, Helen Fox Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Yesterday we discussed the nature of will in so far as will is embodied in the human organ. Today we will use this knowledge of man's relationship to will to fructify our consideration of the rest of the human being. You will have noticed that in treating of the human being up to now I have chiefly drawn attention to the intellectual activity, the activity of cognition, on the one hand, and the activity of will on the other hand. I have shown you how the activity of cognition has a close connection with the nerve nature of the human being, and how the activity of will has a close connection with the activity of the blood. If you think this over you will also want to know what can be said with regard to the third soul power, that is, the activity of feeling. We have not yet given this much consideration, but today, by thinking more of the activity of feeling, we shall have the opportunity of entering more intensively into an understanding of the two other sides of human nature, namely cognition and will. Now there is one thing that we must be clear about, and this I have already mentioned in various connections. We cannot put the soul powers pedantically side by side, separate from each other, thus: thinking, feeling, willing, because in the living soul, in its entirety, one activity is always merging into another. Consider the will on the one hand. You will realise that you cannot bring your will to bear on anything that you do not represent to yourself as mental picture, that you do not permeate with the activity of cognition. Try in self-contemplation, even superficially, to concentrate on your willing, you will find that in every act of will the mental picture is present in some form. You could not be a human being at all if mental picturing were not involved in your acts of will. And your willing would proceed from a dull instinctive activity, if you did not permeate the action which springs forth from the will with the activity of thought, of mental picturing. Just as thought is present in every act of will, so will is to be found in all thinking. Again, even a purely superficial contemplation of your own self will show you that in thinking you always let your will stream into the formation of your thoughts. In the forming of your own thoughts, in the uniting of one thought with another, or passing over to judgments and conclusions—in all this there streams a delicate current of will. Thus actually we can only say that will activity is chiefly will activity and has an undercurrent of thought within it; and thought activity is chiefly thought activity and has an undercurrent of will. Thus, in considering the separate faculties of soul, it is impossible to place them side-by-side in a pedantic way, because one flows into the other. Now this flowing into one another of the soul activities, which is recognisable in the soul, is also to be seen in the body, where the soul activity comes to expression. For instance, let us look at the human eye. If we look at it in its totality we shall see that the nerves are continued right into the eye itself; but so also are the blood vessels. The presence of the nerves enables the activity of thought and cognition to stream into the eye of the human being; and the presence of the blood vessels enables the will activity to stream in. So also in the body as a whole, right into the periphery of the sense activities, the elements of will on the one hand and thought or cognition on the other hand are bound up with each other. This applies to all the senses and moreover it applies to the limbs, which serve the will: the element of cognition enters into our willing and into our movements through the nerves, and the element of will enters in through the blood vessels. But now we must also learn the special nature of the activities of cognition. We have already spoken of this, but we must be fully conscious of the whole complex belonging to this side of human activity, to thought and cognition. As we have already said, in cognition, in mental picturing lives antipathy. However strange it may seem, everything connected with mental picturing, with thought, is permeated with antipathy. You will probably say, “Yes, but when I look at something I am not exercising any antipathy in this looking.” But indeed you do exercise it. When you look at an object, you exercise antipathy. If nerve activity alone were present in your eye, everything you looked at would be an object of disgust to you, would be absolutely antipathetic to you. But the will, which is made up of sympathy, also pours its activity into the eye, that is, the blood in its physical form penetrates into the eye, and it is only by this means that the feeling of antipathy in sense-perception is overcome in your consciousness, and the objective, neutral act of sight is brought about by the balance between sympathy and antipathy. It is brought about by the fact that sympathy and antipathy balance one another, and by the fact also that we are quite unconscious of this interplay between sympathy and antipathy. If you take Goethe's Theory of Colour, to which I have already referred in this connection, and study especially the physiological-didactic part of it, you will see that it is because Goethe goes more deeply into the activity of sight that there immediately enters into his consideration of the finer shades of colour the elements of sympathy and antipathy. As soon as you begin to enter into the activity of a sense organ you discover the elements of sympathy and antipathy which arise in that activity. Thus in the sense activity itself the antipathetic element comes from the actual cognitive part, from mental picturing, the nerve part—and the sympathetic element comes from the will part, from the blood. As I have often pointed out in general anthroposophical lectures there is a very important difference between animals and man with regard to the constitution of the eye. It is a significant characteristic of the animal that it has much more blood activity in its eye than the human being. In certain animals you will even find organs which are given up to this blood activity, as for example the ensiform cartilage, or the “fan.” From this you can deduce that the animal sends much more blood activity into the eye than the human being, and this is also the case with the other senses. That is to say, in his senses the animal develops much more sympathy, instinctive sympathy with his environment than the human being does. The human being has in reality more antipathy to his environment than the animal only this antipathy does not come into consciousness in ordinary life. It only comes into consciousness when our perception of the external world is intensified to a degree of impression to which we react with disgust. This is only a heightened impression of all sense-perceptions; you react with disgust to the external impression. When you go to a place that has a bad smell and you feel disgust within the range of this smell, then this feeling of disgust is nothing more than an intensification of what takes place in every sense activity, only that the disgust which accompanies the feeling in the sense impression remains as a rule below the threshold of consciousness. But if we human beings had no more antipathy to our environment than the animal, we should not separate ourselves off so markedly from our environment as we actually do. The animal has much more sympathy with his environment, and has therefore grown together with it much more, and hence he is much more dependent on climate, seasons, etc., than the human being is. It is because man has much more antipathy to his environment than the animal has that he is a personality. We have our separate consciousness of personality because the antipathy which lies below the threshold of consciousness enables us to separate ourselves from our environment. Now this brings us to something which plays an important part in our comprehension of man. We have seen how in the activity of thought there flow together thinking (nerve activity as expressed in terms of the body) and willing (blood activity as expressed in terms of the body). But in the same way there flow together in actions of will the real will activity and the activity of thought. When we will to do something, we always develop sympathy for what we wish to do. But it would get no further than an instinctive willing unless we could bring antipathy also into willing, and thus separate ourselves as personalities from the action which we intend to perform. But the sympathy for what we plan to do is predominant, and a balance is only effected by the fact that we bring in antipathy also. Hence it comes about that the sympathy as such lies below the threshold of consciousness, and part of it only enters consciously into that which is willed. In all the numerous actions that we perform not merely out of our reason but with real enthusiasm, and with love and devotion, sympathy predominates so strongly in the will that it penetrates into the consciousness above the threshold, and our willing itself appears charged with sympathy, whereas as a rule it merely unites us with our environment in an objective way. Just as it is only in exceptional circumstances that our antipathy to the environment may become conscious in cognition, so our sympathy with the environment (which is always present) may only become conscious in exceptional circumstances, namely, when we act with enthusiasm and loving devotion. Otherwise we should perform all our actions instinctively. We should never be able to relate ourselves properly to the objective demands of the world, for example in social life. We must permeate our will with thinking, so that this will may make us members of all humanity and partakers in the world's process itself. Perhaps it will be clear to you what really happens if you think what chaos there would be in the human soul if we were perpetually conscious of all this that I have spoken of. For if this were the case man would be conscious of a considerable amount of antipathy accompanying all his actions. This would be terrible! Man would then pass through the world feeling himself continually in an atmosphere of antipathy. It is wisely ordered that this antipathy as a force is indeed essential to our actions, but that we should not be aware of it, that it should lie below the threshold of consciousness. Now in this connection we touch upon a wonderful mystery of human nature, a mystery which can be felt by any person of perception, but which the teacher and educator must bring to full consciousness. In early childhood we act more or less out of pure sympathy, however strange this may seem; all a child does, all its romping and play, it does out of sympathy with the deed, with the romping. When sympathy is born in the world it is strong love, strong willing. But it cannot remain in this condition, it must be permeated with thought, by idea, it must be continuously illumined as it were by the conscious mental picture. This takes place in a comprehensive way if we bring ideals, moral ideals, into our mere instincts. And now you will understand better the true significance of antipathy in this connection. If the impulses that we notice in the little child were throughout our life to remain only sympathetic, as they are sympathetic in childhood, we should develop in an animal way under the influence of our instincts. These instincts must become antipathetic to us; we must pour antipathy into them. When we pour antipathy into them we do it by means of our moral ideals, to which the instincts are antipathetic, and which for our life between birth and death bring antipathy into the childlike sympathy of instincts. For this reason moral development is always somewhat ascetic. But this asceticism must be rightly understood. It always betokens an exercise in the combating of the animal element. This can show us to what a great extent willing in man's practical activity is not merely willing but is also permeated with idea, with the activity of cognition, of mental picturing. Now between cognition or thinking on the one hand and willing on the other hand we find the human activity of feeling. If you picture to yourselves what I have now put forward as willing and as thinking, you can say: From a certain central boundary there stream forth on the one hand all that is sympathy, willing, and on the other hand all that is antipathy, thinking. But the sympathy of willing also works back into thinking, and the antipathy of thinking works over into willing. Thus man is a unity because what is developed principally on the one side plays over into the other. Now between the two, between thinking and willing, there lies feeling, and this feeling is related to thinking on the one hand and to willing on the other hand. In the soul as a whole you cannot keep thought and will strictly apart, and still less can you keep the thought and will elements apart in feeling. In feeling, the will and thought elements are very strongly intermingled. 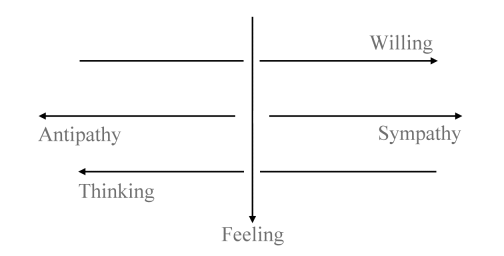 Here again you can convince yourselves of the truth of these remarks by even the most superficial self-examination. What I have already said will lead you to this conviction, for I told you that willing, which in ordinary life proceeds in an objective way, can be intensified to an activity done out of enthusiasm and love. Then you will clearly see willing as permeated with feeling—that willing which otherwise springs forth from the necessities of external life. When you do something which is filled with love or enthusiasm, that action flows out of a willing which you have allowed to become permeated by a subjective feeling. But if you examine the sense activities closely—with the help of Goethe's theory of colour—you will see how these are also permeated by feeling. And if the sense activity is enhanced to a condition of disgust, or on the other hand to the point of drinking in the pleasant scent of a flower, then you have the feeling activity flowing over directly into the activity of the senses. But feeling also flows over into thought. There was once a philosophic dispute which—at all events externally—was of great significance—there have indeed been many such in the history of philosophy—between the psychologist Franz Brentano and the logician Sigwart, in Heidelberg. These two gentlemen were arguing about what it is that is present in man's power of judgment. Sigwart said: “When a man forms a judgment, and says, for example, ‘Man should be good’; then feeling always has a voice in a judgment of this kind; decision concerns feeling.” But Brentano said, “Judgment and feeling (which latter consists of emotions) are so different that the faculty of judgment could not be understood at all if one imagined that feeling played into it.” He meant that in this case something subjective would play into judgment, which ought to be purely objective. Anyone who has a real understanding for these things will see from a dispute of this kind that neither the psychologists nor the logicians have discovered the real facts of the case, namely that the soul activities are always flowing into one another. Now consider what it is that should really be observed here. On the one hand we have judgment, which must of course form an opinion upon something quite objective. The fact that man should be good must not be dependent on our subjective feeling. The content of the judgment must be objective. But when we form a judgment something else comes into consideration which is of a different character. Those things which are objectively correct are not on that account consciously present in our souls. We must first receive them consciously into our soul. And we cannot consciously receive any judgment into our soul without the co-operation of feeling. Therefore, we must say that Brentano and Sigwart should have joined forces and said: True, the objective content of the judgment remains firmly fixed outside the realm of feeling, but in order that the subjective human soul may become convinced of the rightness of the judgment, feeling must develop. From this you will see how difficult it is to get any kind of exact concepts in the inaccurate state of philosophic study which prevails to day. One must rise to a different level before one can reach such exact concepts, and there is no education in exact concepts to-day except by way of spiritual science. External science imagines that it has exact concepts, and rejects what anthroposophical spiritual science has to give, because it has no conception that the concepts arrived at by spiritual science are by comparison more exact and definite than those commonly in use to-day, since they are derived from reality and not from a mere playing with words. When you thus trace the element of feeling on the one hand in cognition, in mental picturing, and on the other hand in willing, then you will say: feeling stands as a soul activity midway between cognition and willing, and radiates its nature out in both directions. Feeling is cognition which has not yet come fully into being, and it is also will which has not yet fully come into being; it is cognition in reserve, and will in reserve. Hence feeling also, is composed of sympathy and antipathy, which—as you have seen—are only present in a hidden form both in thinking and in willing. Both sympathy and antipathy are present in cognition and in will, in the working together of nerves and blood in the body, but they are present in a hidden form. In feeling they become manifest. Now what do the manifestations of feeling in the body look like? You will find places all over the human body where the blood vessels touch the nerves in some way. Now wherever blood vessels and nerves make contact feeling arises. But in certain places, e.g., in the senses, the nerves and the blood are so refined that we no longer perceive the feeling. There is a fine undercurrent of feeling in all our seeing and hearing, but we do not notice it, and the more the sense organ is separated from the rest of the body, the less do we notice it. In looking, in the eye's activity, we hardly notice the feelings of sympathy and antipathy because the eye, embedded in its bony hollow, is almost completely separated from the rest of the organism. And the nerves which extend into the eye are of a very delicate nature and so are the blood vessels which enter into the eye. The sense of feeling in the eye is very strongly suppressed. In the sense of hearing it is less suppressed. Hearing has much more of an organic connection with the activity of the whole organism than sight has. There are numerous organs within the ear which are quite different from those of the eye, and the ear is thus in many ways a true picture of what is at work in the whole organism. Therefore the sense activity which goes on in the ear is very closely accompanied by feeling. And here even people who are good judges of what they hear find it difficult to discriminate clearly—especially in the artistic sphere—between what is purely thought-element and what is really feeling. This fact explains a very interesting historical phenomenon of recent times, one which has even influenced actual artistic production. You all know the figure of Beckmesser in Richard Wagner's “Meistersinger.” What is Beckmesser really supposed to represent? He is supposed to represent a musical connoisseur who quite forgets how the feeling element in the whole human being works into the thought element in the activity of hearing. Wagner, who represented his own conceptions in Walther, was, quite one-sidedly, permeated with the idea that it is chiefly the feeling element that should dwell in music. In the contrast between Walther and Beckmesser, arising out of a mistaken conception—I mean mistaken on both sides—we see the antithesis of the right conception, viz. that feeling and thinking work together in the hearing of music. And this came to be expressed in a historical phenomenon, because as soon as Wagnerian art appeared, or became at all well known, it found an opponent in the person of Eduard Hanslick of Vienna, who looked upon the whole appeal to feeling in Wagner's art as unmusical. There are few works on art which are so interesting from a psychological point of view as the work of Eduard Hanslick On Beauty in Music. The chief thought in this book is that whoever would derive everything in music from a feeling element is no true musician, and has no real understanding for music: for a true musician sees the real essence of what is musical only in the objective joining of one tone with another, and in Arabesque which builds itself up from tone to tone, abstaining from all feeling. In this book, On Beauty in Music Hanslick then works out with wonderful purity his claim that the highest type of music must consist solely in the tone-picture, the tone Arabesque. He pours unmitigated scorn upon the idea which is really the very essence of Wagnerism, namely that tunes should be created out of the element of feeling. The very fact that such a dispute as this between Hanslick and Wagner could arise in the sphere of music is a clear sign that recent psychological ideas about the activities of the soul have been completely confused, otherwise this one-sided idea of Hanslick's could never have arisen. But if we recognise the one-sidedness and then devote ourselves to the study of Hanslick's ideas which have a certain philosophical strength in them, we shall come to the conclusion that the little book On Beauty in Music is very brilliant. From this you will see that, regarding the human being for the moment as feeling being, some senses bear more, some less of this whole human being into the periphery of the body, in consciousness. Now in your task of gaining educational insight it behoves you to consider something which is bringing chaos into the scientific thinking of the present day. Had I not given you these talks as a preparation for the practical reforms you will have to undertake, then you would have had to plan your educational work for yourselves from the pedagogical theories of to-day, from the existing psychologies and systems of logic and from the educational practice of the present time. You would have had to carry into your schoolwork the customary thoughts of the present day. But these thoughts are in a very bad state even with regard to psychology. In every psychology you find a so-called theory of the senses. In investigating the basis of sense-activity the psychologist simply lumps together the activity of the eye, the ear, the nose, etc., all in one great abstraction as “sense-activity.” This is a very grave mistake, a serious error. For if you take only those senses which are known to the psychologist or physiologist of to-day and consider them in their bodily aspect alone, you will notice that the sense of the eye is quite different from the sense of the ear. Eye and ear are two quite different organisms—not to speak of the organisation of the sense of touch which has not been investigated at all as yet, not even in the gratifying manner in which eye and ear have been investigated. But let us keep to the consideration of the eye and ear. They perform two quite different activities so that to class seeing and hearing together as “general sense-activity” is merely “grey theory.” The right way to set to work here would be to speak from a concrete point of view only of the activity of the eye, the activity of the ear, the activity of the organ of smell, etc. Then we should find such a great difference between them that we should lose all desire to put forward a general physiology of the senses as the psychologies of to-day have done. In studying the human soul we only gain true insight if we remain within the sphere which I have endeavoured to outline in my Truth and Science, and also in The Philosophy of Freedom. Here we can speak of the soul as a single entity without falling into abstractions. For here we stand upon a sure foundation; we proceed from the point of view that man lives his way into the world, and does not at first possess the whole of reality. You can study this in Truth and Science, and in The Philosophy of Freedom. To begin with man has not the whole reality; he has first to develop himself further, and in this further development what formerly was not yet reality becomes true reality for him through the interplay of thinking and perception. Man first has to win reality. In this connection Kantianism, which has eaten its way into everything, has wrought the most terrible havoc. What does Kantianism do? First of all it says dogmatically: we look out upon the world that is round about us, and within us there lives only the mirrored image of this world. And so it comes to all its other deductions. Kant himself is not clear as to what is in the environment which man perceives. For reality is not within the environment, nor is it in phenomena: only gradually, through our own winning of it, does reality come in sight, and the first sight of reality is the last thing we get. Strictly speaking, true reality would be what man sees in the moment when he can no longer express himself, the moment in which he passes through the gateway of death. Many false elements have entered into our civilisation, and these work at their deepest in the sphere of education. Therefore we must strive to put true conceptions in the place of the false. Then, also, shall we be able to do what we have to do for our teaching in the right way. |
| 93a. Foundations of Esotericism: Lecture XXXI
05 Nov 1905, Berlin Tr. Vera Compton-Burnett, Judith Compton-Burnett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| With Tolstoi everything is fructified through the West European culture, but in a way different from that of others before him. With powerful simplicity he utters what no Kant and no Spencer could have expressed. What there appears over-ripe appears in him as something still unfulfilled. |
| 93a. Foundations of Esotericism: Lecture XXXI
05 Nov 1905, Berlin Tr. Vera Compton-Burnett, Judith Compton-Burnett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Our Fifth Root-Race, the present Post-Atlantean humanity, was preceded by that of Atlantis, on the now submerged continent between Europe and America. The Atlanteans can in no way be compared with the human beings who today inhabit our Earth Globe. For even the remnants of that old race have learnt a variety of things from the later inhabitants of the Fifth Continent and we are therefore unable to reconstruct from them the conditions of that civilisation. At the beginning of the Atlantean civilisation there were no tools. By means of clairvoyant forces it was possible for the Atlantean to make the earth serve his needs. The preparation of metals for such uses only appeared towards the end of the Atlantean Epoch. A small group was separated off from the population of Atlantis, just as now in the Theosophical Society a separation should once again take place. It was their task to carry over a new civilisation into the Fifth Root-Race. You would find the place where those who were chosen lived, a small colony, in present England and Ireland. At that time this was where the original Semites lived. They were the first people who were in a position to think with their intellect. All the ideas of the Atlanteans were still of the nature of pictures. The rounded shape of the front of the brow, the formation of the part of the brain on which thought depends, first appears with the population of the original Semites, who were in no way similar to the present Semitic race. This original Semitic people who, one can say, discovered thinking, journeyed through Europe into Asia and there founded a civilisation. They formed the Fifth Sub-Race of the Atlanteans. The seven Sub-races of the Atlantean RootRace were as follows: Firstly the Rmoahals, secondly the Tlavatlis, thirdly the original Toltecs, fourthly the original Turanians, fifthly the original Semites, sixthly the original Accadians, seventhly the original Mongolians. The Fifth Root-Race therefore arose from the Fifth Sub-Race of the Atlanteans. When we look towards Asia we find there as, the First Sub-Race of the Fifth Root-Race, the Ancient Indian race, that people who later journeyed in a more Southern direction and there became the ancestors of the later Indians. The most essential characteristic of this ancestral race, who had travelled towards the north of India, was that it developed no real sense for material culture. It possessed spiritual vision of the highest order combined with a completely undeveloped sense for the material. The ancient Indians were turned away from the world; their souls were completely similar to the Atlanteans, in that they were able to develop a superlative, glorious picture world. Through the practise of Yoga, working from within outwards, they later evolved what today seems to us a learned conception of the world. Of this, what has been handed down as external tradition, only fragments remain. The Vedas and the Bhagavad Gita no longer give any real picture of the mighty conceptions of the Indians, but only echoes. In the Vedanta philosophy also there is only an abstract remainder of the original teaching of the Indians, which was handed down by word of mouth. Think of the faculty which appeared in the later Kabbalistic teaching in a form which elaborated matters in minute detail with subtle intricacy, think of this faculty applied to lofty cosmic thoughts. When later the Jew was able to apply thought to such things in the Kabbalistic teachings, it followed that the later Jewish occult teaching was only a decadent reflection, an echo of that finely articulated thought system of the primeval Indians. And what the teaching of the Brahmans became is by no means only religion in the sense of later systems, but knowledge, poetry and religion in a single great whole. All this was, as it were the finest flower, the extracted essence of what had developed in the old Atlantean civilisation. The Europeans also came over from Atlantis to Western and Central Europe and here there developed a quite different teaching. Groups of people settled who were not yet advanced enough to be chosen to found new civilisations, but yet possessed in germinal form what in India came to expression in so magnificent a way, but which here remained at a much earlier stage. What had its start in Europe moved ever further and further towards Asia. A common teaching formed its foundation, but in Europe this remained at a somewhat primitive level. The Indian teaching was expressed in the Vedas. ‘Veda’ means the same as ‘Edda’, only the content of the Vedas is more finely developed than that which remained here in Europe in a more primitive form as the Edda, which was only written down at the end of the Middle Ages. We must realise that this great primal spiritual teaching underwent a certain modification brought about by the migrating peoples. Its original greatness consisted in grasping the mighty divine unity which was recognised by the spiritual vision of the (ancient) Indians. This was no longer so with the next, the (ancient) Persian Race. In the wisdom arising from this primeval Indian vision the concept of time was almost entirely absent. It was with the Second Sub-Race, the ancient Persian, that the concept of time made its appearance. Time, it is true, was recognised by the Indian but was more uniform; the concept of history, the progression from the imperfect to what is more perfected, was lacking. Thinking was governed by the idea that everything has emanated from divine perfection. Persian thinking was governed by the concept of time. Zervan Akarana is one of the most important Divinities of the Persians and this is in fact Time. How did one arrive at the concept of time? Whoever seeks above all the primal unity of the Godhead, as in the case of the ancient Indians, must conceive it as the absolute Good. Evil, the imperfect in the world, was for the ancient Indian nothing but illusion; ‘illusion’ was a very important concept. These ancient people said: Nothing whatever exists in the world that is imperfect and evil. If you believe that something evil exists, you have not looked at the world in a way sufficiently free from illusion. Rust, for instance, which eats into iron, is elsewhere very beneficial: you must only consider where it is. When you look at a criminal through the veil of illusion, he will appear to you as such; if however you turn away from illusion you will realise that there is no such thing as evil.—This teaching is inwardly connected with a turning away from the world. It was otherwise with the Second Sub-Race. There, with the earliest of the Persian peoples, the Good was given a particular place in the World-process, was regarded as the goal. It was said: The Good must be sought for. The world is good and evil, Ormuzd and Ahriman; and what conquers the evil is Zervan Akarana, Time. This is how good and evil came into the early Persian world-conception as the principle of evolution. The Zarathustran teaching rests on the placing of evil in the world, and on the time-concept. Man is placed into life in order to conquer evil. This conception is connected with the fact that the Second Sub-Race was not one that was estranged from the world, but worked within it. Active, productive in various branches of human work, attention directed to the outer world, concerned as to how someone could himself create good out of the world: this was the Second Sub-Race. With the Persians therefore a whole company of Gods makes it appearance; not characteristics of one God, but a plurality of Gods; because the world, if not regarded as illusion, but as reality, presents a plurality, a multiplicity. The Gods which were venerated there were more or less personal-spiritual Divinities. The earliest initiates, who founded the ancient Indian teaching, were also the teachers of the Second Sub-Race, the ancient Persian Race. Here they adapted the whole teaching to a working people. They created that religion which was brought to fruition by the various Zarathustras.82 A further initiation advanced towards the Near East: to Egypt, to the Babylonians, Assyrians, Chaldeans, these forefathers of the Arabs. There the Third Sub-Race was developed. This Third Sub-Race was such that it now sought to bring both directions—the inner nature of man and the outer world—into harmony with each other. Whether you look for the fundamental conception of this Third Sub-Race in Chaldea or Egypt, everywhere you will find a pronounced awareness of the connection between human work and the forces of Nature. This is an essential difference when compared with the Persian Race. In Persia you have two powers, the good and the evil, which do battle with one another. Now man tries to bring the different nature forces or beings into his service. What developed as Persian religion was mainly built up on human morality and industry. Now in the Third Sub-Race the consciousness developed that one does not master nature only by means of bodily strength and moral behaviour, but best of all through knowledge. In those lands where a skillful agriculture was pursued as in Egypt and Chaldea, there developed a co-ordination of heavenly-spiritual powers with what was carried out by human work. Knowledge of the meteorological environment and the heavenly bodies evolved there. Strength for work was sought for in the knowledge of Nature. So it came about that man directed his gaze to the stars, and astronomy was brought into connection with humanity on the Earth. Man's origin was sought for in the stars. Thus, in this sense we have for the first time to do with science. Now in the Third Sub-Race, instead of inner perception, we have practical knowledge. So we hear of great initiates who taught geometry, the practice of surveying, technical skills. The fructification of human activity with cosmic wisdom brought down from the spiritual world makes its appearance in the Third Sub-Race. With this, something was given which translated the whole conception of human life into a kind of heavenly science. With the different peoples this found expression in various ways. In the case of the Egyptians, Osiris, Isis and Horus were conceived of as representatives of astronomical phenomena. Three different Sub-Races developed in Asia. Taking their start from Atlantis, a colony led by initiates traveled over to Asia. A special result of this was the ancient Indian civilisation, a second, the ancient Persian; the third result was the Egyptian-Chaldean civilisation: they all had a common initiation-source. In Europe however groups always remained behind which fell away from what culminated with such magnificence in the three great civilisations. These separate cultural streams were distributed in Europe in the most varied way. In Europe too there were initiates who formed Mystery Schools towards the end of the period of which we are speaking: they were called Druids: Drys means Oak. The strong oak was the symbol of the early European priest-teachers, for what dominated the peoples in the North was the thought that their old form of culture would necessarily have to decline. There the Twilight of the Gods was taught and the future of Christianity came to magnificent expression through these Northern prophets in what later became the Siegfried Saga.83a This may be compared with the Achilles Saga.83b Achilles is invulnerable in his whole body with the exception of the heel, Siegfried with the exception of the spot between the shoulders. To be invulnerable in such a way signifies to have been initiated. In Achilles you have the initiate of the Fourth Sub-Race which lies on the ascending curve of man's cultural development: therefore all the upper parts of Achilles are invulnerable; only the heel the lower nature is vulnerable, just as Hephaistos is lame. The German Siegfried was also an initiate of the Fourth Sub-Race, but vulnerable between the shoulder blades. This is his vulnerable spot, first made invulnerable by the One who bore the cross. With Siegfried the Gods reach their downfall, the Northern Gods approach their end (Twilight of the Gods). This gives the Northern saga its tragic note, for it not only points to the past, but to the Twilight of the Gods, to the time which is to come. The Druids gave to man the teaching of the declining Northern Gods. Thus in what was still symbolic form, the battle of St. Boniface84 with the Oak represents the battle of the Druids with the old Priesthood. Everywhere in the North one can point to the traces of what came to expression over in Asia. For instance Muspelheim and Niflheim are a counterpart of Ormuzd and Ahriman. The giant Ymir, out of whom the whole world is made, corresponds to the cutting into pieces of Osiris. In the most detailed way one can follow the connection between the European peoples of the North and the other civilisations. When in the South of Europe the Fourth Sub-Race was developing, the Northern tribes had also made the transition into the Fourth Stage so that in the Germanic peoples Tacitus85 found much that was related to the Southern culture. Irmin86 for example is the same figure as Hercules. Tacitus also tells us of a kind of Isis worship there in the North. So the older stages of civilisations progressed towards what was to come as Christianity. So think of Europe, Central Asia and Egypt as sown with the seed of what had developed under the influence of the Initiation Schools. These Initiation Schools sent out from their midst the founder of the Fifth [Fourth] Sub-Race, who had long been prepared in the shelter of the Mysteries. This is the personality who in the Bible is called Abraham. He came from Ur in Chaldaea and developed as an extract of the three older civilisations. The task which was represented in Abraham was to carry into the human realm all that had been held in veneration in the outside world; to create initiates who laid great value on what was human, in order to found the cult of the personality. This brought about personal attributes in the Jewish patriarchs. Here we have to do with duplicity and cunning. Jacob gains his inheritance by employing ruse and cunning in order to take what he wants from his brother. This is the reality out of which our present-day civilisation developed: it is founded on intelligence and possessiveness. In the stories of the Old Testament this is magnificently expressed as a kind of dawning of the new. It would be impossible to present this origin in a more powerful way. Esau is still a hairy man, that means he represents the human type which is still more enmeshed in the physical; Jacob represents one who relies on his intelligence and guile and thereby achieves what is now actually developing in human nature. The overcoming of physical force through intelligence is here inaugurated. The initiators do not always introduce something great into the world, but what must of necessity come about. ‘Israel’ means: He who leads man to the invisible God, who dwells within. Isra-el: El means the goal; Isra = the invisible God. Until then God was visible, whether it was the one who gave the urge towards Good and Evil as with the Persians, whether the God who had his body in the stars, in the Universe: This God was experienced as something visible. And now we have the Jewish initiation portrayed in Joseph and his twelve brethren. It is a beautiful and powerful allegory. The allegorical now makes its appearance: the intellect, when it wishes to be effective, becomes the recounter of allegories. How Joseph was initiated was first recounted. He was removed from his normal surroundings, sold for twenty pieces of silver and cast into a pit, where he remained for three days. This indicates an initiation. Then he comes to Egypt where his activities bring new life. And now we have finally indicated the transition which began at that time from the knowledge of God in the stars to the knowledge of man. Joseph was rejected because he had dreams. He had the following dream: Sun, Moon and eleven stars bowed down before him. The eleven stars are the eleven signs of the Zodiac. He felt himself to be the twelfth. The symbolism of the Star-Religion was now led over into the human. In the twelve brothers, the starting point of the twelve tribes' the knowledge of God in the stars was led over into the personal. “Now you surely do not wish to assert,” said his father—“that your brothers will bow down to you.” Here the change is given us. The divine knowledge of the stars is replaced by a knowledge attached to the personal human. This finds its form in the Mosaic law. Out of the three Ancient Civilisations, through the initiation of the Jewish Patriarchs, this Fourth Civilisation, the primal Jewish, was derived. This we have as the Fourth Sub-Race, for there belong to it also the civilisations of Ancient Greece and Rome. The civilisations of Greece and Rome (Roman law) both become great just through this personal element, until eventually this thought incarnated, reaching its culmination in Christianity. So it is in this lesser racial branch that the actual stream of the Fourth Sub-Race makes its appearance. The Graeco-Latin stream is a higher form of the Judaic; here the cult of the personal is intensified. There is no contradiction between this descent to the deepest point and then the ascent.  Everywhere [within the Fourth Sub-Race] we can observe this. The personal had actually to come to expression in the way described in the Esau and Jacob Saga in order to find its purification in the beauty of the human culture of the Greeks and the greatness of the human culture of the Romans. In the Odysseus Saga the ancient civilisation of the priests was conquered by cunning. It was out of the civilisations that arose from this that Christianity could first develop, which in truth contains all the ancient cultures in itself and can therefore also absorb them. In accordance with his parentage Jesus Christ was a native of Galilee ... ‘Galilean’ means: ‘The Stranger’, someone who does not really belong; ‘Galilee’ means a small isolated territory where someone could be brought up who, in his native milieu had to take into himself, not only the Jewish, but also all the ancient forms of culture. Out of the impact between the Romans and the Northern peoples there now developed the Fifth Sub-Race in which we ourselves live. It has still kept an impulse from the old Initiation Schools in the Moorish, and Arabian influence which came over from Asia. It is always the same influence, the same Initiation School. We can trace how the Irish monks, as also those who work in scientific fields, are essentially inspired by the Moorish-Arabian science. This gives the same fundamental character in a new-form, in a way in which it could now be received. It is here that Christianity first finds its real expression. It has merely passed through the ancient Greek civilisation for as long as the Fifth Period of Culture was being prepared; and then finds here firm ground, embodying itself in a whole range of nations. Everything at that time was permeated and inspired by Christianity. Our present time with its materialistic culture is the last radical expression of what was then inaugurated. The birth of this new culture is symbolically presented in the Lohengrin Saga. Lohengrin is the initiator of the ‘city-state’, and the city life which leads up to a new cultural stage is symbolised by Elsa of Brabant. Into all these streams others penetrate, for instance the Mongolian tribes. What originally came over from the West was related to what came with the Huns from the East. So from East and West something came together that was related: the Mongolian and Germanic tribes. Those who originated from the West were left-behind descendants of the Atlanteans, as were also the Mongolians from the East. Fundamentally both streams were related. It is always one stream which crosses another. Both, however, have a common native ground since they both originated from Atlantis. Now here in the North, everything that has remained from earlier times took on a more established form. At the same time as the epoch of the Jewish Prophets, in the centuries before Christ, we find here indications of a great, primeval, Atlantean initiate. Wod-Wodha-Odin.87 This is a modernised Atlantis, in a new form, an atavism, a throwback into the Atlantean Age. And this happens everywhere, over in Asia also. In Asia W, the sound V, becomes B, Wodha = Bodha = Buddha. Buddhism appears as a throwback into the Atlantean Age. This is why we find Buddhism most widespread with what has remained over from the Atlanteans in the Mongolian peoples. And where the very pillars of its greatness make their appearance in Tibet, there we have a modern, monumental expression of Atlantean culture. One must get to know such relationships between peoples, then one will also understand history. When Attila,88 the fighter for monotheism, appears in Europe, it was Christianity which first halted him, because there he was confronted with something greater than anything the Huns possessed. The monotheism of the Huns was, as the outcome of an Atlantean civilisation, of a magnitude which they found in no other peoples that they encountered on their way. Christianity alone made a forceful impression on them. Many things in historical development are to be understood in the light of these great considerations. The well-known traveler, Peters,89 certainly feels that the old Bodhism and the Wotanism can flow together, but he does not know that we in Europe have not only to be representatives of what comes from the ancient past, but something new, a new spiral. Into the old part of the spiral there strikes the very newest, the wisdom pointing to the future. This is related to the old wisdom as clear day consciousness is related to trance consciousness. With completely clear day consciousness future peoples will develop a spiritual culture which will be different from the old. For this reason Theosophy must not be only what is carried over from the old, from Buddhism and Hinduism; this would certainly collapse. Something new must arise out of the seeds which slumber in the East of Europe, coming together with everything that is being worked out there. The inherent culture of the future lies in the unfolding of what is now in a seed condition in the Folk-elements of Eastern Europe. We ourselves in Central Europe are the advance post. Eastern Europe must provide the means, the human material for what is here being founded in advance. The Rosicrucian Schools always taught that Central and Western Europe are only advance posts of what will develop in the European East, what will proceed from the fructification of the Folk element and European knowledge. With Tolstoi everything is fructified through the West European culture, but in a way different from that of others before him. With powerful simplicity he utters what no Kant and no Spencer could have expressed. What there appears over-ripe appears in him as something still unfulfilled. But it is always so with what is in a seed condition. Not out of the fine perfected plant, but out of the seedling does the new, future plant grow. Whatever one may experience, one can look with complete trust towards the future. For just as the crystal first develops out of an alkaline solution only after it has been vigorously stirred, so also something new can only develop after great upheavals.
|
| 109. Rosicrucian Esotericism: Evolutionary Stages of our Earth before the Lemurian Epoch
09 Jun 1909, Budapest Tr. Helen Fox Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| As far as is possible in terms of philosophical thinking, the Kant-Laplace theory is an entirely intelligible exposition of this first form of our earth. It speaks of a kind of archetypal nebula in which everything was dissolved and out of which the whole solar system came forth. |
| 109. Rosicrucian Esotericism: Evolutionary Stages of our Earth before the Lemurian Epoch
09 Jun 1909, Budapest Tr. Helen Fox Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The lecture yesterday brought our study of the evolution of our planet to the stage known as Old Moon. We heard that the first embodiment of our planet was that of Old Saturn, the second that of Old Sun and the third that of Old Moon. We came to the point in yesterday's lecture where it was made clear that if everything had progressed exactly as hitherto, man would not have been able to keep pace with the tempo of the cosmic evolution of other beings. Hence a kind of severance took place at a certain point during the Old Moon embodiment. The Sun, progressing as it was within the cosmic expanse, separated from the planetary body together with the finest substances and higher beings. The less progressed part of the planetary body, namely, Old Moon itself, still containing all that constitutes our present earth and present moon, remained as a kind of cloud-body. Certain conditions brought about a densification or hardening on Old Moon and the same happened to the beings inhabiting it. When the Sun had separated, its forces worked upon Old Moon from outside. The subsequent human-animal-plant kingdom that came into existence on Old Moon now received the forces of the Sun from outside. After the separation, the three kingdoms on Old Moon came into existence. As yet there was no mineral kingdom but what took shape, after the hardening process, as the lowest kingdom was a kind of mineral-plant kingdom—mineral substance that was plantlike in character, or, if you prefer, plant substance that was mineral in character. This formed the ground of Old Moon; it was a kind of semi-solid, semi-fluid foundation. On the earth today we walk about on a mineral ground, on Old Moon it was semi-solid, semi-fluid ground, a kind of plant-mineral soil. Think of a mass of spongy, plantlike substance on which human beings walked. This was the character of the lowest kingdom on Old Moon, a kingdom that was at the same time half-living. The ground of our earth today has become comparatively static; volcanic activity is the only reminder of a certain inner life. On Old Moon there were no such conditions. We may perhaps speak later on about what an occultist has to say on the subject of earthquakes and volcanic activity. Just as organs in a plant grow and subsequently die, so did this half-living substance on Old Moon. The Old Moon was like a great organism, living and mobile, on which the beings living might have felt like parasites of today. These Old Moon plants were composed of mineral substance, had life in them and were mobile; they were plant-mineral in character. Nothing would have been found resembling our rocks of today; instead, there were horny or woody formations. In the environment of Old Moon, like a kind of atmosphere, were a few cloud-masses composed of a half-watery, half-living substance in which the beings of the next kingdom, half animal, half plant in character, were embedded. If you were to crush a tree, causing something akin to the feeling experienced by an animal, that would be remotely comparable with what was experienced by this animal-plant kingdom, which could not exist as such on the earth today. As has often been said, not only are there pupils in school who make no progress but in the whole process of evolution there are always beings who remain at a standstill and who, together with the forms that belong to them and express what they are, become retarded. Thus, on the earth itself there were still certain moon beings who were not sufficiently advanced to keep abreast of evolution on the earth. These beings were obliged to create in their outer expressions the condition that had been essential to their life on Old Moon. As you know, plants on Old Moon were not rooted in mineral soil as they are today but in the half-living ground of the planet. Mistletoe, for example, is a descendant, a straggler, of an Old Moon form; it is obliged to take root in plant-soil. In folk myths there are many indications of this, for example, in the legend of Baldur and Loki. The latter is a being belonging to Old Moon, whereas Baldur is a being inwardly connected with earth and sun evolution. To interpret a legend or myth it is necessary to know in which sphere of occult investigation the connections can be discovered. External science could be so enriched by the fruits of clairvoyance that it would recognize in a legend much more than folk fantasy. Spiritual science must teach one to investigate with the whole soul instead of with the intellect only. There was still a third kingdom on Old Moon, between the animal and human kingdoms; it was the animal-human kingdom. The forms of those animal-men were quite different from what is pictured by materialistic science today. They were animal-men although certain important members of their constitution were not yet actually within them. While he is asleep today, man's physical and etheric bodies remain in the bed and his astral body is outside. Fundamentally speaking, during sleep he is therefore in the physical world with only the lesser half of his constitution. Man's physical and etheric bodies belong to an earlier, cosmic stage of consciousness. Clairvoyant vision reveals this condition to have been permanent on Old Moon. The astral body then was never entirely within the physical and etheric bodies but was nevertheless connected more fundamentally and definitely with the human being than is the case during sleep today. The head of the man of Old Moon was not self-enclosed as is the case today. A residue of what the organs in the head were at that time is the place at the top of a baby's head that stays soft and open for a long time. On Old Moon the head of the human being was still open. Were you to draw a line vertically downward from this soft area, you would meet the pineal gland. Today it is stunted and withered but it was an important organ during the Old Moon embodiment. It was a kind of sense organ that connected man's physical and etheric bodies with his astral body. Through this organ, which was a delicate, luminous body, man's astral body radiated into the other bodies. His consciousness was neither that of sleep nor of waking life. He did not perceive outer objects. His consciousness might be compared with that of the dream to-day. The pineal gland at that time was a kind of warmth organ, emitting powerful, luminous rays of warmth. When on Old Moon man was moving about, the function of this organ was to show him the direction he must take. Man's perception on Old Moon consisted in something like a dream picture rising up within him. There was as yet no seeing or perceiving objects but man felt an inner up-and-down surge of living pictures of which the dream pictures of today are only a feeble shadow. Everything a man set out to do on Old Moon, how he searched for his food and so forth, was always activated by these pictures that were connected with the outer world. He could allow himself to be directed and led by them. When he was looking for food he was guided by certain pictures that rose up before him, and he was warned of danger also by them. The astral body extended far beyond the physical and the etheric bodies; the form of the physical body alone could be called human. On Old Moon man's inner warmth was not yet constant. Today, on the earth, this has been achieved. On Old Moon man absorbed warmth from the warmth around him and emitted it again, just as he inhales and exhales air today. The process became visible in his organ of warmth. It gleamed and was luminous when he was absorbing warmth and darkened when he was exhaling it. If you could have seen what was happening, the process would have suggested the image of a fire-breathing dragon. All these happenings have a deep significance. Figures such as the Archangel Michael with the fire-breathing dragon under his feet, or St. George. fighting with the dragon, are pictures reminiscent of those conditions. The fire breather of Old Moon, the ancient Dragon, is a figure that once actually existed. It portrays a stage that would have to be surmounted. This is the explanation of such matters that is derived from occult knowledge. Later on, when spiritual science is more widely known, there will be a different view of truths that have been preserved in imagery and pictures of this kind. This animal-man form was quite different from that of man today because the astral body did not sink into the physical body as deeply as it did later on the earth. Man is the figure he is today because the astral body eventually sank right down into him. It could be said that what did not, during the Old Moon period of evolution, allow itself to descend into the depths of the physical world, now resolved to do so during the earth period. But if this process in the cosmos had taken place at an earlier time, man would have remained at a much lower evolutionary stage. During the period of earth evolution, he succeeded, with the help of the spirit, in acquiring for himself the noble, godlike form that is now his. If the possibility of developing this stature had already existed on Old Moon, the descent of the astral body would have taken place prematurely. The divine Guides have always chosen the right moment. The essential achievement of Old Moon evolution was that time was left for the evolution of the physical body, and on the earth man was to be permeated by the astral body after having evolved physically on Old Moon at a lower stage. Then again there took place a certain recession of the Moon into the Sun, which had previously separated; the Old Moon globe was again absorbed by the Sun and everything passed into a cosmic sleep, a pralaya. This began at the time when the Moon returned again into the Sun. Hence the evolution of Old Moon proceeded by the following stages: firstly, a kind of preparation; secondly, separation into Sun and Moon; thirdly, formation of three kingdoms on Old Moon; fourthly, return into the Sun; fifthly, ebb; sixthly, the cosmic sleep. The fourth metamorphosis of our earth, our own planet earth itself, then came forth from the cosmic sleep. This first configuration of the earth was, of course, quite different from its configuration today. When the earth emerged from the cosmic night, from the darkness of twilight, it was gigantic in size, for again sun and moon were contained within it; the separations took place later on. So enormous was the size of the earth that it reached as far as the Saturn of today. Differentiation in the solar system did not take place until a much later time. As far as is possible in terms of philosophical thinking, the Kant-Laplace theory is an entirely intelligible exposition of this first form of our earth. It speaks of a kind of archetypal nebula in which everything was dissolved and out of which the whole solar system came forth. Through the rotation of this nebula, rings took shape; they densified and then, still as the result of rotation, the planets were formed. In schools this process is often illustrated by means of an experiment. A globule of oil in liquid of equal density is made to rotate by a simple mechanical device. It can then be observed that this globule flattens, that drops separate from it and form themselves again into globules that circle round the central globule. In this way one can see in miniature a kind of planetary system coming into being through rotation. This has an immensely suggestive effect. Why should we not picture the process in this ways This experiment shows how a planetary system comes into existence through rotation; it is there before our very eyes. But one thing is forgotten. One of us, or the teacher, actually causes the rotation! Nothing is really explained by this external illustration. No cosmic system comes into existence out of nothingness. It does not arise of itself from the nebula, but it comes into existence because many spiritual beings have been working on it and at a certain point in their evolution have drawn out the finest substances from the chaotic root substance and cast out the coarser substances, namely, the moon. During the first period after pralaya, the earth, in which all the substances and beings were again united, recapitulated the Saturn condition. At the beginning of this phase of evolution the earth was not a globe of gas as has often been falsely assumed, but a globe of warmth. For it (the earth) was re-capitulating the condition of the Saturn embodiment and extended to the sphere of the present Saturn. At a certain stage the spiritual beings involved take their substances with them. Spirit is the foundation of everything, both when the Sun separates and during the evolution of Old Moon. No external factor was responsible here; it was an inner necessity for one section of the beings. The higher beings separate what they need from the chaotic substance. Everywhere it is the spirit that directs the external reality. When the earth first came into existence everything was contained in it; the spiritual beings indwelling it were at different stages of their evolution. We shall bear this in mind during the following studies. Thus after pralaya the earth first of all recapitulated the Saturn condition; it was a condition of warmth. Then this gigantic globe of warmth condensed to the gaseous state and only when a definite point had been reached was it possible for the globe to form the fluid element and recapitulate the Old Moon condition. At this point on the earth there was a repetition of what had previously happened on Old Moon: the sun separated from the earth and earth-plus-moon became one independent body, containing the substances and beings of earth and moon, as they are still present today. Thus for a time earth and moon, and sun were one united whole. The earth-plus-moon was ejected because man could no longer keep pace with the tempo of the sun. Had the sun remained in the earth man would have been old practically at birth. The beings of the cosmos are at entirely different stages of evolution. It will only be possible to indicate the most important features of this evolution during the fourth period, that of the earth. Even the more mature beings belonged to grades at every possible level. There were some who could neither profit by the rapid tempo of the sun nor by the slow tempo of the earth. These beings departed already before the separation, when sun, earth and moon were still united. They created special arenas for their activity and these were the domains suitable for their rulership. It was thus that the outer planets, Saturn, Jupiter and Mars, were formed. During the recapitulation of the Saturn embodiment, Uranus, Vulcan and Saturn separated from the earth. During the recapitulation of the sun embodiment, Jupiter and Mars separated. After the sun had left the earth, Mercury and Venus separated from it. After the separation of the sun, the earth cast out the moon. The dispersal of Old Moon was brought about by the forces of the progressed beings who drew out the solar body, while the normal and retarded beings produced the moon circling around it. In all the mysteries these happenings were called the strife in heaven. The detached planetoids are the ruins of that battlefield. It is here that the primal secret of the origin of evil must be sought. The planetary spirits involved could not have waited until the sun separated from the earth because they would not have found the right soil for their activity; evolution at this time was turning into different channels. The planetary conditions of space and movement are all the expression and effect of the activity of their beings; these conditions indicate the evolutionary rank of the spiritual beings inhabiting the planets. Beings who had believed that they, too, could accompany the sun because this had formerly been possible but who could not now do so, separated from the sun, but only after it had itself separated from the earth. These beings separated from the sun after this event and are at a far higher stage of evolution than men. Venus and Mercury are the two bodies that, having separated from the sun after the latter's separation from the earth, formed the inner planets of our solar system. After the severance from the sun a difficult, sombre period now began for the earth, in a certain respect its darkest, hardest era. While still united with the moon, the earth drew into itself all the forces that were retarding evolution. To obstruct life is characteristic of the forces principally active in the moon. During this period, these obstructive forces were working far too strongly in the earth. If the earth had remained connected with them, life would not have taken its course in the right tempo. Man would have hardened to the stage of mummification. The earth would have become a veritable cemetery, one vast graveyard containing statues of mummified human bodies. No procreation would have been possible. When the sun had left the earth, fearful desolation and hardening of all life took place. So already at that time there were periods when the human physical body was abandoned by its spiritual members, just as today the physical body is abandoned by its spiritual members at death. In that past era, withdrawal and emergence of the being of spirit and soul from the physical already took place and a new search for the physical body began, as happens today when incarnations are to take place. But more and more frequently it happened that when the being of soul and spirit desired, while the moon was still united with the earth, to find a human body again, none was to be found, because bodies were no longer fit to receive the being of spirit and soul. Just imagine that great masses of human beings were to have died today and because of the character of the physical substance these bodies had become so decadent that the souls would have said: We cannot make use of these bodies, they are too decadent for us, they offer no possibility of further evolution. Suppose that because of an extensive spread of alcoholism, for example, successive generations had gradually become so degenerate that the bodies were simply useless for the descending souls. This is more or less a picture of the state of the earth at that time, before the exit of the moon. Everything that should have been habitable down below was often hardened, crusted, withered, mummified. There was actually a period when souls were seeking in vain for bodies for their own evolution on earth. The consequence was that certain beings simply could not at that time have returned to the physical plane as men. They could not have incarnated again on the earth. These beings then went to other cosmic bodies that had separated from the sun, namely, to Venus, Jupiter, Saturn and Mars. There was a time when the majority of these beings who should normally have incarnated on the earth according to their nature and their stage of evolution, placed themselves under the protection of the beings of Mars, Jupiter, Venus or Saturn, having ascended to and populated these cosmic bodies. Only the strongest souls found it possible to cope with the stubborn bodies and keep them flexible. Please understand me well. It was only the best soul material that then came again to the earth, because its power to master the stubborn bodies was the greatest. But under such conditions evolution could not have progressed. The beings of the highest rank belonging to our solar system now adopted a new procedure. The most impermeable substances were extracted and separated from the earth; the severance of the moon was brought about. The result of this was that the forces that had remained behind were no longer frustrated in their evolution. But it was not until later that this moon became what it is today. The time had now come when the physical and etheric evolution of man could find the tempo befitting its stage. The forces both of the sun and the moon now worked upon the earth from outside, maintaining the balance. Gradually, while the moon was emerging, a kind of softening, an amelioration of the bodies of men, again took place. The period just described is called in occultism the Lemurian epoch, the epoch of the separation of the moon during the physical embodiment of the earth. The epoch when the sun left the earth is called the Hyperborean age, and the epoch when the sun, moon and earth were still united is called the Polarian age. During the whole period when the sun was separated from the earth and the moon produced a hardening process on the earth to begin with and then left the earth during the whole of that period, sublime beings were influencing the differentiation. Their most important servants were the Spirits of Form, called the Exusiai in Christian esotericism, also Spirits of Revelation, Powers. On Saturn it was the Thrones, the Spirits of Will who made the sacrifice of pouring out from their own substance the material for man's physical body. On Old Sun it was the Dominions or Spirits of Wisdom who provided the substance for the etheric body, and on Old Moon it was the Spirits of Movement or Mights who made possible the formation of the astral body. On the earth the Spirits of Form or Powers instill the ego, bringing it about that in this phase of evolution the ego enters gradually into what had come into existence, namely, man's physical body, etheric body and astral body. This is the work of the Spirits of Form. In order that an ego-man could come into existence at all as the expression of ego consciousness, and that this coordination of the physical, etheric and astral bodies could take place, everything that has now been described was essential. The separation of sun and moon from the earth was necessary; it was also necessary for man to undergo a process of hardening followed by a certain softening. This could take place because the wise beings who guided and directed these happenings undertook it all as probationary measures for the good of evolution. A great deal in the evolutionary process of the earth is still done today by the sublime beings concerned, as probationary measures. What, then, is the anthroposophical movement? It came into the world because the lofty beings we call the Masters, who live in human physical bodies but have reached the far higher stage of evolution than the average man of today, poured out a certain amount of wisdom from the last third of the nineteenth century onwards. The living influx of this wisdom from higher realms into our culture is the actual basis of our anthroposophical movement. Do not imagine that there was no possibility of the attempted influx of wisdom falling upon deaf ears in humanity. Even if there had been deaf ears, the Masters would have said that an attempt must be made later on, when human beings would be ready to receive the wisdom. In occultism this is known as the test of maturity in men. The fact that wisdom pours into humanity from higher beings such as these is not in itself sufficient; what matters is how it is received; the success of the test depends upon that. Such tests have already been made several times but have not always succeeded. It was often within narrow limits that humanity proved to be ripe for the tests; receptive souls and hearts were not always to be found. When the ego of humanity was to be instilled, the test consisted in gradual attempts to permate what had formerly been astral body only, with the ego. Then it turned out that the astral body, permeated by the ego, was incapable of penetrating the physical body. Adjustment was therefore necessary and this was made possible by the separation of the moon. It was in the middle of the Lemurian epoch that the entry of the ego, the Christ principle, was first achieved. But the following was connected with this. During and after the separation of the moon, the earth was depopulated. We have heard that the bodies had become so contaminated that they could no longer provide habitations for the souls. Cosmic happenings such as these have been preserved in legend and saga, but occult investigation reveals their true origin and teaches us that while the separation of the moon was taking place, when the earth was depopulated, many souls were searching for suitable embodiment in cosmic space; they departed from the earth and assumed bodies on other planets. But when the moon had finally left, it became apparent that the earth was capable again of providing suitable bodies. Now, the souls, who during the latest Lemurian epoch and thereafter in the Atlantean period had gone to the planets, presented them-selves again on the earth and incarnated in the bodies there. Groups of human beings now formed on the earth. Some provided bodies for souls coming from Jupiter incarnations, or from Mars, Venus or Saturn. These souls now found bodies that were appropriate for them. This grouping of souls gave rise to the birth of races. Hence there is a certain connection between the races and cosmic bodies and thus it was possible to speak of Saturn men, Jupiter men and so on. What can be called the concept of race had now, for the first time, its justification. On Old Moon, and also on the earth while it was still united with the moon, there were human beings at different stages of evolution. This can be perceived right on into the Lemurian epoch, when owing to the exodus of the moon, differentiation took place in humanity. Thereafter the concept of race arose and from then on began to have a certain meaning, a certain significance. Race is something that comes into being and subsequently passes away again. The epoch of the formation of the races is that embraced by Lemuria and Atlantis. Today only stragglers of the races are present. |
| 201. Man: Hieroglyph of the Universe: Lecture XII
08 May 1920, Dornach Tr. George Adams, Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Spiritual Science must endeavour to bring natural scientific study and Christology into harmony; for where has Christology any place if the Kant-Laplace theory holds sway and we look back to a primeval mist out of which everything has been formed? |
| 201. Man: Hieroglyph of the Universe: Lecture XII
08 May 1920, Dornach Tr. George Adams, Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
You will remember that I have discussed in detail how much criticism has come from many sides of the idea of a connection between the Christ Event, the appearance of Christ on Earth, and Cosmic events such as the course of the Sun, or the relation of the Sun to the Earth. The connection can only be understood when one studies more deeply all that we have hitherto said as to the movements of the stellar system. Let us make a beginning in this direction today, for you will see that ultimately astronomy cannot really be studied at all without entering into a study of the whole being of Man. I have already mentioned this, but we shall see how deeply grounded is the statement in the whole being of the world, for we can only understand something of the nature of the world or of the nature of Man when we consider the two together, not separately, as is done at present. You will observe a curious fact in relation to this very matter, namely, that materialism, if only it is not directly acknowledged to be such, is preferred by the religious denominations to Spiritual Science. That is, both Protestants and Roman Catholics prefer to consider the outer world in its various realms in a materialistic sense, rather than to enquire how the Spiritual works in the world and presents itself in material phenomena. In confirmation of this you need only consider the Jesuits' views of Natural Science. These are strictly materialistic; from their point of view the outer world, the Cosmos, is only to be understood in the light of quite materialistic interpretations. The utmost care has been taken to protect in this way a certain form of faith, which has been cultivated since the Council held in Constantinople in 869—to protect it by keeping external science on the level of materialism. Of course in the widest circles, illusions have arisen through the apparent conflict with materialism even in scientific realms. This however is only apparent, for it does not matter whether one says that there is spirit somewhere, or whether one denies spirit altogether, if the material world itself is not explained spiritually. You know perhaps that the acme of modern interpretation of external nature is Astro-physics, the theory that sets out to study the material starry world, to establish the material unity of the world accessible to the senses. Now one of the greatest Astro-physicists is a Roman Jesuit, Father Secchi. There is no difficulty in standing on the ground of modern material science and at the same time adhering to this shadow of religious belief. This means that as a matter of fact, a materialistic interpretation of the heavens stands nearer today to the religious creeds, and especially to one of the Jesuit persuasion, than does Spiritual Science, for this particular creed is especially concerned not to explain the world by showing the relation of the material to the spiritual. The spiritual must form the content of an independent form of belief in which nothing is said of the scientific study of the Universe; the latter is to remain materialistic, for the moment it ceases to be so it would have to go into what relates to the spiritual—it would have to speak of spirit. What has just been said must be taken seriously, otherwise we should overlook the significant fact that the Jesuit scientists are the most extreme materialists in the domain of Natural Science. They continually allege that Man cannot approach the spiritual by research into Nature, and they take trouble to keep the spiritual as far removed as possible from such research. This can be traced even in Father Wasmann's studies of ants. After these preliminary remarks, let us recall an important fact which apparently takes its course entirely in the spiritual world, but which, when we consider this part of our argument more closely, will make clear to us a parallel phenomenon between spiritual life and the life of the external starry world. As you know, we divide the post-Atlantean time into epochs of civilisation, naming the first the old Indian, the second the old Persian, the third the Chaldean-Babylonian-Egyptian, the fourth the Graeco-Latin; and then there is the fifth, in which we now live, beginning in the middle of the fifteenth century. A sixth will follow this, and so forth. I have frequently shown how the fourth epoch began in the continuous stream of the post-Atlantean time, about the year 747 BC., and ceased—speaking roughly, I always say about the middle of the fifteenth century, but to speak more accurately, it really ended in the year AD. 1413. That was the fourth; and we are now in the fifth. If we thus consider the succession of civilisations, we can describe their characteristics, bearing in mind the descriptions given in Occult Science. Thus we can describe the Graeco-Latin, in which the Event of Golgotha occurred, but in doing so we need not refer to that Event, for we can describe the epoch by connecting it with the preceding one. It is possible to describe the successive epochs in their fundamental nature, and to have an epoch from 747 BC. to AD. 1413 so running its course that nothing in history shows that during this time an important event occurs. Let us recall the time of the occurrence of the Event of Golgotha, remembering all we know concerning the civilisations of the most advanced people of the time—the Greek, the Roman and the Latin. Let us reflect that to these people the Event of Golgotha was an unknown affair. It occurred in a small corner of the world, and the first mention of its effects is to be found in Tacitus, the Roman historian, one hundred years later. It was not observed by its contemporaries, least of all by the most cultured. Thus the fact comes into evidence in the historical stream of evolution that there was no necessity inherent in the regular progress of the evolution of mankind from the first three epochs of civilisation to the fourth, that the Event of Golgotha should take place. This fact should receive close attention. The Event actually took place 747 years after the beginning of the fourth post-Atlantean period. In trying to understand the Event of Golgotha, we may say that it gave purpose and meaning to the life of the Earth, that the Earth would not have had this meaning if evolution had simply gone on as the outcome of the first, second and third post-Atlantean epochs. The Event of Golgotha came as an intervention from other worlds. This fact is not sufficiently considered. In modern times several historians have alluded to it, but they have not been able to make anything of it. In fact, history practically omits the Event of Golgotha. At most the historians describe the influence of Christianity in the successive post-Christian centuries, but the actual intervention of the Mystery of Golgotha itself is not described in an ordinary course of history. It would indeed be difficult to describe it, if one kept to the ordinary methods of history. Certainly remarkable men—oddly enough, clergy among them—have attempted to explain the causes of the Event of Golgotha. Pastor Kalthoff, for instance, and many others. Pastor Kalthoff tried to explain Christianity from the consciousness and the economic conditions of the last centuries preceding the appearance of Christ. But what did this explanation amount to? In effect it said: People lived in certain economic conditions, and eventually the idea of Christ arose, the dream of Christ, as it were, the ideology of Christ; and from these arose Christology. It arose in humanity only as an idea. People like Paul, and a few others, described what had thus arisen as an idea as though it had occurred as a fact in a remote corner of the world!—Such explanations mean a doing-away with Christianity. It is a noteworthy phenomenon of the nineteenth and beginning of the twentieth centuries that Christian pastors should set themselves the task of saving Christianity, by eliminating Christ. People were ashamed to admit the facts of the rise of Christianity outright. They found it more satisfactory to explain the rise of Christology, to explain it simply as an idea. Various streams of thought found their way into this domain, and one special province of science has become remarkable in this connection, arising in the materialistic stream of culture which reached its culminating point in Marxism. Thus Kalthoff is a kind of Marxist Pastor who tries to explain Christology out of a sort of pious Marxism. Others have ridden other hobby horses in seeking an explanation for the phenomenon of Christianity; why then should not each explain Christianity or explain Christ Jesus, according to his own fancy? A psychiatrist explains Christ according to psychiatry, simply by saying that the way in which Christ appeared in His time can be explained today from the standpoint of psychiatry as due to an abnormal consciousness. This is no isolated case. And these are phenomena which must not be disregarded, otherwise we do not see what is happening at the present time, for they are signs of present day life as a whole. We must clearly recognise that which has given the Earth a meaning, was an intervention from another world. We must distinguish two streams in human evolution, which indeed run side by side today, but only met for the first time at the beginning of our era. One is the Christian stream, which was added to the continuous current from olden times. Natural Science, for instance, has not yet accepted the Event of Golgotha and flows on in the continuous stream as though that Event had never occurred. Spiritual Science must endeavour to bring natural scientific study and Christology into harmony; for where has Christology any place if the Kant-Laplace theory holds sway and we look back to a primeval mist out of which everything has been formed? Would Christianity ultimately have any real world-significance for Man on Earth if the stars were regarded as they are by Father Secchi? For the starry heavens are regarded by him materialistically, not as though an Event of Golgotha had been born from out of them. And that becomes the chief ground for leaving it to other powers to say how Man should think of the Event of Golgotha. If Man can develop nothing from Cosmic knowledge concerning the Event, some other source must be found to tell him what he ought to think of it, and it is obvious that Rome is that source. All these things are so consistently—in a sense, so grandly—thought out, that it is inexcusable to be under any illusions about them at the present difficult and fateful time. These 747 years fall in the world's evolution as a period which speaks with the utmost significance. It tells us of all that is connected with the old evolution, all that recalls, and is related to the past periods of time. The new beginning commenced at the end of this epoch, 747 years after, let us say, the founding of Rome—which was really 747, not the point of time given in the ordinary history books. Here we have a fresh start, and if we now go back and take the periods of time, we shall have to say that everywhere we must add fresh turning-points of time to those already rightly assigned. An entirely new division of the course of time was brought about by the Event of Golgotha's falling in this period, inserted into human evolution from outside, as it were. We must clearly realise the existence of these two streams in world evolution in so far as Man is involved in it. If we hold fast to this we can now see something more. We know that according to the view of ordinary astronomy, the Moon moves round the Earth. (In reality she does not do this as generally as described; she too describes a lemniscate; but for the moment we will disregard this.) The Moon moves round the Earth. While so doing she also revolves around herself. I have already explained this. She is a polite lady and always turns the same side to us, her back is always turned away from the Earth. Not however quite exactly; we can only say that virtually, speaking generally, she always turns the same side to the Earth. A seventh part of the Moon indeed goes round the edge, as it were, so that really it is not quite always the front of the Moon that is turned towards us, for after a time a seventh part comes forward from the back, and another seventh part retires. This is compensated by the further movements; the whole seventh does not quite go over, it returns; and the Moon reels, as she goes round the Earth—she actually reels. I will only mention this here; in any elementary astronomy book you can look up further details. Could we transport ourselves to a far-distant spot in Cosmic space, which according to the calculations of astronomy would be only a far-distant star, this rotation of the Moon on its own axis would from there take somewhat more than 27 days. If however, we transport ourselves to the Sun, we see that the movements of the Sun and Moon are not uniform, they move with dissimilar velocities; this rotation of the Moon seen from the Sun is not the same as seen from a distant star, but takes rather more than 29 days. Thus we may say that the stellar day of the Moon is 27 days, and its solar day 29 days. This of course is connected with all the intervolving which takes place in the Universe. As we know, the Sun rises at a different vernal point every Spring, moving round the whole ecliptic, round the whole Zodiac in 25,920 years. These reciprocal movements bring it about that the stellar day of the Moon is considerably shorter than its solar day. Bearing this in mind we may say: Here too is something remarkable. Every time we make an observation we notice a difference from one full Moon to another in the mutual aspects of Sun and Moon, a difference of almost 2 days. That shows us that we have to do with two movements in Cosmic space, which indeed go together but do not point back to the same origin. What I have set forth here from a Cosmic point of view, can be compared with what I have set forth previously from an ethical-spiritual point of view. There is an interval between the beginnings of the individual epochs of civilisation in the one stream and the beginnings of those connected with the Christ Event. It is always necessary when it is full Moon, as regards sidereal time, to wait for the accomplishment of the solar time. That lasts longer. There is again an interval. Thus in the Cosmos we have two currents, two movements, one in which the Sun takes part, and another, the Moon; and they are of such nature that we may say: If we start from the Moon-stream, we find the Sun-stream intervening in it, just as the Christ-Event intervenes in the continuous stream of evolution, as though coming from a foreign world. To the Moon-world the Sun-world is a foreign world, from a certain point of view. Now let us consider this subject from yet a third standpoint. This we can do by trying to remember exactly how the human memory works, especially when we include the reminiscence of dreams. We find, for instance, that what has taken place quite recently, although it does not enter the inner movements and course of the dream, plays into its picture world. Do not misunderstand me. We can of course dream of something that happened to us many years ago, but we do not do so unless something has recently occurred which is related by some thought or feeling to the earlier years. The whole nature of dreams is in some way connected with quite recent occurrences. If one wishes to observe such matters, it must be assumed that one is a person who notices the fine details of human life; if such be the case, observation will furnish as exact results as any exact science. To what is this due? It is due to the fact that a certain time is required in order that what we experience in our soul may be imprinted by the astral body upon the etheric. Approximately from two and a half to three days, though sometimes after only one and a half or two days, but never without having slept upon it, what we have experienced in our intercourse with the world is imprinted by the astral upon the etheric body. It always takes a certain time to be established there. Now compare this fact with another—viz. the fact that in everyday life we alternately separate physical body and etheric body from the astral body and Ego in sleep, and in waking unite them. We may therefore say that altogether between birth and death there is a rather looser connection between the physical and etheric bodies on the one hand and the Ego and astral body on the other. For the physical and etheric bodies remain always together between birth and death, and the astral body and Ego keep together also, but not the astral and etheric bodies; every night they separate. There is thus a looser connection between the astral and etheric bodies than between the etheric and physical; and this is again expressed in the fact that there must in a sense be a certain parting-asunder of the astral and etheric bodies before what we have experienced in the astral body is imprinted upon the etheric body. When some event influences us, it does so of course in the waking condition. This means it works upon the physical, etheric and astral bodies and the Ego. There is however, a difference in their reception of its working. The astral body takes it up at once. The etheric needs a certain time for the impression to be so established that there should be complete harmony between the astral and etheric. Does not this clearly and distinctly show that although we confront an event with all four principles of the human being, there are two currents which do not run the same course in their connection with the outer world, one stream needing longer than the other? There we have the same as we have in history, the same too as we have in the Cosmos—Moon and Sun, Heathendom and Christendom; and now, etheric and astral. Always a differentiation in time. Thus we find this interaction of two streams appearing in our ordinary life, two streams which come together and give a common resultant for life, but yet cannot be grasped so simply as to permit of the causes and effects of the one stream coinciding with the causes and effects of the other. These things are of the highest importance for the consideration of the Universe and of life, and cannot be dispensed with if one wishes to understand the Universe. There are other facts too which are also entirely overlooked. And what do all these things betoken? They indicate the existence of a certain harmony between cosmic life, historical life and the life of individual men; but a harmony not constructed as is usual today where there is a desire to account for everything by a fundamental law of bio-genesis. The consequence is that we cannot have a single Astronomy but need different Astronomies, one of the Sun, another of the Moon. If we have two clocks, one always a little slower than the other, then the latter will always be in advance; but we should never be able to assume that what happens on the one has its cause on the other. That would be impossible. So too, although there is a certain conformity to law in the one being always the same amount behind the other, the two streams of which we have been speaking have nothing to do with one another; they only work together as I look at them together. Solar astronomy has nothing to do with lunar astronomy. The two only work conjointly in our Universe. It is important to bear this in mind, and just as we have to distinguish between the solar and lunar astronomy as regards the regulation of the movements of the Sun and Moon, so too must we distinguish in history between what takes place in us by reason of the movement in the periods of civilisation, and what takes place in us through our being in the cycle of time whose central point is the Event of Golgotha. These two things work together in the world, but if we wish to grasp them, we must discriminate between them. We see the prototype of the historical in the cosmic, and we see the ultimate expression—I do not say the effect—but the last expression of these universal facts in our own life in the two or three days which must elapse before our thoughts have become so far firm that they are no longer above in the astral body where they may appear as dreams, as it were, of themselves, but are below in the etheric body and must be brought up by our own active memory or by something that recalls them. Thus within us one movement flows into the other. Just as we have to realise that there is a lunar current that, as it were, generates independent systems or structures of movement, so we must realise that we in our human being are closely connected as regards our physical and etheric bodies with something beyond the human, while on the other hand, in our astral body and Ego we are closely related to something else beyond the human. Concerning these things a veil of darkness is spread by modern observation, which confuses everything, and assumes a cosmic mist which forms into a ball from which the Sun, Moon, Planets emerge. This is not the case, the Sun and Moon are not from the same origin but are two streams running side by side; and just as little can Man's human Ego and astral body be traced to the same origin as his physical and etheric bodies. They are two different streams. In the book Occult Science it will be seen that these two streams must be traced back to the Sun period. Then to be sure, on going back from the Sun to Saturn, one comes to a sort of unity. This however, lies very far back indeed; from the Sun onwards, there is continually the tendency for two streams to run side by side. In this description I have wished to show how necessary it is to throw light on the parallel between cosmic existence, historical existence and human existence, in order to arrive at a judgement of how Man has to relate to the cosmic movements. We have seen that if he places himself rightly, the result is not one astronomy, but two; a solar and a lunar astronomy. So too we have a human development of a heathen nature—natural science is still heathen—and a human development of a Christian nature. In our day many have the tendency to prevent these two streams, which have met on Earth in order to work together, from coming together. Consider for instance, how the whole purport of a book such as that of Traub [*Rudolf Steiner als Philosoph und Theosoph, by Friedrich Traub, Tubingen, 1919.]—the rest of the book has no meaning without this—consists in the assertion: ‘Yes, Dr. Steiner wishes to unite the two streams, heathen and Christian. We will not let that happen. We want natural science to remain heathen, so that there may be no necessity to bring about anything in Christendom which may reconcile it with natural science.’ of course, if Natural Science is allowed to be heathen, Christianity cannot unite with it. Then it can be said: ‘Natural Science is carried on externally, materialistically; Christendom is founded on faith. The two must not be reconciled.’ Christ however, truly did not appear on Earth in order that side by side with his Impulses the heathen impulse should increase in power; He came to permeate the heathen impulse. The task of the present time is to unite what man would keep asunder—Knowledge and Faith—and this must come to pass. Therefore attention must be drawn to such things, as I have done in one of my recent public lectures. On the one side the Church has reached the conclusion that Cosmology is not to be admitted into Christology, and on the other hand a Cosmology is reached by the principle of the indestructibility of matter and force. [*The word “force” on this page is generally rendered “Energy” in English scientific writing (Indestructibility of Matter and Energy).] But if matter and force are regarded as indestructible and eternal, it leads to the treading under foot of all ideals. And then Christianity too is meaningless. Only when what constitutes matter and its laws is regarded as a transitory phenomenon, and when the Christ-Impulse becomes a seed of what will exist when matter and force no longer rule as they do now according to law but have died away, then alone will Christianity, and then alone will ethical ideals and human worth, have a true meaning. There are two great antitheses: The one arising from the final logical conclusion of heathenism—‘Matter and Force are immortal’, and the other arising from Christianity—‘Heaven and Earth shall pass away, but My words shall not pass away.’ These are the two greatest contrasts which can be expressed in a concept of the world, and our age has indeed every need not to be confused about such things, but with a mind-awake, earnestly to look at what must be attained as a right concept of the world, in which moral human value and the Christian Impulse in the evolution of the world are not lost sight of in the illusion of indestructible matter and indestructible force. More of this in the next lecture. |
| 191. Cosmogony, Freedom, Altruism: A Different Way of Thinking is Needed to Rescue European Civilization
11 Oct 1919, Dornach Tr. Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| And then, as the climax of all that was cold and dreary, came the Konigsberg-Kant-school with its Critique of Pure Reason alongside its Critique of Applied Reason—Ethics alongside Science,—making a most terrible gulf between what in man's nature must be felt and lived as a single whole. |
| 191. Cosmogony, Freedom, Altruism: A Different Way of Thinking is Needed to Rescue European Civilization
11 Oct 1919, Dornach Tr. Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The hour is so late, that I shall make this lecture a short one, and leave over till tomorrow the main substance of what I have to say in these three lectures. To-morrow the Eurhythmies are put earlier, so that it will be possible to have a longer lecture. I pointed out yesterday that in order to master the conditions of our present declining civilisation, one needs to differentiate,—so to differentiate between the various groups of peoples massed together over the face of the earth, that one's attention is actually directed to what is living and working in each of the separate groups, in particular among the Anglo-American peoples, among the peoples of what is properly Europe, and among the peoples of the East. And we have seen that the aptitude for founding a cosmogony suited to the new age is to be found pre-eminently among the Anglo- American peoples,—the faculty for developing the idea of freedom, amongst the peoples of Europe, whilst that for developing the impulse of altruism, the religious impulse with all that it connotes by way of human brotherhood, is to be found amongst the population of the East. There is no other way in which a new civilisation can be founded than by making it possible hereafter for man, all the world over, to work together in real co-operation. But, my dear friends, in order that this may be possible, in order that any such real co-operation may be possible, several things are necessary. It Is necessary to recognise, dispassionately and as a matter of fact, how much our present civilisation lacks, and how strong the forces of decline in this present civilisation are. When one considers the forces present in our civilisation, one cannot say: “It is altogether bad;” that is not the way to look at it; in the first place, it would be an unhistoric point of view; in the second place, it could lead to nothing positive. The impulses that reside in our civilisation were, in some age, and in some place, justified. But everything that in the historic course of mankind's evolution leads to ruin, leads to ruin for the very reason that something which has a rightful title in one age and one place has been passed on to another age and another place, and because men, from various Ahrimanic and Luciferic motives, cling to whatever they have grown accustomed to, and are not ready to join in with that actual forward movement which the whole cosmic order requires. Our age prides itself on being a scientific one. And, at bottom, it is from this, its scientific character, that the great social errors and perversions of the age proceed. That is why it is so imperative that the light should shine in upon our whole life of thought and action, inasmuch as the activities of modern times are entirely dependent on the modern system of thought. We noticed yesterday, in the general survey into which we were led, how the collective civilisation of the earth was made up of a scientific civilisation, a political civilisation tending towards freedom, and of an altruistic economic civilisation that really is derived from the altruistic religious element. People nowadays,—as I said before, yesterday,—when they consider the forces actually at work in our social structure, remain on the surface of things; they are not willing to penetrate deeper. The lectures in our class-rooms teach what professes to pass for economic wisdom, drawn from the natural science methods of the present day; but what lives in men, and what stirs the minds and the being of men,—that is regarded as a sort of unappetising stew. No attention is paid to what are really its true features. Let us turn first to the civilisation of Europe. What is the pre-eminent trait of this European civilisation? If one follows up this trait of European civilisation, one finds that one has to go a long way back in order to understand it. One has to form a clear idea of how, out of the ancient primal impulses of the original Celtic population, which still really lies at the base of our European life and being, there gradually grew up, by admixture with the various later strata of peoples, our present European population, with all its religious, political, economic and scientific tendencies. In Europe, in contradistinction to America on the West and Asia on the East,—in Europe a certain intellectual strain was always predominant. Romanism—all that I Indicated yesterday as the specifically Roman element—could never have so got the upper hand, unless intellectualism had been a radical feature of European civilisation. Now there are two things peculiar to intellectualism. In the first place, it never can rouse Itself to make a clean sweep of the religious impulses within it. Religious impulses always acquire an abstract character under the influence of intellectualism. Nor can intellectualism ever really find the energy for grappling with questions of practical economics. The experiments now being carried out in Russia will hereafter show how incapable European intellectualism is of introducing order into the world of economics, of industry. What Leninism is shaping is nothing hut unadulterated intellectualism. It is all reasoned out; an order of society built up by thought alone. And they are attempting the experiment of propping up this brain spun communal system upon the actual conditions prevailing amongst men. Time will show—and very terribly—how impossible it is to prop up a piece of intellectual reasoning upon a human social edifice. But these things are what people to-day refuse as yet to recognise in all their full force. There is unquestionably among the population of Europe this alarming trait, this sleepiness, this inability to throw the whole man into the stream so needed to permeate the social life of Europe. But the thing that above all others must be recognised is the source from which our European civilisation is fed,—whence this European civilisation is, at bottom, derived. Of itself, of its own proper nature, European civilisation has only produced a form of culture that is intellectual, a thought-culture. Prosaicness and aridity of thought dominate our science and our social institutions. For many, many years, we have suffered from this intellectualism in the parliaments of Europe. If people could but feel how the parliaments of Europe have been pervaded by the intellectualist, utilitarian attitude, by this element that can never soar above the ground, that lacks the energy for any religious impulse, that lacks the energy for any sort of economic impulse! As for our religious life, just think how we came by it. The whole history of the introduction and spread of this religious life in Europe goes to show that Europe, within herself, had no religious impulses. Just think, how flat and dull the world was, how interminably flat and dull—prosaic to the excess at the time of the expansion of the Roman Empire. Yet that was only the beginning of it. Just conceive what Europe would have become if Roman civilisation in all its flat prosaicness had gone on without the impulse that came over from the Asiatic East, and which was religious, Christian,—what it would have been without the Christian impulse, which sprang from the p lap of the East, which could only spring from the lap of the East, never from that of Europe. The religious impulse was taken over as a wave of culture, of civilisation, from the East. The first and the only thing Europe did was to cram this religious impulse, that came over from the East, with the concepts of Roman law, thread this Eastern impulse through and through with bald, abstract, intellectualist, legal forms. But this religious impulse from the East was, at bottom, alien to the life of Europe, and remained alien to it. It never completely amalgamated with the being of Europe. And Protestantism acted in a most remarkable way as what I might call a test-tube, in which they separated out. It is «just like watching two substances separating out from one another in a test-tube, to watch how European civilisation reacted with respect to its religious element. In the seventh, in the sixth, seventh, eighth, ninth, tenth centuries a kind of experiment was being made to combine religious feeling and sentiment with scientific and economic thought into one homogeneous substance; and then, actually, just as two substances react in a test-tube and separate out, so these two separated out,—the cold intellectualist thought and the religious impulse fell apart and deposited Protestantism, Lutheranism. Science on the one side, one truth; on the other side the rival truth, Faith. And the two shall mix no further. If anyone tries to saturate the substance of Faith with the substance of Thought, or to warm the substance of Thought with the substance of Faith, the experiment is regarded as downright sacrilege. And then, as the climax of all that was cold and dreary, came the Konigsberg-Kant-school with its Critique of Pure Reason alongside its Critique of Applied Reason—Ethics alongside Science,—making a most terrible gulf between what in man's nature must be felt and lived as a single whole. These are the conditions under which European civilisation still exists. And these are the conditions under which European civilisation will be brought ever nearer and nearer to its downfall. It was as an alien element from the East that Europe adopted the religious impulse, and it has never combined organically with the rest of her spiritual and physical life. So much with regard to the spiritual life of Europe. You see, my dear friends, the progress of modern civilisation has had Its praises sung long enough. They have gone on singing its praises until millions of human beings in this civilised world have been done to death, and three times as many maimed for life. It has been blessed in unctuous phrases from the pulpits of the churches, till untold blood has been shed. Every lecturer's desk has sounded the praises of this progress, until this progress has ended in its own annihilation. There can be no cure before we look these things straight in the face. And to-day, people of the Lenin type and others come and beat their brains over socialist systems and economic systems, and fancy that with these concepts which have long since proved inadequate to direct European civilisation, they can now, without any new concepts, without any revolution of thought, effect a reform in our economic system, in our system of society. I think I have here, once before, spoken of the beautiful concepts that our learned professors arrive at when they are dealing with these subjects. But it is so beautiful that I must really come back to it once more. There is a well-known political economist called Brentano, Lujo Brentano. Not long ago an article appeared by him, entitled: “The Business Director (Der Unternehmer).” In it Brentano tries to construct the concept of the Business Director the Capitalist Director. He enumerates the various distinctive marks of the capitalist director. The third of these distinctive marks, as given by Lujo Brentano, is this: That he expends the means of production at his private venture, at his own risk, in the service of mankind. Mark of the capitalist director! Then that excellent Brentano goes on to examine the function of the Worker, of the ordinary Labourer, in social life; and now, see what he says: That the labour-power, the physical labour-power of the labourer is the labourer's means of production; he expends it at his own venture and risk in the service of the community. Therefore, the labourer is a Business Director (Untemahmer); there is absolutely no difference between a labourer and a business director; they are both one and the same thing! You see, what they nowadays call scientific thought has by now got into such a muddle that when people are constructing concepts, they are no longer able to distinguish between two opposite poles. It is not quite so obvious here, perhaps, as in another case of a Professor of Philosophy at Berne, one of whose specialities was that he wrote such an awful lot of books, and had to write them so awfully fast, that he had not time to consider exactly what it was he was writing. However, he lectured on philosophy at the Berne University. And in one of the books by this Professor of Philosophy at Berne, this statement occurs:—A civilisation can only he evolved in the temperate zone; for at the North Pole it cannot be evolved, there it would be frozen up; nor could it be evolved at the South Pole, for there the opposite would occur, it would be burnt up! That is actually the fact. A regular Professor of Philosophy did once write in a book that it is cold at the North Pole and hot at the South Pole, because he was writing so fast that he had no time to consider what he was writing. Well, that excellent Brentano's blunders in political economy are not quite so readily perceived; but at bottom they proceed from just the same surface view of things, from which so much in Europe has proceeded. People take for granted what already exists, and starting from this, proceed to build up their whole system of concepts just on what exists already. That is what they learn from natural science, from the natural science methods. This is how the science institutes do it; and in our day,—the age when people set no store by authority and take nothing on faith, (of course not!)—that is what they obediently copy. For nowadays, if a man is an Authority, that is sufficient reason for what he says being true,—not a reason for turning to his truth because one sees it to be true, but because he is an Authority. And people regard economic facts, too, in this way. They regard economic facts as being all exactly on a par with one another. Whereas, as a matter of fact, they are made up of mixed elements, each of which requires individual consideration. That is a thing that one would so like to tell the people of the present day; for people of the present day suffer under a poverty of concepts that has grown positively alarming. This poverty of concepts is really such that anyone who has got any feeling for ideas finds to-day that quite a small number of ideas dominate our spiritual life, and they meet him at every turn. If anyone is hunting for ideas, this is what he finds; he takes up a work on Physics; it contains a certain limited number of ideas. Next, he studies, say, a work on Geology; there he finds fresh facts, but precisely the same ideas. Then he studies a biological work; there he finds fresh facts, but the same ideas. He reads a book on Psychology, dealing with the life of the soul. There he finds more facts, which really only consist of words, for they only know the soul really as a collection of words. When they talk of the will, there is a word there; but of the actual will itself they know nothing. When they talk of Thought they know nothing of real thinking; for people still only think in words. Nor do they know anything of feeling. The whole field of Psychology is to-day just a game of words, in which words are shaken up together in every conceivable kind of way. Just as the bits in a kaleidoscope combine into all sorts of different patterns, so it is with our concepts. They are jumbled up together into various sciences; but the total number of ideas is quite a small one, and keeps meeting one again and again. These ideas are forcibly fitted on to the facts. And people have no desire to find the concepts that fit the facts, to examine into the ideas that fit the facts. People simply do not notice things. In a certain town in Central Europe, not long ago, there was a conference of Radical Socialists. These Radical Socialists were engaged in planning out a form of society suitable for adoption in Europe. The form of society as there planned by them was almost identical with what you can read in a collection of articles that appeared in the “Basler Vorwärts” of this week,—a series of articles in the Basel “Vorwärts,” putting forward in outline a scheme of society almost identical with what was thought out some time back in a Mid-European town. And what is the special feature of this scheme of society as planned out there? People think it very clever, of course. They think that it cannot be improved on. But it is what it is, solely for the reason that it was drawn up by men who, as a matter of fact, had never really had anything to do with industrial and economic life, who had never acquired any practical acquaintance with the real sources and mainsprings of industrial and economic life. It was a scheme invented by men who have taken an active part in the political life of recent years. Well, you know what taking an active part in the political life of recent years means,—one was either elector or elected; one was elected either -in the first ballot, or in the second ballot. Say that one did not succeed in getting elected in the first ballot. Well, one had raised those huge sums of money, of course, subscriptions had been collected, and the huge sum raised, in order that one might have enough voters to get elected. The money was all spent; one had vented a terrible lot of abuse on the rival candidate the fellow was a fool, a knave and a cheat, If nothing worse. And came the second ballot. So far, no one had got an absolute majority, and now it was a question of electing one of those who had had proportional majorities. Now there was a change in the proceedings. Now, one-third of the election money was returned by one's opponent,—the same who was a fool, knave, cheat, etc. One accepted the returned money, and all of a sudden one's speeches took a different tone; there is nothing for it, one said, but to elect the man (the man who before was a knave, fool, cheat, etc),—he will have to be elected. After all, one had got back a third of the election money, and, inspired by this return of a third of the election money, one was gradually converted into his active supporter. For, after all, one of the two must be elected; the other man had no chance; all that could be done was to save a third of the election expenses. So they had taken an active part in political life. So, too, no doubt, they had had a voice in the political administrations, but they had no notion, not the remotest, vaguest notion, of industrial and economic life. They simply took the political ideas they had acquired,—ideas that had, of course, become much corrupted, but still they were political ideas of a sort,—and they tried now •; to fit them on to industrial and economic life. And accordingly, if these ideas were put into effect, one would get an industrial and economic life organised on purely political lines. Industrial economic organisation has already become confounded with political organisation,—so impossible has it become for people to keep apart things that have become so welded, so wedged together. But the time has come when it is urgently necessary to carry into many, many places an insight into what really exists. And that is a thing for which people to-day show no zeal. There is nothing to be expected from the influence of a civilisation which never contemplates external reality,—which wants to bind external reality to a couple of hard and fast concepts; nor need one hope with this little set of concepts to draw near to that true reality which is the business of anthroposophical science to discover. For it is this true reality that the spiritual science of Anthroposophy has to seek and find. Therefore, the spiritual science of Anthroposophy must not be taken after the pattern of what people were often pleased to call “religious persuasions.” That, you see was what one suffered from so terribly in the course of the old Theosophic movement. What more was the old Theosophic movement than just that people wanted a sort of select religion? It consisted in no new impulse proceeding from the civilisation of Europe itself. It consisted merely in emotions, which were to be had out of the old religious element just as well. Only people had grown tired of these old religious concepts and ideas and feelings, and so had taken up something else. But the same atmosphere pervaded it as pervaded the old persuasion. They wanted to feel good, with an evangelical sort of goodness if they had been evangelicals, or with a catholic kind of goodness if they had been Catholics; but they did not at bottom want the thing really needed, namely, an actual new religious impulse along with other impulses, because the life of the European peoples has grown up habituated to an alien religious impulse, that of Asia. That is the point. And until those things are organically interwoven that were inorganically intermixed,—till then, European civilisation will not rise again. It cannot be taken too seriously; it must pervade everything that is going to live in science, in economic, in religion, in political life. We will speak more of this, then, tomorrow. To-morrow the eurhythmic performance takes place here at 5 o'clock. Then, after the necessary interval, that is, I take It, about half past seven tomorrow, there will be the lecture. |
| 213. Human Questions and Cosmic Answers: The Relation of the Planets to Man's Life of Soul
01 Jul 1922, Dornach Tr. Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Such questions have, of course, constantly formed part of philosophical discussions: Is the world of space, the spatial cosmos, finite or infinite? However much discussion there may be—Kant's Critique of Pure Reason is right in this respect—questions such as those of the spatial or temporal limits of the manifested universe will never be led to a conclusion by discussion carried on from within the physical body. |
| 213. Human Questions and Cosmic Answers: The Relation of the Planets to Man's Life of Soul
01 Jul 1922, Dornach Tr. Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In the lecture yesterday I described the external aspect, as it were, of what I am going to speak about today. I tried to show how man and the cosmos together form one whole, and how what is present in the individual human being is connected in manifold ways with processes and with beings of the cosmos. If what I shall be saying today is not to seem groundless and incomplete, you must bring it into relation with the two preceding lectures. The individual human being can be viewed in his external aspect, as he appears to ordinary sight, or to anatomy and physiology. But he can also be viewed in his inner aspect, so that his qualities of soul, his spiritual forces, are revealed. The “whole” that is composed of man together with the cosmos may also be contemplated in two aspects. But these aspects will be the reverse of those presented by the individual man. In his case we speak of an outer and an inner aspect. When we speak of the universe, the cosmos, and of man as a member of this universe, ordinary feeling will tell us that the words must be used in the reverse way. We are actually within this cosmic existence when we think of it as purely spatial; from our own point of vision we look outwards. When, therefore, we are speaking of the universe from the human standpoint, we are speaking from within the universe, for we are standing at some point within it. Seen from this point of view the universe presents to us its physical, material aspect. The human being presents his physical aspect when we view him from outside, and his aspect of spirit-and-soul when we view him from within. The universe presents its aspect of spirit-and-soul when we view it from outside. The concepts that must be applied here will be difficult, for they have almost entirely dropped out of use in modern language. But modern language cannot penetrate directly into the realm of the spiritual. Words that are suitable have first to be coined. Any attempt to fathom the realities of the spirit-and-soul by using words with their ordinary meanings is an absurdity. In order to picture what I have just tried to characterise, the following must be said. In the case of a human being we speak of his external aspect as that which presents itself to the senses. If we speak of him from the inner aspect, we speak of his nature of spirit-and-soul. In the case of the universe, the cosmos, we must picture the reverse: we are at some point within the universe and from there it presents its physical aspect to us. If we are able to view the universe from outside, the aspect of spirit-and-soul is revealed to us. The natural question is this: Is it possible to view the universe from outside? As we know, man alternates between the conditions in which he lives from birth until death and those he experiences between death and a new birth, and it is the external aspect of the universe that reveals itself during his existence between death and a new birth. If you will read in my book, Theosophy, the description given of the conditions in which man lives between death and a new birth you will find it amply indicated there that words must be used in a different sense. The world, the universe, in which we find ourselves between birth and death is manifold enough, but it becomes even more manifold, far richer, when contemplated during the life between death and a new birth. Naturally, in such descriptions, a few selected details only can be mentioned. And it has always been my endeavour to add more and more information about matters which, at the beginning, are presented in an elementary way. I want to speak today of the spirit-and-soul of what was described yesterday in its material-physical aspect—the aspect of the cosmos viewed from within. I want now to describe what reveals itself when the cosmos is viewed from outside, when it is contemplated from a vantage-point of spirit-and-soul on the path of the experiences stretching between death and a new birth. From the different studies pursued here you know that this kind of contemplation is necessary, and you know too that no ordinary, logical exposition of the subject could ever reach the reality. It can therefore only be a matter of describing the vista that reveals itself when the methods referred to in anthroposophical literature are applied. A vantage-point of vision lying outside the physical-material cosmos is reached only by degrees. When a man has reached this vantage-point—it cannot be until some while after his death—then for the first time he finds the solution of those questions which cannot be solved by the intellectual methods we employ while in the body. Such questions have, of course, constantly formed part of philosophical discussions: Is the world of space, the spatial cosmos, finite or infinite? However much discussion there may be—Kant's Critique of Pure Reason is right in this respect—questions such as those of the spatial or temporal limits of the manifested universe will never be led to a conclusion by discussion carried on from within the physical body. Under these conditions it is equally possible to prove that the universe is finite or that it is infinite. The questions are resolved only when the vantage-point of vision can be shifted, when a man is able to contemplate the world from the other side—not, therefore, from a point within it, but from outside it. In the middle stages at least of the life between death and a new birth, man is on yonder side of the boundary of the material-physical cosmos. The boundary of the material-physical cosmos actually lies midway between what is seen from the earthly viewpoint and what is seen during the life between death and a new birth. This too is wisdom: To know what questions can indeed be asked in earthly existence but not answered there, because thinking can take place only on the physical foundations of the bodily nature. Such questions can be answered only when, outside this physical existence, a man is able, either through initiation or through death, to change the vantage-point of his vision. Now if this vantage-point is, in fact, changed, we experience it from within; we are not within it as we are between birth and death, but we experience it from outside, view it from outside. But the strange fact is that the manifoldness presented by human beings disappears when we pass into yonder world. And whereas we behold many structures, many configurations, of the cosmos—actually as many as there are human souls connected with the earth—when we are looking back upon the earth we see man once only, both in time and in space. Between death and a new birth we behold many worlds and only one “manhood,” one human nature. Without pondering upon this in meditation from every angle—it is of tremendous importance although in human words no more than the merest indications can be given—it is really not possible to have a clear conception of the radical difference in the picture of the world when it is experienced between birth and death and when it is experienced between death and a new birth. Between birth and death we experience one world and many men; during the life between death and rebirth we experience many worlds—representing our unitary world—and only one human nature. When from our life between death and rebirth we look back upon earthly life, men are not seen in their manifoldness but all are embraced in one single human nature. Everything, therefore, is completely reversed and attention must be called to this radical reversal. For it is essential to realise once and for always how impossible it is to acquire adequate ideas of the spiritual world without concepts that have been completely re-cast. With the easy-going methods by which people usually want to gain ideas of the spiritual world, it is simply not possible to reach ideas that conform with the reality. Man must be willing to metamorphose his ideas, even to the point of complete reversal. That is what many people are not willing to do, hence the battle that is waged against a true science of the spirit. I explained to you yesterday in greater detail how man is related to the Sun-nature on the one side and to the Moon-nature on the other, but also to the natures of the several planets. This was all considered from the standpoint of Earth-evolution. I explained the way in which man is related to the Venus-nature, to the Mercury-nature, and so on, saying that through modern spiritual science we are led again, by an entirely independent path, to knowledge that was cultivated in the ancient Mysteries, through an inspired, dreamlike wisdom. Everything I said yesterday was a presentation of the subject from one aspect. As long as we endeavour to acquire knowledge as the initiate in the ancient Mysteries sought to acquire it during the life between birth and death, we gain ideas about our planetary universe such as were presented yesterday. But the moment we reach a vantage-point outside the cosmos in which we live between birth and death and view its aspect of spirit-and-soul from without, at that moment all the detailed matters referred to yesterday also reveal to us their other aspects, their reversed aspects. It was said that the Mercury-forces in the world—whether in their material or in their planetary aspect—help man as a being of spirit-and-soul to take hold of the solid constituents of his organism. The Venus-forces enable him to take hold of the fluids in his organism. The moment we reverse this whole conception, all these qualities, too, are revealed to us in a quite different guise. If, leaving Neptune and Uranus out of account, we begin with Saturn, the outermost planet of our system, it becomes possible—in contemplating the Saturn-existence as it were from the other side of existence—to understand, by means of all the faculties we possess between death and a new birth, the real nature of man's life of instinct. The essential nature of the life of instinct which wells up in man from subconscious depths of his being cannot be fathomed and understood by means of the faculties acquired only on the Earth; it must be fathomed either between death and rebirth, or in the realm of higher, super-sensible knowledge, in Initiation-Science. So we may say: If, with the eyes of spirit, we contemplate the Saturn-nature from the viewpoint of the Earth, we gain an idea of the forces which help man to feel himself as an independent being of spirit-and-soul in face of the chemical processes working in his organism. The Saturn-existence viewed from outside, in its aspect of spirit-and-soul, reveals to us those forces in the cosmos which implant instincts into man's nature. The Jupiter-existence reveals those elements in man which are more definitely of the nature of soul than are his instincts, namely, his inclinations, his sympathies. For whereas instincts are still entirely of an animal nature, in inclinations an element of soul (animal-psychic) is already evident. The Mars-existence reveals all those impulses which are not, indeed, the moral commandments a man imposes on himself, but moral impulses which spring as it were from his whole character and fundamental disposition. Whether a man is courageous in his moral conduct or whether he is slack in this respect depends upon the forces that come into our ken when we view the Mars order of existence from the other side.—I am speaking, not of the fully conscious moral impulses described in my Philosophy of Spiritual Activity as rooted in pure thinking, but of moral impulses in which there is invariably a considerable degree of unconsciousness. When, therefore, we are considering man's connection with these outer planets, we are led more to the qualities which in a sense are actually bound up with the human organism. What is born with a man, stems from the cosmos, the universe; what wells up in the form of instincts from the whole organism is of the nature of Saturn; what wells up in the form of inclinations, sympathies, is of the nature of Jupiter; what wells up in the form of active forces of initiative but is bound up with the organism, is of the nature of Mars. We come now to those qualities which are a more integral part of man. They also reveal themselves to our vision, inasmuch as they proceed from forces in the cosmos. Leaving aside the Sun-nature for the present, there is, for example, Mercury. It will not generally be believed that man's cleverness, his sagacity, is also grounded in the universe. This is true, nevertheless. And if, entirely without any preconceived ideas, you look at the phenomena of the universe, you will say to yourselves: The activity which your intelligence finally discovers in itself is present in the phenomena of the universe. Intelligence is manifestly present in these phenomena. Now the forces which represent this element of intelligence in the cosmos, and are born with us as our intellectual gifts, our sagacity—these forces pertain to the Mercury-nature in the universe. The Venus-nature has been amply described in traditions and manifests in everything that constitutes love. The Moon-nature comes to expression in the activities of imagination, of phantasy; also in those of memory—not the organic activity underlying acts of remembrance but the activity that is present in the forming and shaping of mental pictures, of ideas. The pictures of memory are really identical in nature with the pictures of imagination, only they arise as faithful reproductions of the corresponding experiences. Therefore we can say: Imagination or phantasy, and memory, the more inward qualities and capacities, are connected with the forces of the Moon, Venus and Mercury. When we contemplate the material-physical aspect of Jupiter, for example, that is to say when we contemplate Jupiter from within the universe, it represents the concentration of those forces—in the sense indicated yesterday—which make it possible for man not to flow away in the light but to maintain himself as an independent being of spirit-and-soul within the light. If the Jupiter-forces are viewed in their aspect of spirit-and-soul, that is to say, from without, then Jupiter reveals those forces which man has within him in the form of inclinations, sympathies and the like. In its outermost aspect Jupiter enables the soul-life to maintain its own independent footing in face of the light. In its aspect of spirit-and-soul, Jupiter enables inclinations, sympathies, to arise, to take shape, to be engendered. When man is passing through these stages after death, or also in the process of Initiation—as I have described them in the book Theosophy—there comes a certain point of time when he ceases to see the stars—whether planets or fixed stars—as they are seen from the earth by means of the senses. It is quite understandable that he should cease to see the stars; but he does not cease to know about them. He knows, firstly, what I described yesterday. And from a certain point of time onwards he comes to know the nature of the stars from the moral aspect. He is now looking back upon the cosmos. But he sees the cosmos as a moral reality, not as a physical reality. And after the intermediate condition during which he sees what I described yesterday, he then sees from outside, especially during the middle period between death and a new birth, not what could be called Saturn in our parlance, but the surging life of instinct in the cosmos which then becomes part of himself when he again passes into physical embodiment on the earth. He sees the weaving life of inclinations, sympathies, and so on.—Materialistic thought may, of course, deny all this, but to do so is about as sensible as to deny the reality of the spirit and soul of a man when confronting the physical body. This vision of the cosmos, of the planetary world, in their moral aspects fills man's existence between death and a new birth. These perceptions are, however, dependent in a certain respect upon how he passes through the gate of death. He beholds the life of instinct, of inclinations, of moral impulses and so on in accordance with the unconscious understanding he acquired during his life on earth. For example, a man who during his life has been on friendly terms with many individuals who are what is called “unconventional” in some respect, a man who is not a philistine in his attitude to others but has a certain kindly understanding of them, letting them be as they are instead of criticising—such a man acquires for himself, in addition to the understanding by which his consciousness is already enriched, an abundance of unconscious forces. A great deal is gained from letting other human beings be as the are, trying to understand them, not picking them to pieces with criticism; but as well as this understanding, in itself an asset to his consciousness, he acquires, as I say, a wealth of unconscious impulses. Equipped with these impulses, he will then be well able to observe the mysteries of the Saturn-existence from the other side of life, from the side of the life between death and a new birth. The mysteries of planetary existence reveal themselves in many different aspects. According to a man's capacity for understanding them, he combines these forces into a whole and so incorporates them into his own nature when he returns into earthly existence. And now you can surely feel that through this vision a man gains knowledge and experience, just as he does here on the earth. On the earth he gets to know one human being after another; thereby he acquires knowledge of man. He also gains experiences in accordance with what is revealed to him from the other side of life. But these latter experiences, which are acquired during the second half of the life between death and a new birth, become creative forces, and the man bears them into the organism he receives through heredity. You will realise that this is connected with the forming of karma, that something takes place here which may be called the technique of the forming of karma. Between death and a new birth man acquires the experiences that are necessary to enable him to implant his karma into his nature, through these visions that come to him from the other side of life. I have had to describe these matters with a certain subtlety because they are subtle in themselves, and because it is necessary to stress that concepts must be radically transformed if the universe is to be understood. For in everything we see here on the earth, physically to begin with, but then also through deepened spiritual perception, the one side only of existence is revealed. Indeed when we look outwards, the cosmos too reveals only this one aspect of existence. The other aspect reveals itself only when we are able to contemplate the cosmos while we are outside the body, in an existence that is purely of the nature of spirit-and-soul. And then the cosmos is revealed in its aspect of spirit-and-soul, in its moral aspect. In very ancient times of human evolution on the earth, men still brought many “cosmic remembrances” with them when they came into physical existence. Compared with the men of today these primeval men were more animal-like in outer appearance (although the whole crude theory of man's descent from animals is a fallacy)—but for all that, in earthly existence too, they knew something of the other side of life. They had brought this knowledge with them into bodies that were still incompletely developed. In the course of evolution, man has progressively lost his remembrance of the other side of existence in which he lives between death and rebirth; and so he is now obliged to rely upon the experiences offered by earthly existence. Only so can man incorporate into himself a power which can be incorporated into him nowhere else in the universe. For the power to act out of freedom must be, and is, acquired during earthly existence; it will then remain throughout man's earthly and cosmic future. Because, to begin with, these things naturally come as a shock to people, it is still necessary in public lectures to speak in abstract concepts of the fact that while man is within an existence of spirit-and-soul, the universe reveals its reverse aspect. But, as you see, it is also possible to describe the detailed, concrete facts of planetary existence—and one could also go farther out into the world of stars—and in so doing show how man is connected with the whole cosmos. Only with these data of knowledge as a foundation is it possible to speak of the fact that the cosmos as it reveals itself when contemplated from the earth is firstly the physical cosmos (including the earth), then the etheric cosmos. But in ordinary physical space there are, in reality, only the physical cosmos and the etheric cosmos. The moment when, passing through the gate of death or through initiation, man becomes able to experience himself purely as a being of spirit-and-soul—that is to say, to contemplate the universe from the other side—conceptions of space cease to have any meaning for him. As long as the words of human language have to be used, we can say: When we contemplate our spatial universe from outside, it still appears to us as if it were spatial, but it no longer is so. For in truth it must be said: Here we look outwards from a single point, but we must imagine the point dispersed. The point is no longer a point, it is dispersed. We embrace space within ourselves as it were, and behold the non-spatial; just as here we look at space from one single point, when we are outside our body we look back from out of space upon the point. And with this is connected the experience of beholding as many worlds as there are human souls connected with the earth, and only one human nature, one “manhood.” We are each and all of us a single human being when we look at ourselves from outside. That is why the science of Initiation speaks of the mystery of number, because even number itself has meaning only from this or that particular point of vision. What here on earth is a unity—the cosmos—is a plurality when seen from outside. What here on earth is a plurality—namely, human beings—is a unity when seen from outside. To regard something as a plurality or as a unity is also maya, is also illusion, for if viewed from an entirely different point of vision, a unity may reveal itself as a plurality and a plurality as a unity. This is something that has also formed part of mathematical science in the course of its evolution on earth. I have spoken of this before. Today we count by adding one unit to another. We say: one, then two, then by adding another unit we have three, and so on. But in very ancient times men did not count like this. They counted in this way: the unit is one, in the unit there is two, then, still in the unit, three. They did not add one unit to another but the unit was that which embraced all numbers. In the unit all numbers were contained. In our time the unit is contained in all the numbers; in ancient mathematics all the numbers were contained in the unit. This conception sprang from the different modes of thinking, which were in turn connected with the remembrances of an extra-cosmic science still surviving in very early times of evolution.
|
| 233a. Rosicrucianism and Modern Initiation: The Relationship of Earthly Man to the Sun
11 Jan 1924, Dornach Tr. Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| You may feel how the intellect became external by comparing the way in which Aristotle himself imparted his Logic to his pupils with the way in which it was taught much later, say in the seventeenth century.—You will remember how Kant says that Aristotle's Logic has not advanced since his time.—In the time of Aristotle, Logic was still thoroughly human. |
| 233a. Rosicrucianism and Modern Initiation: The Relationship of Earthly Man to the Sun
11 Jan 1924, Dornach Tr. Mary Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
What I have been telling you in recent lectures requires to be carried a little further. I have tried to give you a picture of the flow of spiritual knowledge through the centuries, and of the form it has taken in recent times, and I have been able to show how from the fifteenth until the end of the eighteenth or even the beginning of the nineteenth century, the spiritual knowledge that was present before that period as clear and concrete albeit instinctive knowledge, showed itself in this later age more in a devotion of heart and soul to the Spiritual, to all that is of the Spirit in the world. We have seen how the knowledge man possessed of Nature and of how the spiritual world works in Nature, is still present in the eleventh, twelfth and thirteenth centuries. In a personality like Agrippa of Nettesheim, whom I have described in my book Mysticism and Modern Thought, we have one who was still fully possessed of the knowledge, for example, that in the several planets of our system are spiritual Beings of quite definite character and kind. In his writings, Agrippa of Nettesheim assigns to each single planet what he calls the Intelligence of the planet. This points to traditions which were still extant from olden times, and even in his day were something more than traditions. To look up to a planet in the way that became customary in later Astronomy and is still customary today, would have been utterly impossible to a man like Agrippa of Nettesheim. The external planet, nay, every external star was no more than a sign, an announcement, so to say, of the presence of spiritual Beings, to whom one could look up with the eye of the soul, when one looked in the direction of the star. And Agrippa of Nettesheim knew that the Beings who are united with the single stars are the Beings who rule the inner existence of the star or the planet, rule also the movements of the planet in the Universe, the whole activity of the particular star. And such Beings he called: the Intelligence of the star. Agrippa knew also how, at the same time, hindering Beings work from the star, Beings who undermine the good deeds of the star. They too work from out of the star and also into it; and these Beings he called Demons of the star. And together with this knowledge went an understanding of the Earth, that saw in the Earth too a heavenly body having its Intelligence and its Demon. The understanding however for star Intelligence and star Demonology was little by little completely lost, with all that was involved in it. What was essentially involved in it may be expressed in the following way. The Earth was of course looked upon as ruled in her inner activity, in her movement in the Cosmos, by Intelligences whom one could bring together under the name of the Intelligence of the Earth star. But what was the Intelligence of the Earth star, for the men of Agrippa's time? It is exceedingly difficult today even to speak of these things, because the ideas of men have travelled very far away from what was accepted as a matter of course in those times by men of insight and understanding. The Intelligence of the Earth star was Man himself, the human being as such. They saw in Man a being who had received a task from the Spirituality of the Worlds, not merely, as modern man imagines, to walk about on the Earth, or to travel about it in trains, to buy and sell, to write books, and so forth and so forth—no, they conceived Man as a being to whom the World-Spirit had given the task to rule and regulate the Earth, to bring law and order into all that has to do with the place of the Earth in the Cosmos. Their conception of Man was expressed by saying: Through what he is, through the forces and powers he bears within his being, Man gives to the Earth the impulse for her movement around the Sun, for her movement further in Universal Space. There was in very truth still a feeling for this. It was known that the task had once been allotted to Man, that Man had really been made the Lord of the Earth by the World-Spirituality, but in the course of his evolution had not shown himself equal to the task, had fallen from his high estate. When men are speaking of knowledge nowadays it is very seldom that one hears even a last echo of this view. What we find in religious belief concerning the Fall really goes back ultimately to this idea; for there the point is that originally Man had quite another position on the Earth and in the Universe from the position he takes today; he has fallen from his high estate. Setting aside however this religious conception and considering the realm of thought, where men think they have knowledge that they have attained by definite and correct methods, it is only here and there that we can still find today an echo of the ancient knowledge that once proceeded from instinctive clairvoyance, and that was well aware of Man's task and of his Fall into his present narrow limitations. It may still happen, for example, that one may have a conversation with a person—I am here relating facts—who has thought very deeply, who has also acquired very deep knowledge concerning this or that matter in the spiritual realm. The conversation turns on whether Man, as he stands on Earth today, is really a creature who is self-contained, who carries his whole being and nature within him. And such a personality as I have described will say to you, that this cannot be. Man must really in his nature be a far more comprehensive being—otherwise he could not have the striving he has now, he could not develop the great idealism of which we can see such fine and lofty examples; in his true nature Man must be a great and comprehensive being, who has somehow or other committed a cosmic sin, as a consequence of which he has been banished within the limits of this present earthly existence, so that today he is really sitting imprisoned as it were in a cage. You may still meet with this view here and there as a late straggler, as it were. But speaking generally, where shall we find one who accounts himself a scientist, who seriously occupies himself with these great and far-reaching questions? And yet it is only by facing them that man can ever find his way to an existence worthy of him as man. It was, then, really so that Man was regarded as the bearer of the Intelligence of the Earth. But now, a person like Agrippa of Nettesheim ascribed to the Earth also a Demon. When we go back to the twelfth or thirteenth century, we find this Demon of the Earth to be a Being who could only become what he became on the Earth, because he found in Man the tool for his activity. In order to understand this, we must acquaint ourselves with the way men thought about the relationship of the Earth to the Sun, or of Earthly man to the Sun, in those days. And if I am now to describe to you how they understood this relationship, then I must again speak in Imaginations: for these things will not suffer themselves to be confined in abstract concepts. Abstract concepts came later, and they are very far from being able to span the truth; we have therefore to speak in pictures, in Imaginations. Although, as I have described in my Outline of Occult Science, the Sun separated itself from the Earth, or rather separated the Earth off from itself, it is nevertheless the original abode of Man. For ever since the beginning of the Saturn existence Man was united with the whole planetary system including the Sun. Man has not his home on Earth, he has on Earth only a temporary resting place. He is in truth, according to the view that prevailed in those olden times, a Sun-being. He is united in his whole being and existence with the Sun. And since this is so, he ought as a being of the Sun to stand quite differently on the Earth than he actually does. He ought to stand on the Earth in such a way that it should suffice for the Earth to have the impulse to bring forth the seed of Man in etheric form from out of the mineral and plant kingdoms, and the Sun then to fructify the seed brought forth from the Earth. Thence should arise the etheric human form, which should itself establish its own relationship to the physical substances of the Earth, and itself take on Earth substantiality. The contemporaries of Agrippa of Nettesheim—Agrippa's own knowledge was, unfortunately, somewhat clouded, but better contemporaries of his did really hold the view that Man ought not to be born in the earthly way he now is, but Man ought really to come to being in his etheric body through the interworking of Sun and Earth, and only afterwards, going about the Earth as an etheric being, give himself earthly form. The seeds of Man should grow up out of the Earth with the purity of plant-life, appearing here and there as ethereal fruits of the Earth, darkly shining; these should then in a certain season of the year be overshone, as it were, by the light of the Sun, and thereby assume human form, but etheric still; then Man should draw to himself physical substance—not from the body of the mother, but from the Earth and all that is thereon, incorporating it into himself from the kingdoms of the Earth. Thus—they thought—should have been the manner of Man's appearance on the Earth, in accordance with the purposes of the Spirit of the Worlds. And the development that came later was due to the fact that Man had allowed to awaken within him too deep an urge, too intense a desire for the earthly and material. Thereby he forfeited his connection with the Sun and the Cosmos, and could only find his existence on Earth in the form of the stream of inheritance. Thereby, however, the Demon of the Earth began his work; for the Demon of the Earth would not have been able to do anything with men who were Sun-born. When Sun-born man came to dwell on the Earth, he would have been in very truth the Fourth Hierarchy. And one would have had to speak of Man in the following manner. One would have had to say: First Hierarchy: Seraphim, Cherubim, Thrones; Second Hierarchy: Exusiai, Dynamis, Kyriotetes; Third Hierarchy: Angels, Archangels, Archai; Fourth Hierarchy: Man—three different shades or gradations of the human, but none the less making the Fourth Hierarchy. But because Man gave rein to his strong impulses in the direction of the physical, he became, not the being on the lowest branch, as it were, of the Hierarchies, but instead the being at the summit of the highest branch of the earthly kingdoms: mineral kingdom, plant kingdom, animal kingdom, human kingdom. This was the picture of how Man stood in the world. Moreover, because Man does not find his proper task on the Earth, the Earth herself has not her right and worthy position in the Cosmos. For since Man has fallen, the true Lord of the Earth is not there. What has happened? The true Lord of the Earth is not there, and it became necessary for the Earth, not being governed from herself in her place in the Cosmos, to be ruled from the Sun; so that the tasks that should really be carried out on Earth fell to the Sun. The man of mediaeval times looked up to the Sun and said: In the Sun are certain Intelligences. They determine the movement of the Earth in the Cosmos; they govern what happens on the Earth. Man ought, in reality, to do this; the Sun-forces ought to work on Earth through Man for the existence of the Earth. Hence that significant mediaeval conception that was expressed in the words: The Sun, the unlawful Prince of this world. And now reflect, my dear friends, how infinitely the Christ Impulse was deepened through such conceptions. The Christ became, for these mediaeval men, the Spirit Who was not willing to find His further task on the Sun, Who would not remain among those who directed the Earth in unlawful manner from without. He wanted to take His path from the Sun to the Earth, to enter into the destiny of Man and the destiny of Earth, to experience Earth events and pass along the ways of Earth evolution, sharing the lot of Man and of Earth. Therewith, for mediaeval man, the Christ is the one Being Who in the Cosmos saved the task of Man on the Earth. Now you have the connection. Now you can see why, in Rosicrucian times, it was again and again impressed upon the pupil: “O Man, thou art not what thou art; the Christ had to come, to take from thee thy task, in order that He might perform it for thee.” A great deal in Goethe's Faust has come down from mediaeval conceptions, although Goethe himself did not understand this. Recall, my dear friends, how Faust conjures up the Earth Spirit. With these mediaeval conceptions in mind, we can enter with feeling and understanding into how this Earth Spirit speaks.—
Who is it that Faust is really conjuring up? Goethe himself, when he was writing Faust, most assuredly did not fully know. But if we go back from Goethe to the mediaeval Faust and listen to this mediaeval Faust in whom Rosicrucian wisdom was living, then we learn how he too wanted to conjure up a spirit. But whom did he want to conjure up in the Earth Spirit? He did not ever speak of the Earth Spirit, he spoke of Man. The deep longing and striving of mediaeval man was: to be Man. For he felt and knew that as Earth man he is not truly Man. How can manhood be found again? The way Faust is rebuffed, pushed on one side by the Earth Spirit is a picture of how man in his earthly form is rebuffed by his own being. And this is why many accounts of conversion to Christianity in the Middle Ages show such extraordinary depth of feeling. They are filled with the sense that men have striven to attain the manhood that is lost, and have had to give up in despair, have rightly despaired of being able to find in themselves, within earthly physical life, this true and genuine manhood; and so they have arrived at the point where they must say: Human striving for true manhood must be abandoned, earthly man must leave it to the Christ to fulfil the task of the Earth. In this time, when man's relation to true manhood as well as his relation to the Christ was still understood in what I would call a superpersonal-personal manner—in this time Spirit-knowledge, Spirit-vision was still a real thing, it was still a content of experience. It ceased to be so with the fifteenth century. Then came the tremendous change, which no one really understood. But those who know of such things know how in the fifteenth, in the sixteenth centuries, and even later, there was a Rosicrucian school, isolated, scarcely known to the world, where over and over again a few pupils were educated, and where above all, care was taken that one thing should not be forgotten but be preserved as a holy tradition. And this was the following.—I will give it to you in narrative form. Let us say, a new pupil arrived at this lonely spot to receive preparation. The so-called Ptolemaic system was first set before him, in its true form, as it had been handed down from olden times, not in the trivial way it is explained nowadays as something that has been long ago supplanted, but in an altogether different way. The pupil was shown how the Earth really and truly bears within herself the forces that are needed to determine her path through the Universe. So that to have a correct picture of the World, it must be drawn in the old Ptolemaic sense: the Earth must be for Man in the centre of the Universe, and the other stars in their corresponding revolutions be controlled and directed by the Earth. And the pupil was told: If one really studies what are the best forces in the Earth, then one can arrive at no other conception of the World than this. In actual fact, however, it is not so. It is not so on account of man's sin. Through man's sin, the Earth—so to speak, in an unauthorised, wrongful way—has gone over into the kingdom of the Sun; the Sun has become the regent and ruler of earthly activities. Thus, in contradistinction to a World-System given by the Gods to men with the Earth in the centre, could now be set another World-System, that has the Sun in the centre, and the Earth revolving round the Sun—it is the system of Copernicus. And the pupil was taught that here is a mistake in the Cosmos, a mistake in the Universe brought about by human sin. This knowledge was entrusted to the pupil and he had to engrave it deeply in his heart and soul.—Men have overthrown the old World-System (so did the teacher speak) and set another in its place; and they do not know that this other, which they take to be correct, is the outcome of their own human guilt. It is really nothing else than the expression, the revelation of human guilt, and yet men take it to be the right and correct view. What has happened in recent times? (The teacher is speaking to the pupil.) Science has suffered a downfall through the guilt of man. Science has become a science of the Demon. About the end of the eighteenth century such communications became impossible, but until that time there were always pupils here and there of some lonely Rosicrucian School, who received their spiritual nourishment imbued as it were with this feeling, with this deep understanding. Even such a man as Leibnitz, the great philosopher, was led by his own thought and deliberation to try and find somewhere a place of learning where the relation between the Copernican and Ptolemaic Systems could be correctly formulated. But he was not able to find any such place. Things like this need to be known if one is to understand aright, in all its shades of meaning, the great change that has come about in the last centuries in the way man looks on himself and on the Universe. And with this weakening of man's living connection with himself, with this estrangement of man from himself came afterwards the tendency to cling to the external intellect that today rules all. Is this external intellect verily human experience? No, for were it human experience, it could not live so externally in mankind as it does. The intellect has really no sort of connection with what is individual and personal, with the single individual man; it is well nigh a convention. It does not flow out of inner human experience; rather it approaches man as something outside him. You may feel how the intellect became external by comparing the way in which Aristotle himself imparted his Logic to his pupils with the way in which it was taught much later, say in the seventeenth century.—You will remember how Kant says that Aristotle's Logic has not advanced since his time.—In the time of Aristotle, Logic was still thoroughly human. When a man was taught to think logically, he had a feeling as though—if again I may be allowed to express myself in imaginative terms—as though he were thrusting his head into cold water and thereby became estranged from himself for a moment; or else he had a feeling such as Alexander expressed when Aristotle wanted to impart Logic to him: You are pressing together all the bones of my head! It is the feeling of something external. But in the seventeenth century this externality was taken as a matter of course. Men learned how from the major and minor premise the consequent must be deduced. They learned what we find treated so ironically in Goethe's Faust:
Whether, like Alexander, one feels the bones of one's head all pressed together, or whether one is laced up in Spanish boots with all this First, Second, Third, Fourth—we have in either case a true picture of what one feels. But this externality of abstract thought was no longer felt in the time when Logic began to be taught in the schools. Today of course this has more or less ceased. Logic is no longer specifically taught in the schools. It is rather as if there had once been a time when hundreds and hundreds of people had put on the same uniform under direction, and done it with enthusiasm, and then afterwards there came a time when they did it of their own free will without giving it a thought. During all the time however when the Logic of the abstract was gaining the upper hand, the old spiritual knowledge was incapable of going forward. Hence we see it in its turn becoming external, and assuming a form of which examples are to be found in the writings of Eliphas Levi or the publications of Saint-Martin. These are the last offshoots of the old Spirit-knowledge and Spirit-vision. What do we find in a book such as Eliphas Levi's, The Dogma and Ritual of High Magic? In the first place there are all kinds of signs—Triangles, Pentagrams and so forth. We find words from languages in use in bygone ages, especially from the Hebrew. And we find that what in earlier times was life and at the same time knowledge that could pass over into man's action and into man's ideas—this we find has become bereft of ideas on the one hand, and on the other hand has degenerated into external magic. There is speculation as to the symbolic meaning of this or that sign, concerning all of which the modern man, if he is honest, would have to confess that he can find nothing particular in it. There are also practices connected with all manner of rites, while those who spoke of these rites and frequently practised them were far from having any clear notion at all of their spiritual connection. Such books are invariably pointers to what was once understood in olden times, was once an inward knowledge-experience, but when Eliphas Levi, for example, was writing his books, was no longer understood. As for Saint-Martin—of him I have already written in the Goetheanum Weekly. Thus we see how what had once been interwoven into the soul-and-spirit of man's life, could not he held there but fell a victim to complete want of understanding. The common impulse and striving for the Divine that shows itself in the feeling of man from the fifteenth to the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries is genuine and true. Beautiful things are to be found in this impulse, things lovely and sublime. Much that has come from these times and that is far too little noticed today has about it as it were a magic breath—the genuine spell of the Spiritual. Side by side, however, with all this, a seed is sprouting, the seed of the lack of understanding of old spiritual truths. We have therewith a hardening, ossifying process, and a growing impossibility to approach the Spiritual in a way that is in accord with the age. We come across men of the eighteenth century who speak of a downfall of all that is human, and of the rise of a terrible materialism. Often it seems as though what these men of the eighteenth century say applies just as well to our own time. And yet it is not so; what they say does not apply to the last two-thirds of the nineteenth century. For in the nineteenth century a further stage has been reached. What was still regarded in the eighteenth century with a certain abhorrence on account of its demoniacal character, has come to be taken quite as a matter of course. The men of the nineteenth century had not the power to say: Copernicus!—Yes; but such a conception of the Universe was only able to arise because man did not become on Earth that which he should have become, and so the Earth was left without a ruler, and the rulership passed over to the unrighteous lords of the world (the expression occurs again and again in mediaeval writings), these took over the leadership of the Earth—even as the Christ left the Sun and united Himself with the destiny of the Earth. Only now, at the end of the nineteenth century, has it again become possible to look into these things with a clear vision such as man possessed in olden times; only now in the Michael Age has the possibility come again. We have spoken repeatedly of the dawn of the Michael Age, and of its character. But there are tasks that belong to this Michael Age, and it is possible now to point to these tasks, after all that we have been considering in the Christmas Meeting and since, about the evolution of Spirit-vision throughout the centuries. |
| 21. The Case for Anthroposophy: Principles of Psychosomatic Physiology
Tr. Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| But when it comes to feeling (see Lecture 9 in his book), he has this to say: The older psychology, almost without exception, treats of affects as manifestations of a special, independent faculty. Kant placed the feeling of desire and aversion, as a separate faculty, between those of cognition and appetite, and he expressly emphasised that any further reduction of the three to a common source was impossible. |
| 21. The Case for Anthroposophy: Principles of Psychosomatic Physiology
Tr. Owen Barfield Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] My object here is to present in outline certain conclusions I have reached concerning the relations between the psychic and the physical components of the human being. I may add that, in doing so, I place on record the results of a systematic spiritual investigation extending over a period of thirty years. It is only in the last few of those years that it has become practicable to formulate these results in concepts capable of verbal expression, and thus to bring the investigation to at least a temporary close. I must emphasise that it is the results and the results alone that I shall be presenting, or rather indicating, in what follows. Their foundation in fact can certainly be established on the basis of contemporary science. But to do this would require a substantial volume; and that my present circumstances do not permit of my writing. [ 2 ] If we are seeking for the actual relation between psychic and physical, it will not do to take as our starting-point Brentano’s distribution of psychic experience into representation, judgment and the responses of love and hate. Partitioning in this way, we are led to shelve so many relevant considerations that we shall reach no reliable results. On the contrary we have to start from that very trichotomy of representation, feeling and will which Brentano rejected. If we survey the psychic experience of representation as a whole, and seek for the bodily processes with which that experience is related, we shall find the appropriate nexus by relying substantially on the findings of current physiological psychology. The somatic correlatives to the psychic element in representation are observable in the processes of the nervous system, extending into the sense organs in one direction and into the interior physical organism in the other. Here, however wide the divergence in many respects between the anthroposophical point of view and that of contemporary science, that very science provides an excellent foundation. It is otherwise when we seek to determine the somatic correlatives for feeling and willing. There we have first to blaze the requisite trail through the findings of current physiology. And once we have succeeded in doing so, we shall find that, just as representation is necessarily related to nervous activity, so feeling must be seen as related to that vital rhythm which is centred in, and connected with, the respiratory system; bearing in mind that, for this purpose, the rhythm of breathing must be traced right into the outermost peripheral regions of the organism. To arrive at concrete results here, the findings of physiological research need to be pursued in a direction which is as yet decidedly unfamiliar. If we take the trouble to do this, preliminary objections to bracketing feeling with respiration, all disappear, and what at first looks like an objection turns out to be a proof. Take one simple example from the wide range available: musical experience is dependent on some feeling, but the content of musical form subsists in representations furnished by auditory perception. How does musical emotion arise? The representation of the tonal shape (which depends on organ of hearing and neural process) is not yet the actual musical experience. That arises in the measure that the rhythm of breathing, continuing further into the brain, confronts within that organ the effects produced there by ear and nervous system. The psyche now lives, not alone in what is heard and represented, or thought, but in the breathing rhythm. Something is released in the breathing rhythm through the fact that neural process impinges on rhythmic life. Once we have seen the physiology of respiration in its true light, we are led on all hands to the conclusion that the psyche, in experiencing emotion, is supported by the rhythmic process of breathing, in the same way that, in representation and ideation, it is supported by neural processes. And it will be found that willing is supported, in the same way, by the physical processes of metabolism. Here again one must include the innumerable offshoots and ramifications of these processes, which extend throughout the entire organism. When something is “represented”, a neural process takes place, on the basis of which the psyche becomes conscious of its representation; when something is “felt”, a modification is effected in the breathing rhythm, through which a feeling comes to life; and in the same way, when something is “willed”, a metabolic process occurs that is the somatic foundation for what the psyche experiences as willing. It should be noted however that it is only in the first case (representation mediated by the nervous system) that the experience is a fully conscious, waking experience. What is mediated through the breathing-rhythm (including in this category everything in the nature of feelings, affects, passions and the like) subsists in normal consciousness with the force only of representations that are dreamed. Willing, with its metabolic succedaneum, is experienced in turn only with that third degree of consciousness, totally dulled, which also persists in sleep. If we look more closely at this series, we shall notice that the experience of willing is in fact wholly different from the experience of representation or ideation. The latter is something like looking at a coloured surface: whereas willing is like looking at a black area in the middle of a coloured field. We see nothing there in the uncoloured part of the surface precisely because—unlike the surrounding part, from which colour impressions are received—no such impressions are at hand from it. We “have the idea” of willing, because within the psyche’s field of ideational experience a patch of non-ideation inserts itself, very much as the interruptions of consciousness brought about by sleep insert themselves into the continuum of conscious life. It is to these differing types of conscious apprehension that the soul owes the manifold variety of its experience in ideation, feeling and willing. There are some noteworthy observations on feeling and willing in Theodor Ziehen’s Manual of Physiological Psychology—in many ways a standard work within the tradition of current scientific notions concerning the relation between the physical and the psychic. He deals with the relation between the various forms of representation and ideation on the one hand and neural function on the other in a way that is quite in accord with the anthroposophical approach. But when it comes to feeling (see Lecture 9 in his book), he has this to say:
Here is a theoretical approach which concedes to feeling no independent existence in the life of the soul, seeing it as a mere attribute of ideation. And the result is, it assumes that not only ideation but feeling also is supported by neural processes. The nervous system is thus the somatic element to which the entire psyche is appropriated. Yet the whole basis of this approach amounts to an unnoticed presupposition of the conclusions at which it expects to arrive. It accepts as psychic only what is related to neural processes and then draws the inference that what is not proper to these processes, namely feeling, must be treated as having no independent existence—as a mere signal of ideation. To abandon this blind alley and return instead to unprejudiced observation of the psyche is to be definitively convinced of the independence of the whole life of feeling. But it is also to appreciate without reserve the actual findings of physiology and at the same time to gain from them the insight that feeling is, as already indicated, peculiar to the breathing-rhythm. The methodology of natural science denies any sort of existential independence to the will. Unlike feeling, willing is not even a signal of ideation. But this negative assumption, too, is simply based on a prior decision (cf. p. 15 of Physiological Psychology) to assign the whole of the psyche to neural process. Yet the plain fact is that what constitutes the peculiar quality of willing cannot really be related to neural process as such. Thus, precisely because of the exemplary clarity with which Ziehen develops the ideas from which he starts, he is forced (as anyone must be) to conclude that analysis of psychic processes in their relation to the life of the body “affords no support to the assumption of a specific faculty of will”. The fact remains that unprejudiced contemplation of the psyche obliges us to recognise the existential independence of the will, and accurate insight into the findings of physiology compels the conclusion that the will, as such, must be linked not with neural but with metabolic processes. If a man wants to form clear concepts in this field, then he must look at the findings of physiology and psychology in the light of the facts themselves and not, as so often happens in the present day practice of those sciences, in the light of preconceived opinions and definitions—not to mention theoretical sympathies and antipathies.1 Most important of all, he must be able to discern very clearly the mutual interrelation of neural function, breathing-rhythm and metabolic activity respectively. These three forms of activity subsist, not alongside of, but within one another. They interpenetrate and enter each other. Metabolic activity is present at all points in the organism; it permeates both the rhythmic organs and the neural ones. But within the rhythmic it is not the somatic foundation of feeling, and within the neural it is not that of ideation. On the contrary, in both of these fields it is the correlative of will-activity permeating rhythm and permeating the nerves respectively. Only materialistic presupposition can relate the element of metabolism in the nerves with the process of ideation. Observation with its roots in reality reports quite differently. It is compelled to recognise that metabolism is present in the nerve to the extent that will is permeating it. And it is the same with the somatic apparatus for rhythm. Everything within that organ that is of the nature of metabolism has to do with the element of will present in it. It is always willing that must be brought into connection with metabolic activity, always feeling that must be related to rhythmic occurrence, irrespective of the particular organ in which metabolism and rhythm are operating. But in the nerves something else goes on that is quite distinct from metabolism and rhythm. The somatic processes in the nervous system which provide the foundation for representation and ideation are physiologically difficult to grasp. That is because, wherever there is neural function, it is accompanied by the ideation which is ordinary consciousness. But the converse of this is also true. Where there is no ideation, there it is never specifically neural function we discern, but only metabolic activity in the nerve; or rhythmic occurrence in it, as the case may be. Neurology will never arrive at concepts that measure up to the facts, so long as it fails to see that the specifically neural activity of the nerves cannot possibly be an object of physiologically empirical observation. Anatomy and Physiology must bring themselves to recognise that neural function can be located only by a method of exclusion. The activity of the nerves is precisely that in them which is not perceptible by the senses, though the fact that it must be there can be inferred from what is so perceptible, and so can the specific nature of their activity. The only way of representing neural function to ourselves is to see in it those material events, by means of which the purely psycho-spiritual reality of the living content of ideation is subdued and devitalised (herabgelähmt) to the lifeless representations and ideas we recognise as our ordinary consciousness. Unless this concept finds its way somehow into physiology, physiology can have no hope of explicating neural activity. At present physiology has committed itself to methods which conceal rather than reveal this concept. And psychology, too, has shut the door in her own face. Look, for instance, at the effects of Herbartian psychology. It confines its attention exclusively to the process of representation, and regards feeling and willing merely as effects consequent on that process. But, for cognition, these “effects” gradually peter out, unless at the same time a candid eye is kept on actual feeling and willing; with the result that we are prevented from reaching any valid correlation of feeling and willing with somatic processes. The body as a whole, not merely the nervous activity impounded in it, is the physical basis of psychic life. And, just as, for ordinary consciousness, psychic life is naturally classifiable in terms of ideation, feeling and willing, so is physical life classifiable in terms of neural function, rhythmic occurrence and metabolic process. The question at once arises: in what way do the following enter and inhabit the organism: on the one hand, sense-perception proper, in which neural function merely terminates, and on the other the faculty of motion, which is the effusion of will? Unbiased observation discloses that neither the one nor the other of these belongs to the organism in the same sense that neural function, rhythmic occurrence and metabolic process belong to it. What goes on in the senses does not belong immediately to the organism at all. The external world reaches out into the senses, as though they were bays or inlets leading into the organism’s own existence. Compassing the processes that take place in the senses, the psyche does not participate in inner organic events; it participates in the extension of outer events into the organism.2 In the same way, when physical motion is brought about, what we have to do with is not something that is actually situated within the organism, but an outward working of the organism into the physical equilibrium (or other dynamic relation) between the organism itself and its environment. Within the organism it is only a metabolic process that can be assigned to willing; but the event that is liberated through this process is at the same time an actual happening within the equilibrium, or the dynamics, of the external world. Exerting volition, the life of the psyche overreaches the domain of the organism and combines its action with a happening in the outer world. The study of the whole matter has been greatly confused by the separation of the nerves into sensory and motor. Securely anchored as this distinction appears to be in contemporary physiological ideas, it is not supported by unbiased observation. The findings of physiology based on neural sections, or on the pathological elimination of certain nerves, do not prove what the experiment or the case-history is said to show. They prove something quite different. They prove that the supposed distinction between sensory and motor nerves does not exist. On the contrary, both kinds of nerve are essentially alike. The so called motor nerve does not implement movement in the manner that the theory of two kinds of nerve assumes. What happens is that the nerve as carrier of the neural function implements an inner perception of the particular metabolic process that underlies the will—in exactly the same way that the sensory nerve implements perception of what is coming to pass within the sense-organ. Unless and until neurological theory begins to operate in this domain with clear concepts, no satisfactory co-ordination of psychic and somatic life can come about.3 [ 3 ] Just as it is possible, psycho-physiologically, to pursue the interrelations between psychic and somatic life which come about in ideation, feeling and willing, in a similar way it is possible, by anthroposophical method, to investigate that relation which the psychic element in ordinary consciousness bears to the spiritual. Applying these methods, the nature of which I have described here and elsewhere, we find that, while representation, or ideation, has a basis in the body in the shape of neural activity or function, it also has a basis in the spiritual. In the other direction—the direction away from the body—the soul stands in relation to a noetically real, which is the basis for the ideation that is characteristic of ordinary consciousness. But this noetic reality can only be experienced through imaginal cognition. And it is so experienced in so far as its content discloses itself to contemplation in the form of coherently linked (gegliederte) imaginations. Just as, in the direction of the body, representation rests on the activity of the nerves, so from the other direction does it issue from a noetic reality, which discloses itself in the form of imaginations. It is this noetic, or spiritual, component of the organism which I have termed in my writings the etheric or life-body. And in doing so I invariably point out that the term “body” is no more vulnerable to objection than the other term “ether”; because my exposition clearly shows that neither of them is predicated materially. This life-body (elsewhere I have also sometimes used the expression “formative-forces body”) is that phase of the spiritual, whence the representational life of ordinary consciousness, beginning with birth—or, say, conception—and ending with death, continuously originates. The feeling-component of ordinary consciousness rests, on the bodily side, on rhythmic occurrence. From the spiritual side it streams from a level of spiritual reality that is investigated, in anthroposophical research, by methods which I have, in my writings, designated as inspirational. (Here again it is emphasised that I employ this term solely with the meaning I have given it in my own descriptions; it is not to be equated with inspiration in the colloquial sense.) In the spiritual reality that lies at the base of the soul and is apprehensible though inspiration there is disclosed that phase of the spiritual, proper to the human being, which extends beyond birth and death. It is in this field that anthroposophy brings its spiritual investigations to bear on the problem of immortality. As the mortal part of the sentient human being manifests itself through rhythmic occurrences in the body, so does the immortal spirit kernel of the soul reveal itself in the inspiration-content of intuitive consciousness. For such an intuitive consciousness the will, which depends, in the somatic direction, on metabolic processes, issues forth from the spirit through what in my writings I have termed authentic intuitions. What is, from one point of view, the “lowest” somatic activity (metabolism) is correlative to a spiritually highest one. Hence, ideation, which relies on neural activity, achieves something like a perfection of somatic manifestation; while the bodily processes associated with willing are only a feeble reflection of willing. The real representation is alive, but, as somatically conditioned, it is subdued and deadened. The content remains the same. Real willing, on the other hand, whether or no it finds an outcome in the physical world, takes its course in regions that are accessible only to intuitive vision; its somatic correlative has almost nothing to do with its content. It is at this level of spiritual reality, disclosed to intuition, that we find influences from previous terrestrial lives at work in later ones. And it is in this kind of context that anthroposophy approaches the problems of repeated lives and of destiny. As the body fulfils its life in neural function, rhythmic occurrence and metabolic process, so the human spirit discloses its life in all that becomes apparent in imaginations, inspirations and intuitions. The body, within its own field, affords participation in its external world in two directions, in sensuous happenings and in motor happenings; and so does the spirit—in so far as that experiences the representations of the psyche imaginally (even in ordinary consciousness) from the one direction, while in the other—in willing—it in-forms the intuitive impulses that are realising themselves through metabolic processes. Looking towards the body, we find neural activity that is taking the form of representation-experience, ideation; looking towards the spirit, we realise the spirit-content of the imagination that is flowing into precisely that ideation. Brentano was primarily sensitive to the noetic side of the psyche’s experience in representation. That is why he characterises this experience as figurative, i.e. as an imaginal event. Yet when it is not only the private content of the soul that is being experienced, but also a somewhat that demands judgmental acknowledgment or repudiation, then there is added to the representation a soul experience deriving from spirit. The content of this experience remains “unconscious” in the ordinary sense, because it consists of imaginations of a spiritual that existentially underpins the physical object. These imaginations add nothing to the representation except that its content exists. Hence Brentano’s diremption of mere representation (which imaginally experiences merely an inwardly present) from judgment (which imaginally experiences an externally given; but which is aware of that experience only as existential acknowledgment or repudiation). When it comes to feeling, Brentano has no eyes for its somatic basis in rhythmic occurrence; instead he limits his field of observation to love and hate; that is, to .vestiges, in the sphere of ordinary consciousness, of inspirations which themselves remain unconscious. Lastly the will is outside his purview altogether; because he is determined to direct his gaze only to phenomena within the psyche; and because there is something in the will that is not encapsulated in the soul, but of which the soul avails itself in order to participate in the outside world. Brentano’s divisive classification of psychological phenomena may therefore be characterised as follows: he takes his stand at a vantage-point which is truly illuminating, but is only so if the eye is focused on the spirit-kernel of the soul—and yet he insists on aiming from there at the phenomena of ordinary everyday consciousness.4
|
| 77a. The Task of Anthroposophy in the Context of Science and Life: Closing Words
30 Jul 1921, Darmstadt Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| The first lecture I had to give within this German Society was concerned with rejecting Kant and Kantianism, in my then awkward, youthfully immature way, that barrier that had been erected against the essence of the world by the special interpretation that phenomena have found in modern science. |
| 77a. The Task of Anthroposophy in the Context of Science and Life: Closing Words
30 Jul 1921, Darmstadt Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Dear attendees, dear fellow students! We have come to the end of this event, and I too would like to express a wish that has already been expressed by the honored organizers: that some satisfying things may have sunk into the souls of our very welcome audience during these days, and that some satisfying things may also remain in their after-feelings. It is natural that in the course of such a short event one can only give a few samples of what anthroposophical spiritual science wants to be and what it wants to be in our time of science and life. The fact that a number of personalities, especially from scientific circles, have come together to pursue anthroposophy out of youthful enthusiasm is one of the most satisfying things for someone who would like to devote his life to everything that lies within this anthroposophical spiritual science. Therefore, you will believe me when I express it from the bottom of my heart when I express my sincere thanks to the esteemed fellow students who have devoted their strength and effort and their good will to this event. I am convinced that all those who have been involved here and who are active in one place or another in our anthroposophical movement also thank the organizers of these college courses most warmly and in the same spirit. These thanks are directed primarily to the working groups of the Federation for Anthroposophical School of Spiritual Science Work in Darmstadt, Frankfurt, Gießen, Marburg, Heidelberg and Würzburg, who have put so much effort into making this event a worthy one. But these thanks are also directed to all participants in this anthroposophical experiment. And now, ladies and gentlemen, dear fellow students, if you would like me to say a few closing words, please do not ask me to say what I have to say, what I would like to say to you now at the end , but let me say a few things that seem necessary to me in part and that are very close to my heart in part, precisely in view of what I have been privileged to experience here among you during these days. The fact that the School of Spiritual Science in Dornach, where it had to be shown during the war how German spiritual life can be presented to the world, has been called the Goetheanum, has been strongly contested from many quarters. I myself have often used the name, but the will to call this educational institution the Goetheanum came from others. But perhaps it may be said that there is something in this name that is connected with my own growth into the Anthroposophical Movement in this life. And so I may begin by clothing what I want to say to you in the images of some reminiscences of my life. When I myself came to the university in Vienna, it was still in those days when what has now gained such immense world significance was only just being established at technical universities: electrical engineering. In Waltenhofen, the Viennese “Technik” had the first representative of electrical engineering, but he had grown out of general physics. And since then, one has been able to follow everything that has come from this particular direction and which, as we have seen, has become so effective that the treatment of light and many other natural phenomena has now led to a world view of a scientific nature, one might say that it is based entirely on the observation of electrical phenomena. The mere elastic atoms, with which we still had to deal with our complicated differential equations, have been replaced by the present-day picture of electrons. And in these decades, something significant in the development of modern humanity has been included. But it also includes what I tried to hint at in yesterday's public lecture: the striving to move beyond the increasingly pervasive materialistic view of the world, which actually celebrates its triumphs in the electron theory, and to return to a spiritual understanding of the world. Within what we can gain from the electron theory, we simply do not find the human being. But we must find the human being again. And perhaps it has become clear to you from the aspirations that underlie our lectures that, first and foremost, we are striving for knowledge of the human being, but such knowledge of the human being that is connected with all other scientific knowledge and with all striving for the world, down to the individual social level, is what is to be brought to life in anthroposophy. For me personally, when I was still allowed to feel as many of you feel today, something came to me in the midst of what surrounded me in my youth from a scientific and technical way of thinking, soon after I entered the Technical University of Vienna. In addition to the other subjects I devoted myself to, I also became a student of my old teacher and friend, the late Karl Julius Schröer. And it is one of the most profound experiences that I felt at the time when Karl Julius Schröer, in the first lecture on German literature, spoke a word that so clearly showed how the renewal of the spiritual life of modern humanity can be born out of German, Germanic being. Perhaps this word no longer seems as significant to you today as it sounded to me at the time. Karl Julius Schröer wanted to characterize how Goethe, Schiller, Herder, Lessing, the German Romantics, the German philosophers, placed themselves in the context of the entire spiritual life of humanity. To this end, he wanted to show that art, that aesthetic experience, had become a sacred matter for humanity in that time for the German, not just a luxurious addition to life. Something that is fundamentally human should flow into art. And that is what Karl Julius Schröer expressed in his own way in the sentence he uttered in the first hour of his lecture: “The German has an aesthetic conscience”. This was also the basis for his treatment of Goethe's Faust, where he tried to present Faust as the hero of invincible idealism, which at that time had to emerge from the depths of German intellectual life into the development of the world and humanity. Then I took part in what Karl Julius Schröer called “Deutsche Gesellschaft” (German Society), by recreating something that Uhland and Grimm had developed in their teaching. Young people gave lectures; they could express themselves as they wished. The first lecture I had to give within this German Society was concerned with rejecting Kant and Kantianism, in my then awkward, youthfully immature way, that barrier that had been erected against the essence of the world by the special interpretation that phenomena have found in modern science. And then I had the good fortune to speak about Johann Gottlieb Fichte to a circle of Viennese students at the University of Vienna's “Deutsche Lesehalle”. I tried to include in what I wanted to say about Fichte everything that seemed to me, in an immature way at the time, to be necessary for a fertilization of intellectual life from a very particular angle. And one of the essays I wrote when I was briefly editing the “Deutsche Wochenschrift” in Vienna had the same title as the second lecture I gave here, albeit in a different form: “The Spiritual Signature of the Present”. But this essay endeavored to point to the true sources of German intellectual life that could lead to a spiritualization of modern culture. I am not saying this to boast in any way, but I would like to present such images so that perhaps one or the other may get a truer picture of what I personally have contributed to the spiritual-scientific-anthroposophical movement than the image that is now being widely spread by untruthful sides. Now, my dear attendees, dear fellow students, I had plenty of opportunities to get to know the forces of decline in modern scientific life at the time. And so it was a great satisfaction for me that during my time in Weimar working at the Goethe-Schiller Archive, I was able to devote myself to Goetheanism, if I may say so, for years through my study of Goethe. One felt very much at the center of German intellectual life. Weimar in the 1980s was still very different from what it is today. There was still a breath over the whole of Weimar that is no longer there today, and from this breath one sensed precisely what is specifically Goethean. At that time I tried to point the way to what was to come by giving a lecture in Weimar on “The Imagination as a Cultural Creator”. What I attempted to give from a scientific-philosophical basis shows you, even in its very first attempts, that it is a matter of drawing the spiritual current from that which was the basis of Goethe's thinking and feeling in all areas of knowledge and life. I certainly did not start from Haeckel; anyone who follows the chapter I wrote in the first introduction to Goethe's natural science writings at the beginning of the 1880s can see that. But anyone who wants to be part of spiritual scientific life must take everything seriously, and actually carry out what they advocate in their ideas. Therefore, those currents of contemporary spiritual life that have entered this life with all their might and strength must also be lovingly experienced; and this immersion in Nietzscheanism and Haeckelism has been perceived as a following [on my part]. But if one wanted to, one could find the sources of anthroposophical spiritual science in my writings that preceded these discussions with Haeckel or Nietzsche. In my Philosophy of Freedom, I first tried to indicate in a practical way how spiritual elements must flow into moral and social action. And when it is emphasized today that my work has been incorporated into that of the Theosophical Society, then, my dear audience, I must always emphasize again that I have never, anywhere, advocated anything other than what I have gained from my own inner path of research. That I was wanted to be heard within the circle of this or that society, that I was invited to work within that society in order to be heard, is something that I consider to be quite possible, indeed necessary. And I will never allow it to be taken from me in the future, to speak wherever I am wanted. Therefore, I must emphasize that I did not seek out the Theosophical Society, but that it came to me. And I must always emphasize that when I had written my first book, “Mysticism in the Dawn of Modern Spiritual Life and its Relation to the Modern World Picture”, which was more derived from the natural sciences, I was told within the theosophical circles, to which I did not belong at the time, that this book contained everything that was actually sought in these theosophical circles. But this did not come from these circles; it was found by the path of research that I found compelled to take from the foundations of natural science up into the spiritual, to anthroposophy. And so the transformation of the “Theosophical Society” into an “Anthroposophical Society” was also given by the facts. But what flowed through the work of these Societies was never different from what flows today. However, it is self-evident that this anthroposophical spiritual science, because it has been cultivated for decades in the most diverse fields, has slowly and gradually developed, and that what had to be said in a more abstract form at the beginning could be formulated in ever more concrete and specific terms. Therefore, when we speak today, we can draw much more from spiritual reality than we could in earlier decades. But spiritual science in the anthroposophical sense would not be alive if it were not so. And those who do not hold with the dead spiritual, but with the living spiritual, will understand this living development. They will understand that just as a mature person can no more be a child than can an anthroposophical spiritual science that has grown old speak in the same way as it spoke when it was still a child. Anyone who wants to look at these things properly will see that it must be exactly as it is, because the matter wants to be thoroughly alive. Even the artistic and medical aspects, which were taken up relatively late, have been organically integrated because the need for them has basically come from the outer world of pure anthroposophy. I would say that we have given in to what had emerged from the necessities of the time, from the signs of the times, more in keeping with destiny. But understanding the signs of the times is what it is all about. My esteemed audience, dear fellow students, I could use many other images to show how what has been incorporated into anthroposophy can be found in the original source of German intellectual life. I will not do so today for the sake of brevity. I have only given the individual examples for the reason that recently the fight against anthroposophical spiritual science has also been waged under the flag of hostility towards all things German. And in the face of what comes out of the most unobjective of motives and out of scientific inability, as for example with the Göttingen Professor Fuchs, and what is combined with all kinds of attacks by various other personalities who have never even sensed a whiff of what anthroposophical spiritual science and anthroposophical spiritual striving really are, and which are directed precisely at the German essence of anthroposophy, in the face of this it must be said: Whatever anyone wants to think or feel about Anthroposophy, we respect; Anthroposophy will face up to anyone who is an honest opponent. I have never opposed the harshest criticism when it has taken the form of judgment. But I will always oppose something else. The criticism of many circles that today approach anthroposophy with hostility is not based on judgment, for easily understandable reasons: because these circles lack this judgment, because they do not want to develop the diligence to really find their way into the anthroposophical and into the way in which this anthroposophical wants to flow into the outer social life; their criticism is based on something else. In the broadest circles today, the numerous attacks, which you have probably also heard about, are based on lies. The lies go as far as the forged letters. The lies go so far that at my April lecture, which was held in Stuttgart in self-defense, one of these attacks was made against me from the audience: it was claimed that I had said this or that in Cologne in the last few months. I had to reply that I had not been to Cologne for years. The person in question referred to a letter that had been written to him from Cologne, and he had the audacity to show me this letter. I had to reply: No matter what it says, it is a forgery, because it is a lie that I have been to Cologne in recent years. — This is typical of the attacks that come from certain quarters. They do not base their arguments on judgment and opinion, it is all a lie. Everyone is entitled to their own judgment and opinion according to their abilities and what they are capable of; I will only oppose these within the limits that they themselves have set. Because an honest opponent strives to get to the bottom of the matter; it would be a sin not to deal with these opponents in complete agreement. But anyone who resorts to dishonesty and even forges letters cannot be argued with in any other way than by calling attention to the fact that he is lying. That is what I would like to express here with these few words, for the reason that I am speaking to dedicated younger people who, out of the depths of their enthusiasm, have made it possible for this lecture course and this lecture event to take place despite the fact that anthroposophy is presented to the world in such a distorted form today. Dear fellow students, insofar as you are interested in anthroposophy as you have shown so far, you will be put in the middle of hard struggles, and you will have to pay particular attention to the dishonesty that permeates these struggles. In many cases, especially in the older anthroposophical movement, as it has developed over the years, something has emerged that makes this movement unsuitable in many ways to face well-organized opposition today. Anthroposophists are often calm people in their minds, who really only want to receive what elevates their minds in a certain way. They are very rarely battle-ready people. That is one side of it. On the other hand, it is the case today that precisely because of this longing for an inwardly pleasing peace of mind, it has very often been the case that when attacks in full dishonesty have come from outside and one has then was compelled to call a lie a lie, the mood has not turned against those who attacked with lies, but against those who had to defend themselves, even from anthroposophical circles. This is something that has become an extremely strong custom, especially in our country.Now, my dear fellow students, those who have already shown how they can find their way into this anthroposophy despite the difficulties that the anthroposophical path presents, how they make sacrifices for it, wherever untruthfulness arises without a judgment about the true form of anthroposophical striving, they may perhaps be expected to unmask the untruthfulness with full force. After all, dishonesty plays a widespread role in the present world in other ways as well, and a good part of how we move forward from forces of decline to forces of ascent will be in developing enthusiasm for truthfulness. Truthfulness is the highest, never the individual party line. The whole system of anthroposophy must be built on truthfulness. For how can anyone who does not understand how to stand up for truthfulness in the outer life penetrate to those regions where one must be guided by truthfulness only through the inner direction, because one cannot always be corrected for being untrue, as one can in the outer life? What could be presented to the world from the regions of supersensible worlds if enthusiasm for truthfulness were not the basis? This enthusiasm for truthfulness – we see it particularly in the discussions about the war guilt – this enthusiasm for truthfulness is also missing today in so many cases, even in those who call themselves the bearers of civilization. This enthusiasm for truthfulness is something we need, and anyone who is as closely connected with Germanness as I am — I mention this in all modesty — will, will be convinced, must be convinced that Germanness will suffer in no way at all if truthfulness is insisted upon, even in the most difficult of matters. All attacks on anthroposophy that come from this quarter bear the stamp of a lack of truthfulness of mind. Therefore, my dear fellow students, do understand how much it must fill me with the deepest satisfaction that you have undertaken this event here despite all that is being directed against anthroposophy in a well-organized manner today. And those of you here today who already feel how sincere these thanks are, will also feel that in the ways that are unfortunately only partially open to us, attempts will be made to work together in the fullest harmony in the further pursuit of the anthroposophical path. I have often had to take refuge in Goetheanism, because of the urge for renewal in modern scientific and technical life. Today some of you, my dear fellow students, are seeking this path through anthroposophy, no doubt from the bottom of your hearts. And it may be said, from an unprejudiced observation of the development of the times: you are seeking this path from the true signs of the times. May we therefore succeed, through our collaboration with those who are already working in one place or another in the anthroposophical movement, in particularly in the most fruitful way developing the work of youthful minds. Then youthful minds will have no reason to turn to Spengler's pessimism. Spengler has, however, recently denied that what he strives for is pessimism. But in any case, anyone who is fully imbued with an inner content of the rising forces of our age in the anthroposophical sense has no reason to turn to Spenglerism. On the other hand, what has made a great impression on all young people, insofar as they have turned to science, if they have ever studied it, can be revived in a new, more spiritualized form: what Fichte once said in his 'Discourses on the Essence and Destiny of the Scholar' at the end of the 18th century. These thoughts can be expressed again, albeit in a transformed form, precisely in order to make fruitful the rising forces in the first third of the twentieth century. In particular, however, one may recall the words that Fichte spoke at the very beginning of his speeches, addressing all those who wanted nothing to do with scooping out of spirituality for real, practical life. To them he said: if they believed that all reality was exhausted in the world of sense, that ideals represented only utopias, then they should be convinced that he who speaks as he does, Fichte, also knows quite clearly, perhaps better than they, that ideals cannot be realized in real life as directly as that to which they always point. But Fichte also added that perhaps such minds cannot be convinced, and that therefore, because the governance of the world did not actually count on them, God may give them food, sun and rain at the right time, and, if it can be, also some good thoughts. Thus spoke Fichte, the idealist, at the end of the 18th century, and thus may we speak again today, from the innermost impulse of anthroposophical spiritual science. I hope that you feel something of this attitude as we part, and that it was this attitude that led you to organize these lectures, this entire event. I speak to you out of the gratitude that arises from all the attention and commitment you have shown to what we have been able to offer you. I speak to you in such a way that I truly believe that it will be of particularly essential importance for the emergence of a new spiritual movement when youthful humanity, touched in its inmost heart, turns to this movement. It will be up to you, dear fellow students, how conditions develop in the coming decades. It will be up to you whether the languishing German nation will be able to rise again. To do this, humanity needs strength, not just words – strength! But strength can only come to present-day humanity from the spirit. In many respects, the young generation has made a start by forming these student groups. They have continued by leading the honored student groups from Darmstadt, Frankfurt, Gießen, Marburg, Heidelberg and Würzburg to this event. May this event be the starting point for fruitful further work, work that will lead to a true dawning of humanity in the coming generations, and in particular in Central Europe. For basically everything that has been achieved here during these days was directed towards this goal, towards this ideal. So, my dear fellow students, let us work together in the spirit of true anthroposophy, so that what humanity needs may flow into it: above all, the strength of youth, the enthusiasm of youth – and that it may also be imbued with the seriousness that young people experience through their engagement with science. We want to stand firmly on the ground of strict scientific observation. But we want to get out of the abstract, out of the merely theoretical, out of the dead webs of concepts. We want to move on to the living grasp of the full reality, which lives itself out not only in the outer world of the senses, but also in the soul and spiritual world. And if I am speaking here in particular to those who, as prospective technicians, are involved in this movement, I may say that this involvement in technical activity seems to me to be particularly significant for a spiritual movement. In the world, things develop in polar fashion. The technician experiences the highest level of scientific thinking in construction, in building, and in the laboratory. By pouring the laws of nature into the outer world, by developing technology, we bring our soul above all to what initially does not contain the spirit, but the human heart approaches everything. The human soul and the human spirit enter into this sphere. It is precisely through our feeling for technology that we must direct our feeling, our thought, to the other pole, to that which, as spirituality, permeates and interweaves the world. Technology is particularly suited to pointing to the other side, to the side of spirituality, because it most deeply intervenes in the outer world of the senses. I therefore believe that especially the prospective engineer can be a source of strength that can contribute the most to the development of humanity by bringing a spiritual attitude, a spiritual worldview. It is in this spirit that I wanted to address these final words of the present event to you all. May they once again end in heartfelt thanks to all those who have contributed to this event, in heartfelt thanks to all those who have turned their attention to this event. |


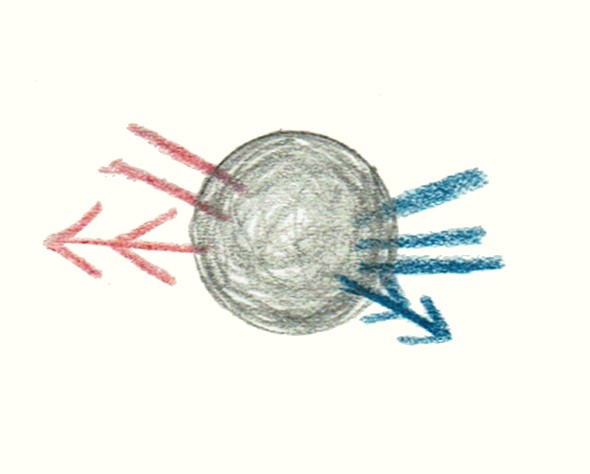 The current of religious impulse had come from the East into European civilisation; and for the economic structure of Europe something again different was needed. The approach of the Fifth post-Atlantean age was also the time for the irruption of those events which set their stamp upon the whole civilisation of the new age and gave to it its special physiognomy. The discovery of America, the finding of a sea-route round the Cape of Good Hope to India, to the East-Indies,—this set its stamp on the civilisation of the new age. It is impossible to study the whole economic evolution of Europe by Itself alone. It is absurd to believe that from the study of existing economic facts one can thereby arrive at the economic laws that sway the common life of Europe. In order to arrive at these laws, one must bear constantly in mind that Europe was able to shift any amount off on to America. The whole social structure of Europe has only grown up owing to the fact that there was an unfailing supply of virgin soil in America, and that everything flung off from Europe passed Westwards into this virgin soil. Just as she had drawn her religions impulse from the East, so she sent forth an economic impulse towards the West. And the whole system of industrial economy peculiar to Europe was conditioned by this Westward outflowing, just as her spiritual life was developed under the inflow of the religious impulse from the East. European life, the whole course of the rise of European civilisation, has gone on through the centuries until now, under the Influence of these two currents. Here, in the middle, was European civilisation; here from the East came the religious impulse pouring in; here, in a westward stream, the economic impulse, pouring out.—Inflow of the religious impulse from the East, outflow of the economic impulse towards the West. Now this, you see, towards the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries reached a sold, of crisis. There came a gradual stoppage. Things no longer went on the same as they had been going for four centuries. And to-day we are still lining in this stoppage and are affected by it. The religious impulse came in as an alien and brought forth our spiritual life. And our economic life came about under a process of being continually drawn off and weakened. If America had not been there, and if our industrial economy had been obliged to grow up solely according to its own principles,—had it not been able continually to fling off what it could not assimilate,—then it could never have developed at all in Europe. Now there is a stoppage; and accordingly, an outlet must be found within. It Is from within that the way must be found to lead off into the right channel what no longer can go on externally in space. It must be done by bringing about the threefold social order. What has been mixed together in inorganic confusion must be combined into an actual organism. There is not one reason, there is every conceivable reason for the adoption of the threefold social order,—scientific reasons, economic reasons, historic reasons. And only he can fully appreciate the claims of the threefold social order, who is in a position to survey all these various grounds on which it rests.
The current of religious impulse had come from the East into European civilisation; and for the economic structure of Europe something again different was needed. The approach of the Fifth post-Atlantean age was also the time for the irruption of those events which set their stamp upon the whole civilisation of the new age and gave to it its special physiognomy. The discovery of America, the finding of a sea-route round the Cape of Good Hope to India, to the East-Indies,—this set its stamp on the civilisation of the new age. It is impossible to study the whole economic evolution of Europe by Itself alone. It is absurd to believe that from the study of existing economic facts one can thereby arrive at the economic laws that sway the common life of Europe. In order to arrive at these laws, one must bear constantly in mind that Europe was able to shift any amount off on to America. The whole social structure of Europe has only grown up owing to the fact that there was an unfailing supply of virgin soil in America, and that everything flung off from Europe passed Westwards into this virgin soil. Just as she had drawn her religions impulse from the East, so she sent forth an economic impulse towards the West. And the whole system of industrial economy peculiar to Europe was conditioned by this Westward outflowing, just as her spiritual life was developed under the inflow of the religious impulse from the East. European life, the whole course of the rise of European civilisation, has gone on through the centuries until now, under the Influence of these two currents. Here, in the middle, was European civilisation; here from the East came the religious impulse pouring in; here, in a westward stream, the economic impulse, pouring out.—Inflow of the religious impulse from the East, outflow of the economic impulse towards the West. Now this, you see, towards the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries reached a sold, of crisis. There came a gradual stoppage. Things no longer went on the same as they had been going for four centuries. And to-day we are still lining in this stoppage and are affected by it. The religious impulse came in as an alien and brought forth our spiritual life. And our economic life came about under a process of being continually drawn off and weakened. If America had not been there, and if our industrial economy had been obliged to grow up solely according to its own principles,—had it not been able continually to fling off what it could not assimilate,—then it could never have developed at all in Europe. Now there is a stoppage; and accordingly, an outlet must be found within. It Is from within that the way must be found to lead off into the right channel what no longer can go on externally in space. It must be done by bringing about the threefold social order. What has been mixed together in inorganic confusion must be combined into an actual organism. There is not one reason, there is every conceivable reason for the adoption of the threefold social order,—scientific reasons, economic reasons, historic reasons. And only he can fully appreciate the claims of the threefold social order, who is in a position to survey all these various grounds on which it rests.